The tricarboxylic acid cycle is a ubiquitous metabolic pathway in aerobic organisms and is distributed in mitochondria. It is called the tricarboxylic acid cycle because that several major intermediate metabolites in this cycle are organic acids containing three carboxyl groups, also known as the citric acid cycle or the TCA cycle. Aiming to help our customers evaluate the energy metabolic status of their cells, Creative Proteomics can provide comprehensive tricarboxylic acid cycle-MFA services to detect the metabolites associated with the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
What is the TCA cycle?
The TCA cycle is a cyclic reaction system consisting of a series of enzymatic reactions, starting from the formation of citric acid from the formation of citric acid by acetyl-CoA, followed by four dehydrogenations, a single substrate level phosphorylation, and finally the production of two molecules of carbon dioxide and the re-formation of oxaloacetate. The TCA cycle is the ultimate metabolic pathway for the thorough oxidation and breakdown of the three major nutrients (carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids), and is also the center of the metabolism of carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid.
Applications of Our TCA cycle-MFA Services
- Explore the viral pathogenesis and antiviral immunity
- Investigate the cellular energy acquisition pathway
- Understand the process of oxidative breakdown of nutrients
- Quantification of targets of important metabolites associated with low energy metabolism
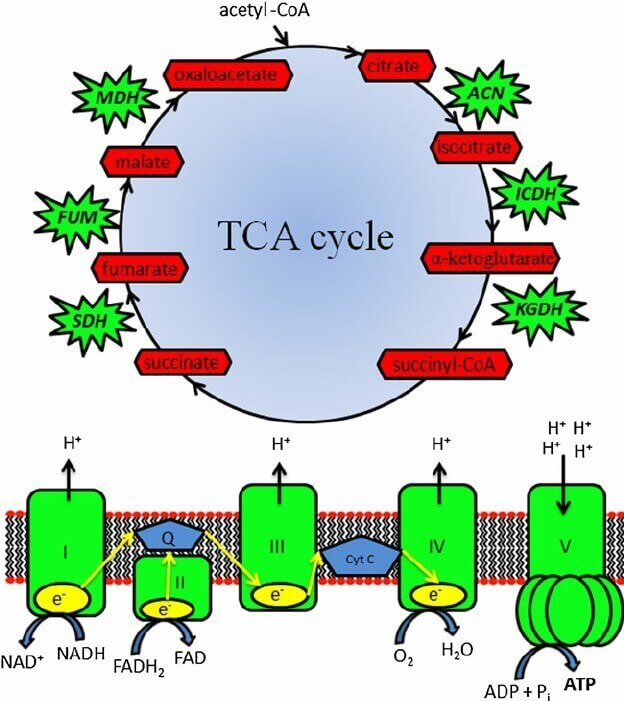 Figure 1. The tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. (Sungwon, H.; et al. 2013)
Figure 1. The tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. (Sungwon, H.; et al. 2013)
Our Services
Creative Proteomics has developed a novel metabolic flux analysis platform to provide TCA cycle-MFA service in a competitive fashion. We can offer a wide range of services to support all research and development activities.
