Metals (Metallomics) Assay Service
Creative Proteomics provides advanced metallomics analysis to accurately measure metal content, chemical forms, and biomolecular associations across diverse sample types.
Our platform supports:
- Toxicology (e.g., Pb, Cd, Hg exposure)
- Nutritional assessment (e.g., Fe, Zn, Se)
- Metalloprotein discovery
- Metal speciation and redox studies
Key Advantages at a Glance
- Sub-ppb Detection Limits for trace and ultra-trace metals
- Total + Speciated Analysis in one workflow
- Full Matrix Compatibility (serum, plasma, tissue, plant, soil, etc.)
- Certified Accuracy using matrix-matched calibration and CRMs
- SEC-ICP-MS Enabled native metalloprotein profiling
Submit Your Request Now
×
What You Will Receive
- Absolute Metal Concentrations (ng/mL, µg/g)
- Metal Speciation Results (oxidation state, ligand-bound forms)
- Metalloprotein Profiles (peak charts and identification summaries)
- LOD/LOQ and CV% Tables
- Reference Comparison Reports (optional)
- Pathway-Level Annotation (on request)
- What We Provide
- Advantages
- Technology Platform
- Sample Requirements
- Demo
- FAQs
- Case Study
What is Metallomics?
Metallomics is a sub-discipline of systems biology that focuses on the comprehensive analysis of metal and metalloid species in biological systems. It provides critical insights into metal ion homeostasis, metal-protein interactions, and metal-based therapeutic mechanisms. Given that over 40% of proteins bind metal ions, and many enzymatic and regulatory processes are metal-dependent, metallomics has emerged as an indispensable tool in biomedical, environmental, and agricultural research.
Why Analyze Metals and Metal-Biomolecule Complexes?
Precise metal quantification and speciation reveal functional, pathological, and nutritional roles of metals in life science research. Key applications include:
- Toxicology: Assessment of heavy metal accumulation (e.g., Pb, Cd, As) in tissues or biofluids.
- Nutrition and Health: Evaluation of essential trace elements (e.g., Fe, Zn, Se) in food, serum, or supplements.
- Metalloenzyme Profiling: Discovery of metal-containing proteins involved in metabolic pathways.
- Drug Mechanism Studies: Characterization of metal-based drug candidates (e.g., platinum compounds).
- Environmental Biomonitoring: Determination of trace metal pollutants in organisms and ecosystems.
Comprehensive Metallomics Services Offered by Creative Proteomics Creative Proteomics
We provide a wide range of targeted and untargeted metallomics services tailored to diverse research needs. All analyses are conducted under stringent quality controls using matrix-matched calibration and certified reference materials.
Our service portfolio includes:
- Total Elemental Analysis: Quantification of metal concentrations in biological fluids, tissues, cells, plants, and environmental samples.
- Metal Speciation Analysis: Differentiation between oxidation states, organic/inorganic complexes, and bioavailable forms.
- Metalloproteomics: Detection and characterization of metalloproteins via hyphenated MS techniques (e.g., SEC-ICP-MS, LC-ICP-MS).
- Isotopic Ratio Analysis: For tracer studies and environmental source attribution using stable isotopes.
- Nanoparticle Metal Analysis: Characterization of engineered and naturally occurring metal-containing nanoparticles.
Detected Elements – List of Quantifiable Metals and Metalloids
| Element | Analyzed Forms | Typical Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) | Fe²⁺ / Fe³⁺, heme-bound, protein-bound | Plasma, tissues, food |
| Zinc (Zn) | Free ions, Zn-metalloproteins | Serum, cell lysates |
| Copper (Cu) | Cu⁺ / Cu²⁺, ceruloplasmin-bound | Blood, brain, plants |
| Selenium (Se) | SeMet, SeCys, inorganic forms | Supplements, yeast, plasma |
| Manganese (Mn) | Total, Mn²⁺, Mn-bound enzymes | Brain, environmental dust |
| Arsenic (As) | As³⁺, As⁵⁺, MMA, DMA | Urine, seafood |
| Lead (Pb) | Total, bioavailable | Hair, soil, water |
| Cadmium (Cd) | Cd²⁺, Cd-metallothionein | Kidney, food, fertilizer |
| Mercury (Hg) | Methyl-Hg, inorganic Hg²⁺ | Fish, blood, sediments |
| Cobalt (Co) | Total, vitamin B12-associated | Serum, microbial cultures |
| Nickel (Ni) | Free ions, Ni-bound proteins | Water, cells, catalysts |
| Chromium (Cr) | Cr³⁺ / Cr⁶⁺ | Blood, soil, workplace air |
Custom panels available upon request.
Why Choose Creative Proteomics for Metallomics Analysis?
