Targeted Lipidomics Service – High-Resolution LC-MS/MS & GC-MS
Accurately quantify lipid species for pathway mapping, biomarker discovery, and disease research.
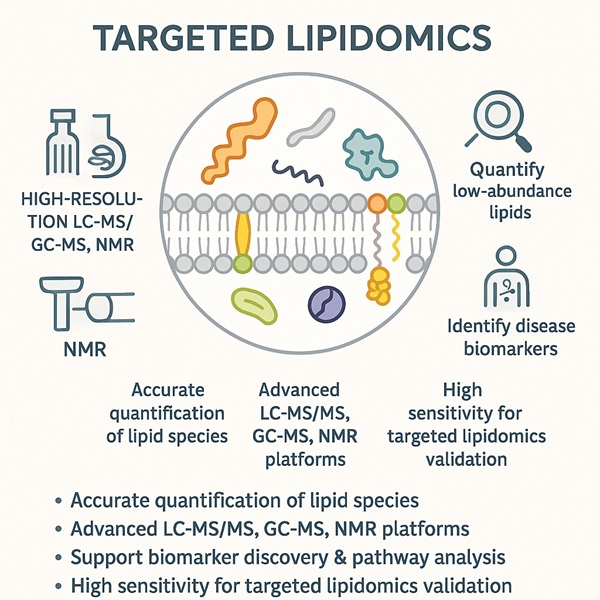
Targeted lipidomics uses advanced LC-MS, GC-MS, and NMR platforms to precisely measure specific lipid molecules. Our service helps researchers distinguish targeted vs untargeted lipidomics, quantify low-abundance signaling lipids, and deliver reliable lipidomics pathway analysis.
- Quantify low-abundance lipid signaling molecules
- Expert advice to select between targeted and untargeted lipidomics strategies
- High-resolution LC-MS/MS, GC-MS, NMR platforms
- Regulatory-ready lipidomics data analysis
Submit Your Request Now
×
- Overview
- Lipidomics Service
- Why Us
- Technical Platforms
- Workflow
- Applications
- Demo
- FAQs
- Case & Publications
- Sample Requirements
Targeted vs Untargeted Lipidomics
Targeted lipidomics focuses on predefined lipid species and delivers precise quantification for hypothesis testing and validation. Untargeted lipidomics casts a broad, discovery-driven net to survey thousands of features and nominate biomarkers. Most projects benefit from a staged approach: untargeted for discovery → targeted for verification.
| Feature | Targeted Lipidomics (PRM/SRM) | Untargeted Lipidomics (Discovery) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Hypothesis-driven validation and absolute/relative quantitation | Discovery-driven profiling and biomarker screening |
| Coverage | Dozens to hundreds of defined lipids | Thousands of features across lipid classes |
| Sensitivity / Linearity | Very high; ideal for low-abundance signaling lipids | High, semi-quantitative; class-level trends |
| Acquisition | PRM/SRM/MRM on LC-MS/MS; isotope-labelled internal standards | DDA/DIA (LC-MS/MS), multi-class libraries, in-silico IDs |
| Best for | Pathway confirmation, clinical-adjacent studies, method transfer | Phenotyping, mechanism exploration, candidate generation |
| Outputs | Absolute concentrations, QC-backed quant tables, acceptance criteria | Feature lists, differential analysis, putative IDs, volcano/PCA/PLS-DA |
How we integrate both
Start with untargeted lipidomics to uncover altered lipid pathways, then move to targeted lipidomics analysis to verify candidates with PRM/SRM and report fit-for-purpose quantitative data.
Common questions we solve
Targeted vs untargeted lipidomics—which should I choose?
If you need discovery, begin untargeted; if you need quantitative verification or method validation, go targeted. We can scope a hybrid plan.
How does lipidomics relate to metabolomics?
Lipidomics is a specialised branch of metabolomics; we connect lipidomics pathway analysis to broader metabolic context when needed.
What Is Targeted Lipidomics?
Targeted lipidomics is a mass spectrometry–based approach that focuses on predefined lipid species to obtain precise, quantitative data. Using high-resolution LC-MS/MS and isotope-labelled standards, it detects low-abundance lipids such as phospholipids, sphingolipids, fatty acids, and sterols, providing accurate concentrations rather than broad surveys.
