Metagenomics, metatranscriptomics, and metaproteomics are some of the more popular technologies applied in cancer research. Meanwhile, the role of metabolomics in understanding these diseases has been explored in the past. Metabolomics is the large-scale analysis of all small biomolecules called metabolites found in the cell. It is comprised of different studies, namely metabolic fingerprinting, metabolic profiling, and target isotope-based analysis, which are interconnected and are usually done together. Metabolic profiling is the analysis, differentiation, and quantitation of a subgroup from the whole metabolic profile of the cell while metabolic profiling focuses on the quantitative study of a particular group of metabolites associated with a specific metabolic pathway, either known or unknown. Target isotope-based analysis, on the other hand, focuses on metabolites related to a specific biochemical process.
Cancer cells are known to have alterations in their metabolism leading to increased productivity and rapid cancer cell growth and proliferation. Some cancer studies are dedicated to understanding the mechanisms wherein such metabolic alterations lead to the development of tumors in the goal to provide effective cancer diagnosis. Similar to metaproteomics, metabolomics is used to identify potential biomarkers for cancer. Also, cancer metabolomics offers a potential advantage to cancer therapy, prevention, and treatment.
Metabolic reprogramming is a major phenomenon of cancer and is said to be essential in facilitating tumorigenesis and malignant phenotype development. Tumor cells are known to become "immortal" due to metabolic changes that favor their growth and differentiation and prevent apoptosis. Metabolomics is said to be useful in understanding such alterations in biochemical pathways in cancer cells which can help in early detection and can be used to predict drug responsiveness of target cells in the development of novel therapeutic medicine. Metabolomics is mainly used in the detection of cancer biomarkers. Studies using this technology have successfully yielded potential biomarkers for colorectal, gastric, pancreatic, breast, ovarian, and other forms of cancers.
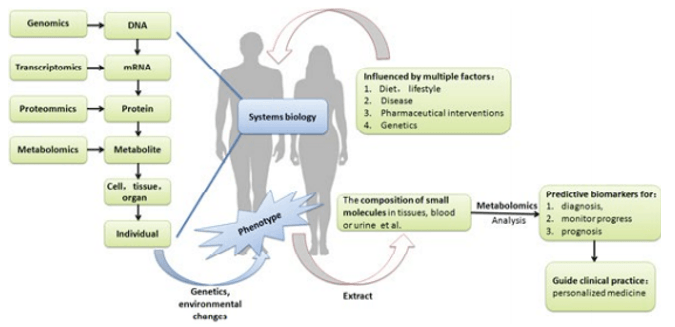 Figure 1. The outline of analytical metabolomics in patients. (Wang, 2018)
Figure 1. The outline of analytical metabolomics in patients. (Wang, 2018)
The figure shows the application of the different omics studies in the diagnosis of a patient. As seen in the figure, metabolomics analysis is done on clinical samples such as tissues, blood, or urine and yields information on potential biomarkers that can be used in diagnosis, progress monitoring, and prognosis of cancer, contributing to designing personalized medicine for cancer patients. Metabolomics offers a wide range of capabilities in understanding the workings of tumor cells and cancer development.
Multi-omics approach in cancer research provides a multi-level analysis of cancer cells and tissue. Starting from the general information in the gene, gene expression at a certain period of time, protein analysis, and analysis of small metabolites in the cell. Each type of omics contributes to the understanding of the behavior of cancer cells in the goal to improve cancer detection, diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment.
Creative Proteomics offers different omics services including metabolomics analysis to aid in your cancer research. Starting from separation, identification, quantification, characterization, quantitative screening, up to the detection of potential biomarkers. We assure you that we provide the best strategies to optimize the collection of information needed for your studies. We use state-of-the-art instrumentations to provide you with reliable results in the shortest time possible. We are one of the most trusted companies in multi-omics services in cancer research. For additional information and other services that we provide, please feel free to contact us.
References:
1. Armitage, E.G., Barbas, C. Metabolomics in cancer biomarker discovery: Current trends and future perspective. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2014, 87,1-11.
2. Beger, R.D. A Review of Applications of Metabolomics in Cancer. Metabolites, 2013, 3, 552-574.
3. Spratlin, J.L., Serkova, N.J., Eckhardt, S.G. Clinical Applications of Metabolomics in Oncology: A Review. Clinical Cancer Research, 2009 January 15; 15(2): 431-440.
4. Wang, L., Liu, X., Yang, Q. Application of Metabolomics in Cancer Research: As a Powerful Tool to Screen Biomarker for Diagnosis, Monitoring and Prognosis of Cancer. Biomarkers Journal, 2018, 4 (S1:12).
* For Research Use Only. Not for use in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Related Services:

 Figure 1. The outline of analytical metabolomics in patients. (Wang, 2018)
Figure 1. The outline of analytical metabolomics in patients. (Wang, 2018)