We deliver reproducible, high-sensitivity data across a broad concentration range with inter-sample and inter-batch consistency.
- High Sensitivity & Accuracy
- Detection limits: sub-ppb (parts per billion) for most trace elements
- CVs < 3% for replicate injections
- Accuracy within ±5% of certified reference values
- Matrix Versatility: Proven across serum, tissue, urine, saliva, cell extracts, plant material, environmental matrices
- Quantitative and Speciated Data: Identify both total metal levels and chemical forms (valence state, coordination, etc.)
- Metalloprotein Targeting: Capture protein–metal interactions using SEC-ICP-MS or native MS workflows.
- Bioinformatics Support: Functional annotation, metal-pathway mapping, and metalloprotein classification included.
Methods and Instrumentation for Serum Metabolomics Analysis
| Method | Instrument Model | Core Application | Key Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) | Agilent 7900, Thermo iCAP TQ | Trace element quantification in biological and environmental matrices | ✔ Sub-ppb sensitivity ✔ High throughput ✔ Multi-element detection | ✘ Limited in speciation ✘ Matrix interference without collision/reaction cell |
| ICP-OES (Optical Emission Spectrometry) | Agilent 5110 | Moderate-level metal analysis in food, supplements, fermentation broth | ✔ Robust for high concentrations ✔ Faster than ICP-MS for bulk samples | ✘ Lower sensitivity ✘ Limited for trace metals |
| SEC-ICP-MS (Size Exclusion Chromatography hyphenated with ICP-MS) | Agilent 1260 + Agilent 7800 | Metalloprotein detection and characterization | ✔ Preserves native protein-metal complexes ✔ Good for biopharmaceuticals | ✘ Limited resolution for small MW differences ✘ Requires good sample prep |
| LC-ICP-MS (Liquid Chromatography hyphenated with ICP-MS) | Thermo Dionex Ultimate 3000 + Thermo iCAP TQ | Metal speciation in small molecules or organometallic complexes | ✔ Excellent for distinguishing oxidation states ✔ Precise metal-ligand profiling | ✘ More complex method development ✘ Longer runtime |
| HR-ICP-MS (High Resolution ICP-MS) | Thermo Element XR, Thermo Neptune Plus | Isotope ratio analysis, ultra-trace detection, environmental studies | ✔ Sub-ppt level sensitivity ✔ Accurate isotopic ratios | ✘ Expensive and time-consuming ✘ Lower throughput |
Selection Guidance:
- Use ICP-MS for routine trace element quantification.
- Choose ICP-OES for nutrient/metabolite profiling with higher concentrations.
- Apply SEC-ICP-MS when studying metalloproteins or biotherapeutics.
- Employ LC-ICP-MS when metal speciation (e.g., SeMet vs. SeCys) is critical.
- Reserve HR-ICP-MS for isotope tracing or ultra-low background studies.
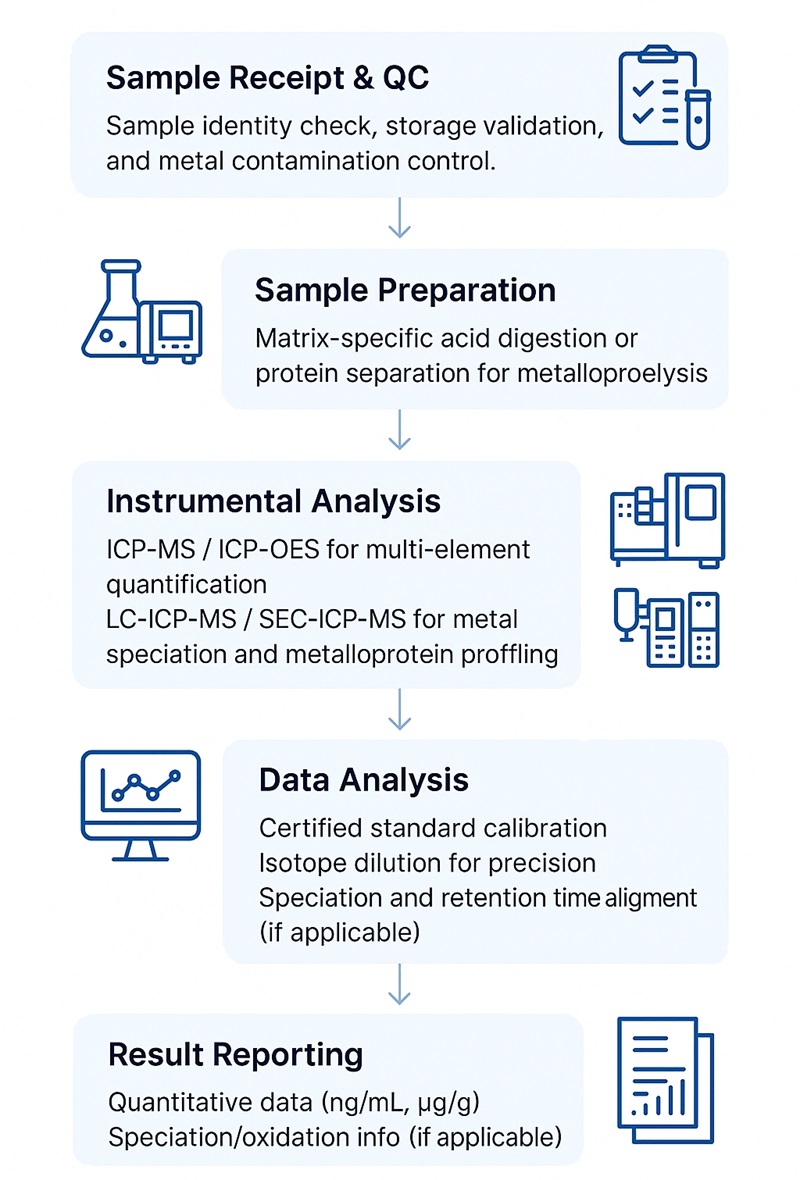
Workflow for Metallomics Assay
Sample Requirements for Metals (Metallomics) Service
| Sample Type | Recommended Amount | Storage Conditions | Transport Guidelines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum / Plasma | ≥ 200 µL | -80°C, metal-free tubes | Dry ice; avoid hemolysis or metal contamination |
| Whole Blood | ≥ 500 µL | 4°C, heparin tubes (metal-free) | Cold packs; do not freeze |