Unlike untargeted lipidomics, which scans widely for discovery, targeted lipidomics is hypothesis-driven—ideal for pathway validation, biomarker verification, and clinical-adjacent studies.
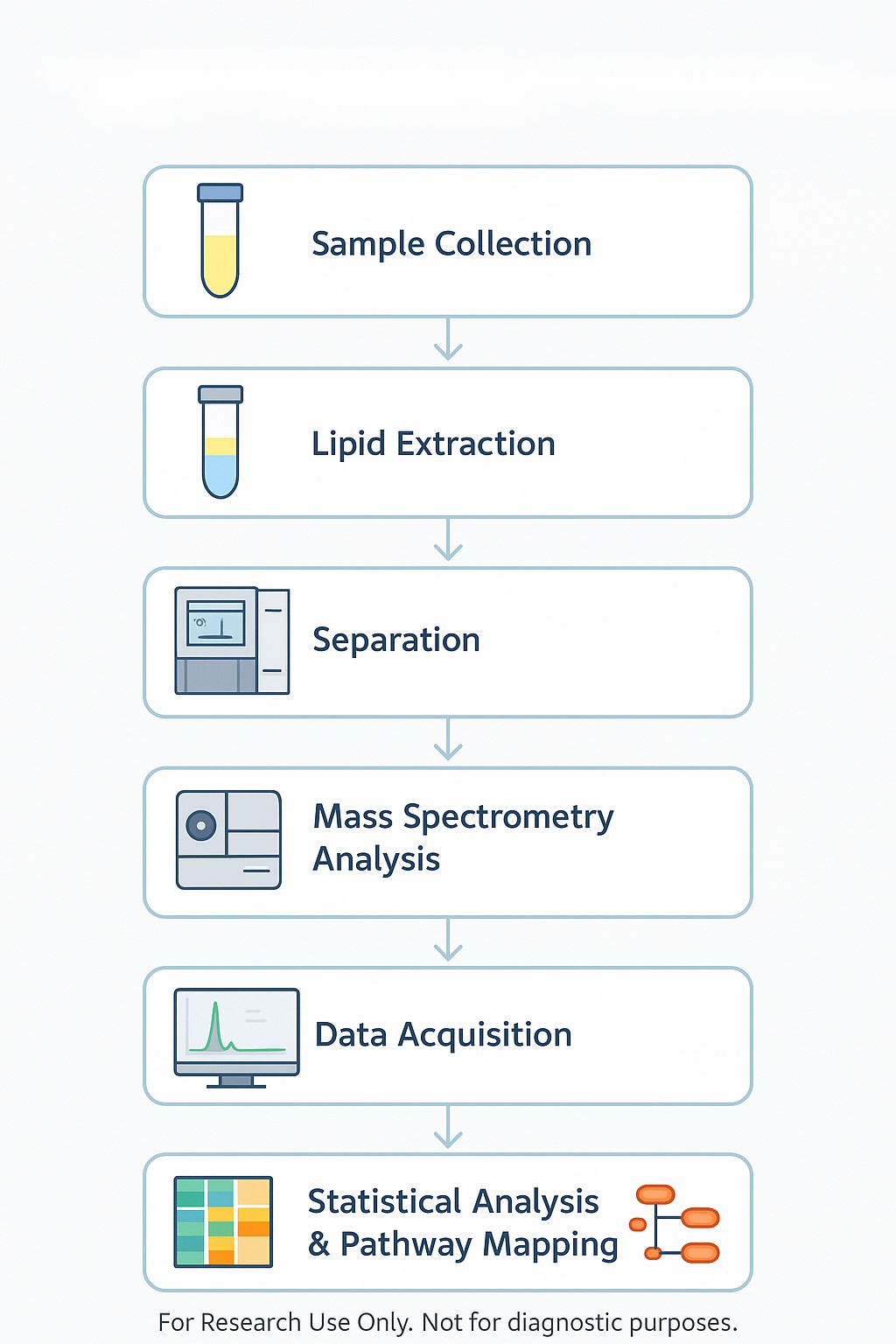
How to Design A Targeted Lipidomics Study
Designing a targeted lipidomics study requires a clear research question, rigorous workflow, and reliable analytical tools. By following a structured research framework, scientists can define hypotheses, select appropriate lipid panels, and generate high-confidence quantitative data. The diagram below outlines the key steps—from study design and sample preparation to LC-MS/MS detection, data analysis, and biological interpretation—helping researchers translate lipidomic insights into disease mechanisms, biomarker validation, and drug development applications.

