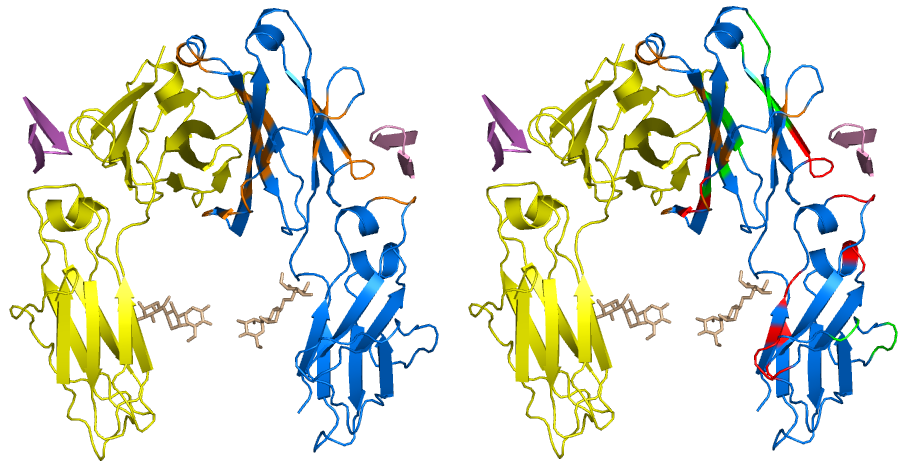
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) are the basis of the cellular structure and functions. It has been estimated that more than 80%
Proteins, biomolecules or macromolecules, perform a wide range of functions in organisms. Almost all of the cellular processes require that
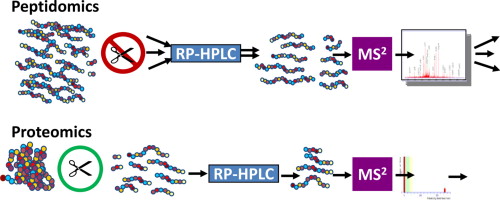
During the completion of the human genome, a wide variety of additional “omics” technologies arose, such as transcriptomics. Peptidomics represents