| Urine | ≥ 2 mL | -20°C or lower | Freeze immediately; ship on dry ice |
| Tissue (e.g., liver, kidney) | ≥ 50 mg (wet weight) | Snap-frozen at -80°C | Dry ice; use metal-free tools during dissection |
| Cell Pellets | ≥ 1 × 10⁶ cells | -80°C | Dry ice; wash with PBS to remove media salts |
| Plant Material | ≥ 100 mg (dry or fresh) | -20°C or freeze-dried | Dry ice or desiccated with silica gel |
| Food / Feed Samples | ≥ 1 g | -20°C | Cold chain or dry depending on matrix |
| Environmental Samples (soil, sediment) | ≥ 1 g | Ambient or 4°C (depending on moisture) | Avoid contact with metal containers |
| Nanoparticles / Suspensions | ≥ 1 mL at known concentration | 4°C, avoid aggregation | Ship cold; store in inert plastic or glass |
Demo Results
FAQ of Metallomics Service
How should I select between ICP-MS and LC-ICP-MS for my project?
If you need total elemental concentration across multiple metals, ICP-MS is optimal. If your goal includes speciation (e.g., Se⁴⁺ vs Se⁶⁺) or distinguishing metal-ligand complexes, LC-ICP-MS is required.
What's the best sample type for studying metal-driven biological processes?
It depends on your research focus:
- Tissue is ideal for storage/exposure studies.
- Plasma or serum is suitable for systemic distribution.
- Cells or pellets work best for intracellular metal profiling or metalloproteins.
Can I include both toxic and essential metals in the same analysis?
Yes. Our ICP-MS panels are optimized for simultaneous detection of both trace essential elements (e.g., Fe, Zn, Mn) and toxic metals (e.g., Pb, Cd, Hg) in a single run.
Will sample preservatives (e.g., EDTA, heparin) interfere with metal analysis?
Certain chelators (like EDTA) can bind metals and impact detection. We recommend using metal-free heparin tubes and consulting us prior to sample collection for best practices.
Can you detect low-abundance metals without signal suppression in complex matrices?
Yes. We use collision/reaction cell technology and matrix-matched standards to minimize polyatomic interference and improve sensitivity in complex biofluids and digests.
How do you ensure consistency between my study groups (e.g., control vs treated)?
We include pooled QC samples, internal standards, and normalization algorithms to ensure valid comparisons across all groups and batches.
Can I trace metal accumulation over time or across compartments (e.g., serum vs liver)?
Yes. Our quantification workflows allow for cross-compartmental comparison and longitudinal tracking using absolute concentration units (e.g., µg/g tissue, ng/mL plasma).
Is it possible to link metal levels with biological functions or pathways?
We offer optional metal-pathway mapping and annotation tools that connect elemental profiles to known enzymatic, redox, and transport functions in human, plant, or microbial systems.
Can you help with study design if I'm unsure which metals or matrices to focus on?
Absolutely. Our scientific team can advise on target element selection, sample type suitability, and analytical depth based on your biological question.
Can you differentiate between intracellular and extracellular metal pools?