Featured Lipid Analysis Service
Need analysis of lipids not listed here? Contact us to discuss custom lipidomics solutions.
Service Contents
- Fatty Acids Analysis Service
- Fatty Acids Derivatives Analysis Service
- Fatty Acids Metabolism Analysis Service
- Glycerolipids Analysis Service
- Phospholipidomics Service
- Glycerophospholipids Analysis Service
- Sphingolipids
- Isoprenoids
- Sterols
- Other Analysis Services
Fatty Acids Metabolism Analysis Service
Glycerophospholipids Analysis Service
- Glycerophospholipids
- Cardiolipins
- phosphatidylcholine (PC)
- phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)
- phosphatidylserine (PS)
- phosphatidylinositol (PI)
- phosphatidylglycerol (PG)
- phosphatidic acid (PA)
Isoprenoids
Other Analysis Services
Complementary Services for Lipidomics Research
Explore complementary lipidomics and metabolomics solutions to support your research.
Broad, discovery-driven lipidomics profiling to screen thousands of lipid features and uncover novel biomarkers across lipid classes.
Integrative bioinformatics mapping of lipid metabolism networks, connecting lipid alterations with biological pathways and disease mechanisms.
Comprehensive untargeted and targeted metabolite profiling to link lipid metabolism with broader cellular and systemic biochemical changes.
Why Choose Creative Proteomics?
State-of-the-art multi-omics platform
We don't just offer lipidomics — we integrate proteomics, metabolomics, glycomics, transcriptomics and lipidomics in a unified workflow. That means you get cross-omics context, deeper mechanistic insight, and fewer sample wastes, all under one roof.
Elite instrumentation & resolution
We deploy Orbitrap, timsTOF, Q-Exactive, and high-sensitivity GC-MS/NMR systems. Our ultra-high resolution capability (>120,000) ensures accurate separations and minimal interference, enabling confident identification of isomers and trace lipids.
Unmatched quantitative performance
Our targeted assays deliver detection limits in the part-per-million (ppm) range and dynamic linear ranges spanning 5–6 orders of magnitude. You'll get precise, reproducible quant data that stand up to peer review and regulatory scrutiny.
Broad applicability, zero restrictions
Our workflows are species-agnostic and not limited by availability of commercial standards. Whether you're working with human, plant, microbial, or exotic organisms, we can adapt without shrinking your analyte list.
High throughput, high efficiency
We process dozens of lipid targets per run, reducing sample volume and cost per assay. This throughput advantage accelerates study timelines and enables larger cohort analyses.
Protocol refinement & software finesse
Our protocols are continuously optimized based on internal metrics and client feedback. We combine the best of commercial tools (e.g. Skyline, XCMS) with in-house software and custom algorithms to resolve complex lipids, coelutions, and ambiguous spectra.
Scientific design + consultative service
From project inception we advise on sample collection, QC, experimental design, isotope labeling, and statistical power. Our team acts as your scientific partner, not just a service provider.
Rapid turnaround & data ownership
While delivering high quality, we commit to competitive lead times. You retain full rights to raw data, processed tables, and annotated spectra.
Regulatory and publication readiness
Our data packages (annotated spectra, QC reports, method logs) are designed to align with journal and regulator expectations (e.g. ICH, FDA guidelines). You can take the data straight to submission or publication.

Download the Targeted Lipidomics Brochure
Get our detailed guide on targeted lipidomics analysis, including workflow, technical platforms, case studies, and sample requirements. Perfect for researchers comparing targeted vs untargeted lipidomics or planning biomarker studies.