Peptidomics can be easily defined as the study of the low molecular weight fraction protein fragments from endogenous protein degradation
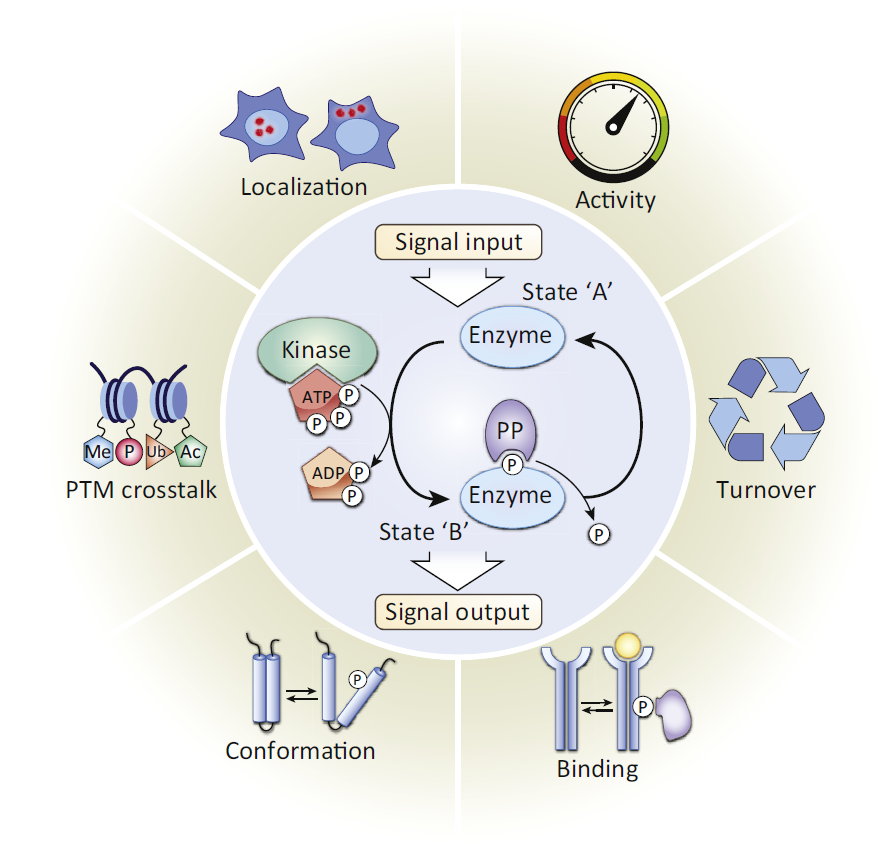
Protein phosphorylation, a reversible process, is characterized by adding phosphate donated from ATP and removing phosphate from a phosphorylated protein
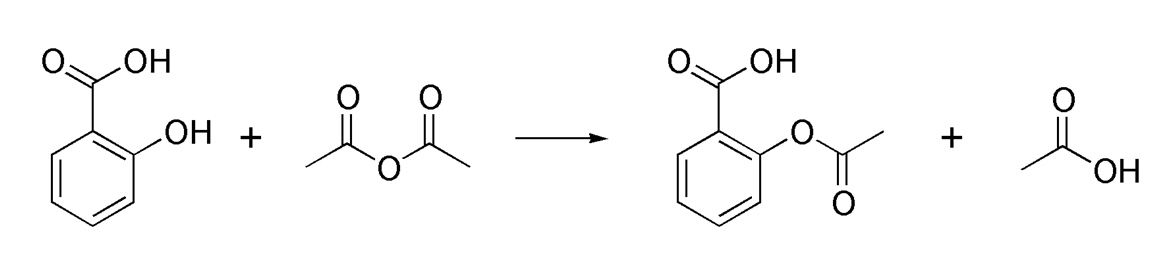
Acetylation refers to a reaction that introduces an acetyl functional group into a chemical compound, in which the hydrogen atom
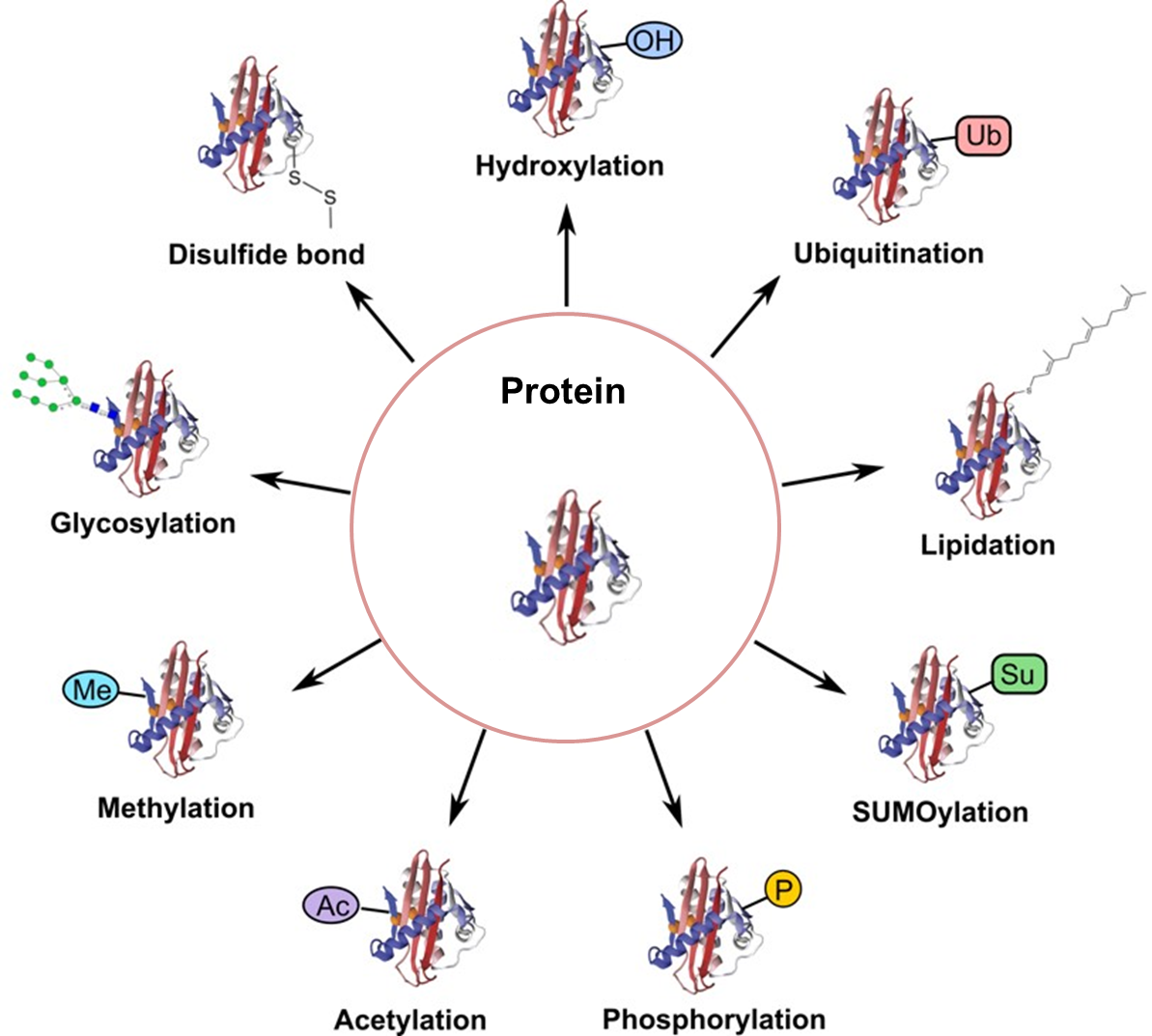
Post-translational modification (PTM) refers to the modification that occurs on a protein after translation catalyzed by enzymes. There are various