Yes—when samples are properly fractionated prior to submission. For example, cytoplasmic vs nuclear vs membrane fractions can be profiled separately to reveal subcellular metal localization. We can provide guidance on pre-analytical workflows.
What if my sample contains nanoparticles or metal-based drugs—can those be analyzed?
Yes. We support particulate vs ionic metal differentiation and can characterize nanoparticle-bound vs free metal species using appropriate digestion or separation strategies.
How can I validate whether a specific protein binds a metal ion?
Our SEC-ICP-MS platform detects metal-protein complexes by co-elution of metal signals with protein peaks. For targeted studies, we recommend combining this with native MS or orthogonal biochemical assays.
Can metallomics data be integrated with transcriptomics or metabolomics?
Absolutely. We provide data in formats compatible with systems biology tools, and can assist in correlating metal levels with gene expression, enzyme activity, or metabolite abundance.
Do you support environmental samples with high matrix complexity (e.g., soil leachate, wastewater)?
Yes. We use matrix-specific digestion and interference suppression techniques to ensure accuracy in highly variable environmental matrices. Please notify us of matrix type in advance for method optimization.
How do you handle outliers or background contamination in metal data?
Our pipeline includes blank subtraction, spike recovery assessment, and robust outlier filtering. Clients receive quality flags with every dataset to support informed interpretation.
Can this service help in identifying metal-based biomarkers?
Yes. Our workflows are frequently used in biomarker discovery, especially for exposure, deficiency, or disease signatures involving trace metals (e.g., Cu in Wilson's disease, Se in oxidative stress).
Do you provide metal-to-metal ratio analysis (e.g., Zn/Cu, Ca/P)?
Yes. Custom metal ratio calculations and comparative plots can be included to support mechanistic studies or nutritional diagnostics.
Learn about other Q&A.
Metals (Metallomics) Service Case Study

Title: Comprehensive assessment of matrix effects in metallomics: Evaluating 27 metals in serum, heparine-plasma-, EDTA-plasma and citrate-plasma by ICP-MS analysis
Journal: Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology
Published: 2025
- Background
- Study Design
- Key Insights
- Application Relevance
- Reference
In large-scale population studies and biobank-based research, the accuracy of elemental analysis depends heavily on sample matrix composition—particularly the type of anticoagulant used during blood collection. This study evaluated how serum, heparin-, EDTA-, and citrate-plasma impact the ICP-MS quantification of 27 biologically and toxicologically relevant metals.
Researchers applied a dilute-and-shoot ICP-MS protocol to evaluate:
- Limits of detection and quantification (LOD & LOQ)
- Repeatability (CV%)
- Agreement with certified reference values
- Matrix-related variability for each metal
All matrices were collected from the same individuals to ensure comparability.
 Overview of the ICP-MS study assessing 27 metals in four blood matrices from 20 volunteers, highlighting sample prep, method validation, and anticoagulant impact.
Overview of the ICP-MS study assessing 27 metals in four blood matrices from 20 volunteers, highlighting sample prep, method validation, and anticoagulant impact.
How Creative Proteomics Supports Similar Projects
At Creative Proteomics, we integrate these insights into our metallomics services to help clients reduce matrix-related variability and obtain high-confidence data:
- Matrix-aware method design (serum, plasma, cells, tissues)
- Anticoagulant compatibility evaluation
- Certified metal-free consumables guidance
- Cross-sample normalization and QC workflows
- Elemental panel customization based on sample origin and research goals
Heparin-Plasma and Serum Deliver More Consistent Results
Over 85% of measured elements in serum and heparin plasma showed <15% coefficient of variation, supporting their suitability for high-confidence elemental profiling.
EDTA and Citrate Plasma Introduce Variability
Elements such as Zn, Ca, Cr, and Mn were systematically underestimated in EDTA and citrate matrices, likely due to chelation or tube-derived contamination.
Accuracy Evaluation
- 7 of 13 certified elements (e.g., Mg, Fe, Se) aligned with reference ranges
- 5 elements (e.g., Zn, Ca, Cr) showed matrix-dependent suppression
- Hg exhibited marginal elevation in some matrices
- Most other elements matched Seronorm™ indicative values, with the exception of Cd, which was lower in EDTA plasma
This study underscores the importance of selecting suitable matrices and validated protocols when designing projects involving:
- Population-scale element profiling
- Longitudinal metal exposure research
- Retrospective analysis using biobank specimens
- Nutritional or environmental metal trend studies
Reference
- Guerra, Giulia, et al. "Comprehensive assessment of matrix effects in metallomics: evaluating 27 metals in serum, heparine-plasma-, EDTA-plasma and citrate-plasma by ICP-MS analysis." Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology (2025): 127667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2025.127667









