O-linked glycosylation has commonly found in secreted and membrane-bound proteins and takes place in the Golgi. It refers to the binding of glycans to serine and threonine, following with a extent to hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine. The main type of O-glycosylation in secreted and membrane-bound proteins appears to be the addition of reducing terminal N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc). The O-linked glycan is also recognized as as 'mucin-type' glycan. In addition to the mucin-type O-linked glycans, many mammalian proteins present mannose (Man), fucose (Fuc), glucose (Glc), Gal or xylose (Xyl) as reducing terminal linkages. This group of O-linked glycan dominated protein localization and transportation, protein solubility, antigenicity and cell-cell interactions.
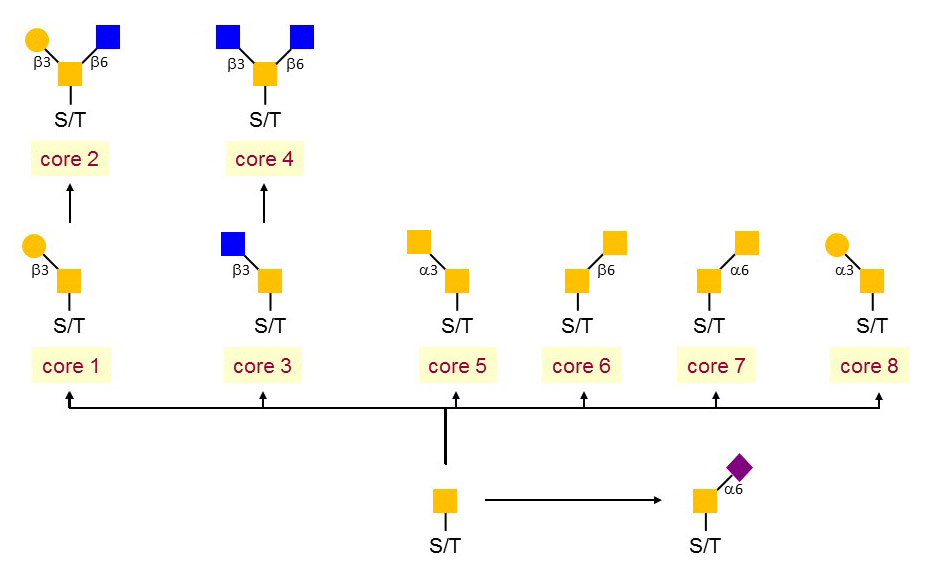 Figure 1. The core structures of mucin-type.
Figure 1. The core structures of mucin-type.
Linkage analysis is a well-established and ingenious approach for linkage positions determination. The principle is to introduce a stable substituent (an ether-linked methyl group) onto each free hydroxyl group of the native glycan. The glycosidic linkages, which are much more labile than the ether-linked methyl groups, are then cleaved by acid hydrolysis, producing individual methylated monosaccharides with free hydroxyl groups at the positions that were previously involved in a linkage. The partially methylated monosaccharides are ring-opened with a reducing agent (normally borodeuteride) to introduce a new hydroxyl group, likely a deuterium atom at C-1, which aids to identify the reducing end of each monosaccharide. All the free hydroxyl groups are then acetylated resulting in partially methylated alditol acetates (PMAAs) that can be identified by GC-MS.
Overview of O-Glycan Linkage Analysis
Creative Proteomics attempts to improve O-glycosylation analysis in four aspects, including O-glycoproteins/peptides enrichment, O-glycan dissociation, O-glycan structure identification and quantitative analysis.
- Sample preparation
- O-glycans release
- Methylation of the released glycans
- Glycans are cleaved with exoglycosidases or acid hydrolysis
- Reduction and derivatization of free hydroxyl groups
- Analyze and quantify by GC-MS
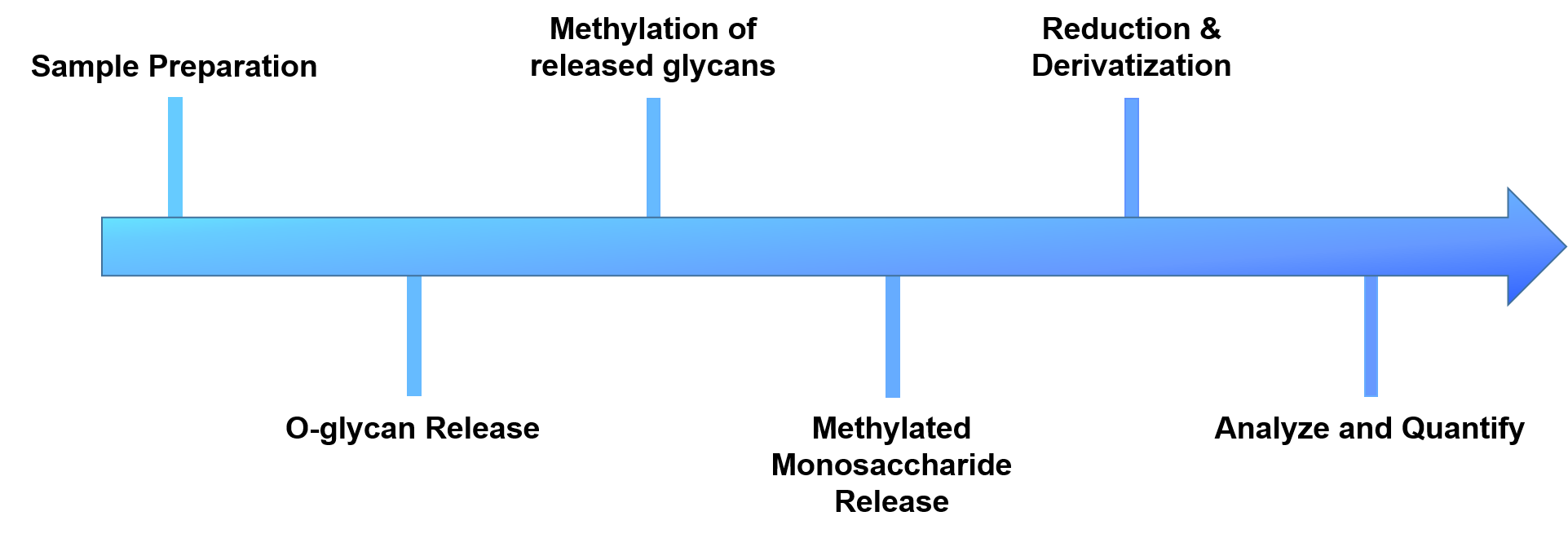 Figure 2. The workflow of our O-glycan linkage analysis.
Figure 2. The workflow of our O-glycan linkage analysis.
Samples Delivery
- If you are providing a tissue sample, please send the tissue to us with dry ice.
- If you are providing a protein sample, use normal tissue or cell lysate for protein extraction.
| The types of samples | Protein | Cell | Animal tissue | Blood (EDTA anticoagulation) | Serum | Urine | Microbial samples |
| Sample size | 100 μg | 1 x 107 cells | 1 g | 1 mL | 0.2-0.5 mL | 2 mL | 200 mg (dry weight) |
If you have any questions regarding sample delivery, please feel free to contact us and our experts are always available.
Creative Proteomics, with highly experienced bio-scientists and advanced analytical techniques in omics research, can provide our clients with a range of glycomics and bioinformatics analysis services. Please feel free to contact us and see how we can help you address your problems.