- Our team has applied high performance liquid chromatography strategy for sample separation and DAD detector identification to provide efficient and accurate detection of the content change of the circulating metabolite of tricarboxylic acid
- At Creative Proteomics, the detectable circulating metabolites of tricarboxylic acid cycle include citric acid, pyruvic acid and succinic acid
- For common tricarboxylic acid cycle metabolites or similar substances metabolized by the above tricarboxylic acid cycle, our experts can perform assays by using standard samples, and for rare tricarboxylic acid cycle metabolites, customized detection is available if standard samples are provided
- For enzymes in the tricarboxylic acid cycle, we are able to use various biochemical assays in combination with the corresponding kits to meet your different needs
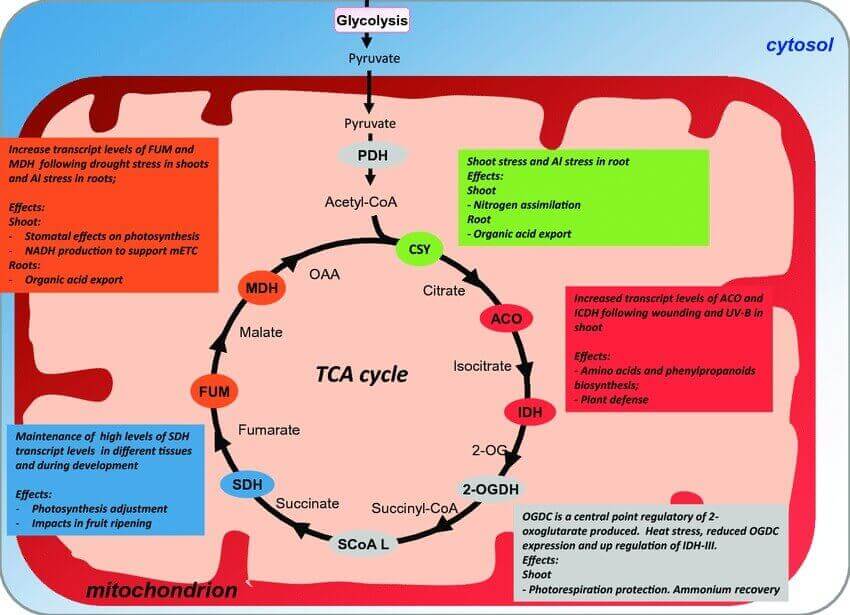 Figure 2. Schematic summary representation of tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and its possible strategic for the metabolic engineering. (Frota, C; et al. 2014)
Figure 2. Schematic summary representation of tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and its possible strategic for the metabolic engineering. (Frota, C; et al. 2014)
Tricarboxylic acid cycle projects
| Citric acid (CA) content | Glycolic acid content | Uridine diphosphate glucose content |
| Isocitric acid content | Phosphoenol pyruvate content | 5-Xylose phosphate content |
| Malic acid content | 6-Phosphogluconate content | Malonyl-CoA content |
| Succinic acid content | Dihydroxyacetone phosphate content | Succinyl-CoA content |
| α-Ketoglutaric acid content | 3-Phosphoglycerol content | Acetyl-CoA content |
| Oxaloacetic acid content | 3-Phosphoglycerol content | Mitochondrial isocitric acid dehydrogenase (ICDHm) content |
| Pyruvate (PA) content | Glucose content | α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (α-KGDH) content |
| Lactate (LA) content | 4-Phosphate-erythritose content | Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) content |
| Mitochondrial citric acid (MCA) content | 1, 6-Diphosphate fructose content | Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) content |
| Acetyl-CoA activity | 1-Phosphate fructose content | NAD+ content |
| mitochondrial isocitric acid dehydrogenase (ICDHm) activity | 6-Phosphate fructose content | NADH content |
| Acetyl-CoA activity | 1, 6-Diphosphate glucose content | NADP+ content |
| Detection of mitochondrial isocitric acid dehydrogenase (ICDHm) activity | 1-Phosphate glucose content | NADPH content |
| α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (α-KGDH) activity | 6-Phosphate glucose content | ATP content |
| Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) activity | 1-Phosphate mannose content | ADP content |
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) activity | 6-Phosphate mannose content | ADP content |
| Total acid content | Phosphoenol pyruvate content | AMP content |
| 2-Phosphoglycerol/3-phosphoglycetic acid content | 5-Phosphate ribose content | cAMP content |
| Glucose adenosine diphosphate content | Detection of 5-phosphate ribulose content | GTP content |
| DL-α-hydroxyglutaric acid content | Glycolic acid content | GDP content |
| 7-Sedum phosphate sedum heptose content | UDP content |
Features of Our MFA Platform
- Developed based on the most updated knowledge of biology, bioinformatics and software development
- Widely applicable to a wide range of metabolic system
- Professional bioinformatics teams & personalized bioinformatics analysis services.
- Advanced instrument platform
- Integrated quantitative methodologies and comprehensive solutions for metabolomics
Based on high-performance quantitative techniques and advanced equipment, Creative Proteomics has constantly updating our metabolic flux analysis platform and is committed to offering professional, rapid and high-quality services of tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle)-MFA at competitive prices for global customers. Our personalized and comprehensive services can satisfy any innovative scientific study demands, please contact our specialists to discuss your specific needs. We are looking forward to cooperating with you!
References
- Sungwon, H.; et al. The unravelling of metabolic dysfunctions linked to metal-associated diseases by blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2013. 405: 1821-1831.
- Frota, C.; et al. Evolution and Functional Implications of the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle as Revealed by Phylogenetic Analysis. Genome Biology & Evolution. 2014. 10: 2830-2848.