What is Hinokitiol?
Hinokitiol, also known as β-thujaplicin, is a naturally occurring tropolone derivative primarily extracted from the heartwood of cupressaceous trees such as Chamaecyparis obtusa. It is a monoterpenoid characterized by its iron-chelating properties, which activate caspase-3, leading to apoptosis. Hinokitiol exhibits a wide array of biological activities, including antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer effects. It is used in various applications ranging from hair tonics and toothpastes to cosmetics and food products, owing to its efficacy against bacteria, fungi, and oxidative stress.
Hinokitiol analysis is crucial for understanding the distribution and concentration of this bioactive compound, which has significant implications for its applications in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and environmental sciences. Accurate analysis aids in assessing its efficacy, safety, and quality in various products, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and optimizing its utilization in therapeutic and industrial contexts.
Hinokitiol Analysis Services Provided by Creative Proteomics
Creative Proteomics provides plant metabolomics analysis services. Our hinokitiol analysis service encompasses a wide range of comprehensive analytical and support offerings, designed to meet diverse research and industrial needs. Our services include:
Hinokitiol Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis: Accurate measurement of hinokitiol concentration and identification of its structural variants to ensure precise characterization.
Hinokitiol Purity Assessment: Determination of hinokitiol purity levels to verify the quality and suitability of the compound for various applications.
Hinokitiol Structural Characterization: Detailed elucidation of hinokitiol's molecular structure, including confirmation of its chemical identity and functional groups.
Hinokitiol Metabolite Profiling: Analysis of hinokitiol's metabolic pathways and identification of its metabolites to understand its biological interactions and degradation.
Techniques and Instrumentation for Hinokitiol Analysis
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS):
Method: Used for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of hinokitiol and its metabolites. Samples are vaporized and analyzed based on their mass-to-charge ratios.
Instrumentation: GC-MS systems, such as those from Agilent Technologies, equipped with advanced detectors and high-resolution mass spectrometers.
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS):
Method: Utilizes liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry for separation and identification. Provides detailed analysis of hinokitiol's structural features and its interaction with other compounds.
Instrumentation: LC-MS systems, including UPLC Q-Tof Premier from Waters, offer high sensitivity and resolution.
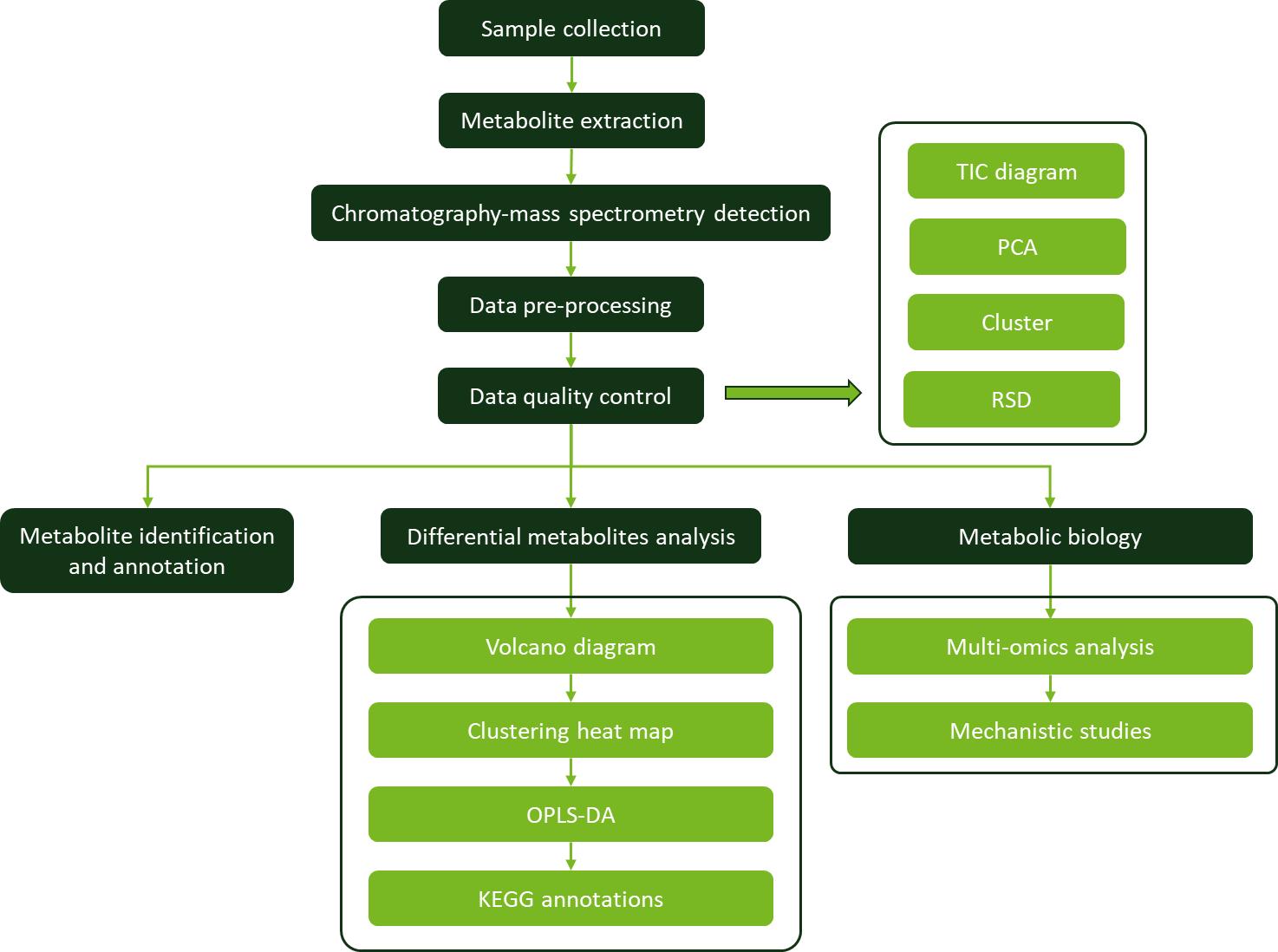
Applications of Hinokitiol Analysis
Hinokitiol analysis has a wide range of applications across various fields:
Pharmaceutical Research: Assessment of hinokitiol's efficacy and safety in drug development, especially for its antimicrobial and anticancer properties.