Technical Platforms
See more Creative Proteomics Mass Spectrometry
The targeted metabolomics service provided by Creative Proteomics is based on our cutting edge separation and analytical platforms. Our experienced technicians have optimized protocols, in order to provide best service to meet customers' requirement.
Lipidomics Analysis Workflow
Data Analysis
| Standard | Analysis content | |
|---|---|---|
| Standard analysis | Quality control | Get high quality data |
| Method evaluation | Assess the quality of the established method | |
| Difference analysis (histogram, violin plot, etc.) | Assess group differences for each lipid molecules | |
| Advanced analysis | Cluster Analysis | Exploring the content trend pattern of lipid molecules |
| Machine learning | Biomarkers screening with good diagnostic performance | |
Applications of Targeted Lipidomics



Identify Lipid Classes with Fragmentation Patterns
Lipid classes, like phosphatidylcholines, exhibit distinct fragmentation patterns , aiding targeted analysis.
Quantify Low-Abundance Lipid Signaling Molecules
Targeted lipidomics enables precise measurement of low-abundance lipids like eicosanoids and S1P, key in signaling and disease, through selective extraction.
Enhance Detection via Lipid Derivatization
Derivatization boosts ionization efficiency and sensitivity for challenging lipids, ensuring accurate detection, especially for unstable or low-abundance species like eicosanoids and phosphoinositides.
Demo for Targeted Lipidomics
Figures come from (Li, Y.et.al, Sci Rep,2023)
FAQ
What is targeted lipidomics analysis?
Targeted lipidomics analysis quantifies specific lipid molecules (like phospholipids, sphingolipids) using high-res LC-MS/MS with isotope standards. It delivers absolute or relative amounts under hypothesis-driven workflows, ideal for validating biomarkers or pathways.
What is the difference between targeted and untargeted lipidomics?
Targeted lipidomics focuses on a defined panel of lipids with high sensitivity (PRM/SRM), whereas untargeted lipidomics casts a broad net to profile thousands of features and discover new candidates. Use untargeted for discovery, targeted for verification.
Can your service detect low-abundance signaling lipids?
Yes. Our methods are optimized for low-abundance lipids using sensitive PRM/SRM acquisition and enriched sample prep, enabling detection and quantification that general profiling might miss.
What sample types and quantities are required?
We accept tissues, serum/plasma, cells, fluids, and more. Typical input is 100–200 mg tissue, >100 µL plasma, or ≥10⁷ cells. Samples must be frozen at –80 °C and free of interfering reagents (e.g. detergents). (We provide full sample prep guidelines.)
Do lipids near glycosylated or conjugated proteins interfere with detection?
They can. If glycans complicate fragmentation or ionization near lipid attachment sites, we recommend partial deglycosylation or tailored digestion while preserving lipid integrity to improve coverage.
How soon can I get a quote and start a project?
Once you submit your sample type, target lipid list, and analytical goals, our team responds with a tailored proposal within 24–48 hours and guides you through next steps.
What is the purpose of lipidomics?
Lipidomics aims to characterize the full lipidome of a biological system to reveal how lipids contribute to cell structure, energy storage, signaling, and disease pathways. It links lipid changes to conditions like metabolic disorders, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
How do you analyse lipidomics data?
We preprocess with normalization, peak detection, and identification, then perform quantification, pathway enrichment, and visualization using bioinformatics tools to correlate lipid profiles with biological states.
What is the difference between lipidomics and metabolomics?
Lipidomics is a branch of metabolomics focused solely on lipids, whereas metabolomics covers all small molecules (lipids, sugars, amino acids, etc.). Both use MS and chromatography, but lipidomics deploys more lipid-specific methods due to structural complexity.
Learn about other Q&A.
Client Case Study Highlight: Targeted Lipidomics for Immunometabolism Research

Sanchez, H.N., Moroney, J.B., Gan, H. et al. B cell-intrinsic epigenetic modulation of antibody responses by dietary fiber-derived short-chain fatty acids. Nat Commun 11, 60 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13603-6
- Background
- Challenges Faced by the Client
- Our Solution: Targeted Lipidomics Service
- Study Impact
- Why Clients Choose Us
- Client Value
Dietary fiber-derived short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are known to influence immune responses, but their exact role in modulating antibody production remained unclear. Our client, an academic immunology group, aimed to quantify SCFAs in multiple tissues (spleen, colon, and mesenteric lymph nodes) to understand their impact on B cell function and immune regulation.