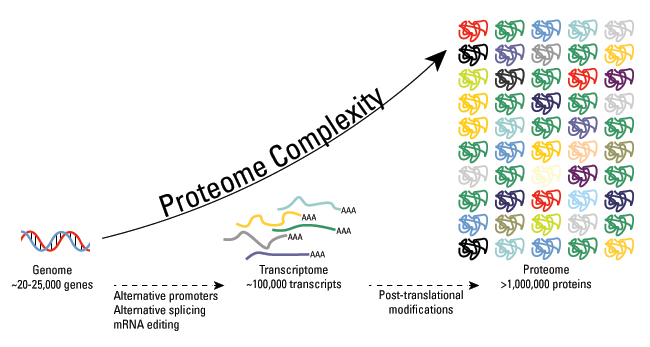
As we know, the human gene set was estimated at about 25,000 genes, while the total number of proteins is
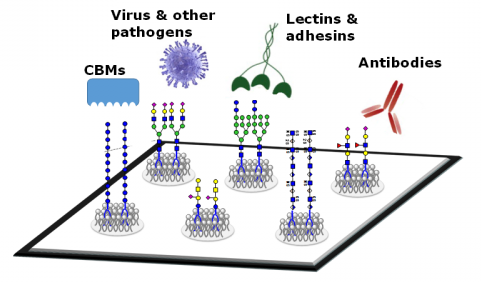
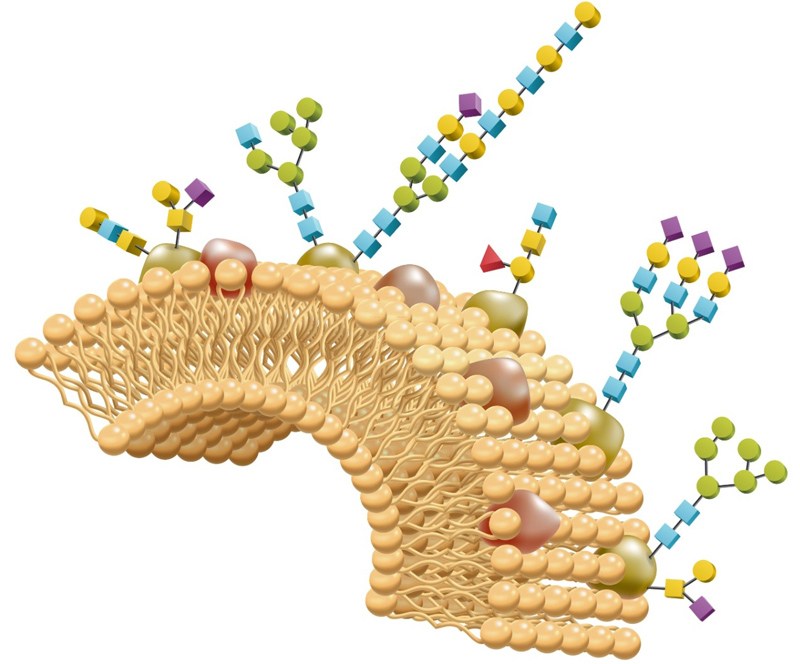
Glycans are defined as the compounds that consist of a large number of monosaccharides linked glycosidically. Glycans have diverse biological
Glycomics, the study of glycans, is applied to biology and chemistry that focuses on the structure and function of carbohydrates,