Environmental Science: Investigation of hinokitiol's role in bioremediation processes and its impact on ecological systems.
Cosmetic Industry: Analysis of hinokitiol's effectiveness in skin care products, focusing on its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Food Industry: Monitoring of hinokitiol levels in food products to evaluate its potential as a natural preservative and antimicrobial agent.
Sample Requirements for Hinokitiol Analysis
| Sample Types |
Sample Size |
Biological Repeat |
| Plant Samples |
Leaf, stem, bark, root, or extract |
Minimum 1 g (fresh weight) or 50 mg (dried weight) |
3-6 |
| Animal Samples |
Tissue, blood, or serum |
Minimum 1 mL (liquid) or 50 mg (tissue) |
| Cell Samples |
Cultured cells or cell lysates |
Minimum 1 million cells or 1 mL of cell lysate |
Q1: Can you provide a detailed report of the analysis results?
A1: Yes, we provide a comprehensive report detailing the results of the hinokitiol analysis. The report includes data on the concentration of hinokitiol, identification of related compounds, and any relevant qualitative or quantitative findings. Our reports are designed to be clear and actionable for your research or application needs.
Q2: Are there any specific storage or handling requirements for the samples before submission?
A2: Yes, proper storage and handling are crucial. Plant and animal samples should be stored at the specified temperatures to prevent degradation. Cell samples should also be kept at -80°C. Ensure samples are well-sealed and labeled to avoid contamination and misidentification during transit.
Case. Simple HPLC Analysis of Hinokitiol in Skin Lotion with Visible Light Detection After Pre-column Dabsylation
Background
Hinokitiol (β-thujaplicin) is a naturally occurring tropolone found in various cupressaceous plants, known for its potent antibacterial properties. It is commonly used in personal care products, including skin lotions and body soaps. The analysis of hinokitiol is challenging due to its chelating ability, instability, and adsorption on stationary phases in chromatographic methods. Previous methods for determining hinokitiol included derivatization with various reagents and detection by HPLC or capillary electrophoresis. However, these methods had limitations such as interference from preservatives like parabens, high costs of reagents, or poor reproducibility.
Samples
The study focused on analyzing two skin lotion samples:
Skin Lotion A: Contained hinokitiol at a labeled concentration of 0.05 g/100 mL.
Skin Lotion B: Also contained hinokitiol, but the concentration was not stated on the label.
Technical Methods Procedure
Derivatization: Hinokitiol was derivatized using 4-(Dimethylamino)azobenzene-4'-sulfonyl chloride (Dabsyl-Cl) in borate buffer (pH 9.5) at 55°C for 10 minutes. The reaction was stopped with L-aspartate.
Chromatography: An LC system with a C18-MS-II column and UV detection at 450 nm was used. The mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile and Milli-Q water with 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid, at a flow rate of 0.40 mL/min.
Standard Solutions: Calibration was done using standard solutions of hinokitiol.
Results
The concentration of hinokitiol in skin lotion A was found to be 559 ± 56 μg/mL, consistent with the labeled concentration.
In skin lotion B, the concentration of hinokitiol was 76.2 ± 2.5 μg/mL.
Recovery of spiked hinokitiol in both lotions was satisfactory, supporting the method's accuracy and reliability.
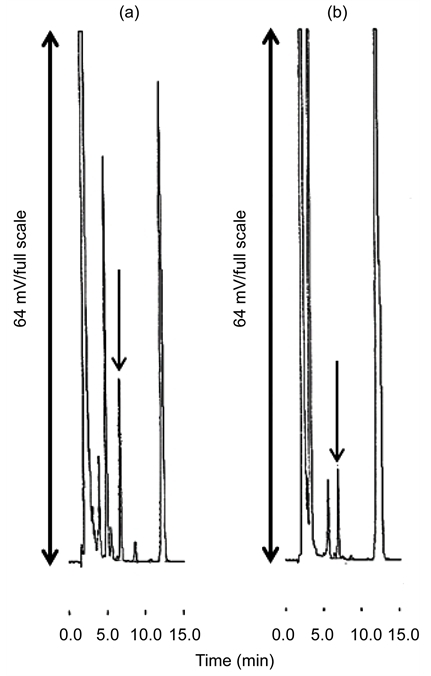 Typical chromatograms of skin lotion sample ((a), 0.25 mL/20mL) and skin lotion sample ((b), 1.0 mL/20mL) after derivatization with Dabsyl-Cl.
Typical chromatograms of skin lotion sample ((a), 0.25 mL/20mL) and skin lotion sample ((b), 1.0 mL/20mL) after derivatization with Dabsyl-Cl.
Reference
- Higashi, Y., & Tohda, S. (2017). Simple HPLC analysis of hinokitiol in skin lotion with visible light detection after pre-column dabsylation. American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 8(5), 345-354.



 Typical chromatograms of skin lotion sample ((a), 0.25 mL/20mL) and skin lotion sample ((b), 1.0 mL/20mL) after derivatization with Dabsyl-Cl.
Typical chromatograms of skin lotion sample ((a), 0.25 mL/20mL) and skin lotion sample ((b), 1.0 mL/20mL) after derivatization with Dabsyl-Cl.