- Difficulty in precise quantification of low-abundance SCFAs across different tissues.
- Need for high sensitivity and reproducibility to detect subtle metabolic differences.
- Requirement for regulatory-aligned data that could support high-impact publication.
Creative Proteomics applied a GC-MS–based targeted lipidomics workflow, optimized for SCFA detection with isotope-labelled internal standards. Our platform ensured:
- High sensitivity for low-abundance metabolites.
- Absolute quantification of multiple SCFAs simultaneously.
- Reproducible data quality suitable for publication in a top-tier journal.
 Figure. GC-MS–based targeted lipidomics quantification of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in spleen, colon tissues, and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs). Data demonstrate tissue-specific SCFA levels that supported the discovery of their role in modulating antibody responses, as published in Nature Communications.
Figure. GC-MS–based targeted lipidomics quantification of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in spleen, colon tissues, and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs). Data demonstrate tissue-specific SCFA levels that supported the discovery of their role in modulating antibody responses, as published in Nature Communications.
The client's research revealed that SCFAs act as key immunometabolic mediators by enhancing antibody responses through epigenetic modulation of B cells. This finding, published in Nature Communications, demonstrated the central role of lipid metabolites in immune regulation and opened new avenues for nutritional interventions in immunotherapy.
- Advanced platforms: GC-MS, LC-MS/MS, and NMR for comprehensive lipidomics.
- Expertise in immunometabolism: Proven experience in quantifying SCFAs and other lipid mediators.
- Publication-ready deliverables: Annotated spectra, quant tables, and QC data aligned with journal and regulatory expectations.
Our service helped the client validate a mechanistic hypothesis, generate regulatory-aligned evidence, and secure publication in a high-impact journal. For biotech and pharma teams, this workflow is directly translatable to biomarker validation, clinical-adjacent studies, and nutritional intervention research.
Start your project today. Contact Creative Proteomics for a customized targeted lipidomics solution.
Publications
Here are some publications in lipidomics research from our clients:

- The olfactory receptor Olfr78 promotes differentiation of enterochromaffin cells in the mouse colon. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44319-023-00013-5
- Prospective randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of a standardized oral pomegranate extract on the gut microbiome and short-chain fatty acids. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13010015
- Annexin A2 modulates phospholipid membrane composition upstream of Arp2 to control angiogenic sprout initiation. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202201088R
- Loss of G0/G1 switch gene 2 (G0S2) promotes disease progression and drug resistance in chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) by disrupting glycerophospholipid metabolism. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.1146
- Evidence for phosphate-dependent control of symbiont cell division in the model anemone Exaiptasia diaphana. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.01059-24
Sample Requirements
| Sample type | Recommended sample size | Pre-treatment and storage |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue | 100-200 mg | Snap freezing in liquid nitrogen, stored at -80℃. |
| Urine | 200-500 μL | 5000×g 4℃ Centrifuge for 30-60min, remove supernatant, store at -80℃. |
| Serum/plasma | >100 μL | Collected serum/plasma, snap freezing in liquid nitrogen, stored at -80℃. |
| Cerebrospinal fluid, amniotic fluid, bile and other body fluids | >200 μL | 4℃ Centrifuge for 10min, (or filter using 0.22μm membrane), remove supernatant and store at -80℃. |
| Suspension cells | >1*107 | Centrifuge and collect cells after liquid nitrogen snap freezing and store at -80℃. |
| Walled cells | >1*107 | Cultured walled cells are stored in 1.5ml centrifuge tubes, snap freezing in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80℃. |
| Cell supernatant | >2 mL | centrifuge at 4℃ for 3 minutes, take the supernatant and store at -80℃. |
Reference
- Li, Yang et al. "Metabolomics-based study of potential biomarkers of sepsis." Scientific reports vol. 13,1 585. 11 Jan. 2023