Protein-DNA Interaction Analysis Service
Protein-DNA interactions play a key role in biological processes, and the precise resolution of them is essential for in-depth studies of gene regulatory mechanisms under physiological and pathological conditions. As a company that has specialized in proteomics research for many years, Creative Proteomics can provide professional protein-DNA interaction analysis service to facilitate your protein research.
What is Protein-DNA Interaction
Interactions between DNA and proteins are associated with many cellular life activities, like DNA replication and recombination, mRNA transcription and modification, virus infection and proliferation, etc. There are many methods used to research protein-DNA interactions, such as EMSA, DNase I footprinting assay, methylation interference, yeast one-hybrid, and ChIP-Seq, etc. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (ChIP-Seq) is a classic method for studying protein-DNA interactions in vivo. It is an antibody-based technique, and is commonly used for the study of protein-DNA interactions such as histones and transcription factors. ChIP-Seq technology combines ChIP with second-generation sequencing technology to efficiently detect DNA segments interacting with histones, transcription factors and others on a genome-wide scale.
The Principle of Protein-DNA Interaction Analysis Methods
EMSA. In the presence of an electric field, DNA migration rate is inversely proportional to the logarithm of its molecular weight. The binding of proteins increases the molecular weight of DNA and blocks its migration.
DNase I footprinting assay.The binding of a specific protein to a DNA segment protects it from DNaseI cleavage. Thus, it does not produce the cleavage molecule, which is separated by gel electrophoresis and appears as a blank area, called a "footprint".
Methylation interference. DMS can methylate the exposed guanine (G) residues in DNA, and hexahydropyridine, in turn, chemically cleaves the methylated G residues specifically, and an experimental method was designed based on this principle.
Yeast one-hybrid DNA-binding proteins bind to DNA cis-acting elements to regulate reporter gene expression, and protein-DNA interactions can be analyzed by phenotypic detection of reporter genes.
ChIP-Seq. ChIP-Seq is based on the principle that it specifically enriches the DNA fragments bound with target proteins by ChIP, and then purifies them and constructs libraries, and next sequences the enriched DNA fragments by high-throughput sequencing. Then, the large number of sequence tags obtained are precisely localized to the genome to obtain DNA segment information in genome-wide interactions with proteins such as histones, transcription factors, etc.
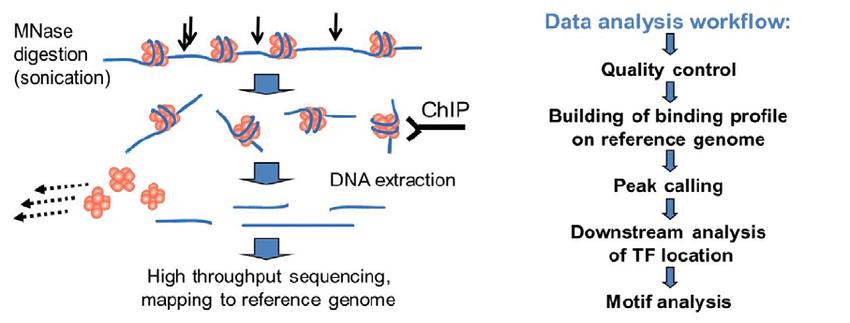
Fig. 1. Schematic of ChIP-Seq (Orlov Y, et al., 2012)
It is best to choose the analysis method that is appropriate for the research needs according to the advantages and disadvantages of each method. The following is an overview of each method's advantages and disadvantages.
Table 1. Advantages and disadvantages of each method
| Methods | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| EMSA | Show the binding site and sequence Highly sensitive Can distinguish different proteins Qualitative and quantitative |
Multiple and complex steps Low affinity binding is difficult to recognize Difficult to realistically reflect in vivo binding |
| DNase I footprinting assay | Large amounts of data Show the binding site and sequence |
Requires a high protein concentration Can disrupt specific interactions High substrate requirement Multiple components cannot be automatically distinguished |
| Methylation interference assay | Analyze the relationship between proteins and G residues at the binding site Identify the precise location of protein-DNA interactions |
Only methylates G and A residues |
| Yeast one-hybrid | High sensitivity Simple operation Rapid |
Prone to false positives and false negatives Some proteins may be toxic Endogenous proteins interfere |
| ChIP-Seq | Directly visualize the dynamic binding in vivo Highly sensitive Can be combined with other technologies |
Experiment conditions must be more stringent Multi-protein binding to the same sequence is difficult to analyze Chromatin can be binded indirectly by proteins |
Our Services
Creative Proteomics provides considerate and high-quality protein-DNA interactions analysis services. And we offer all the analytical methods described above and can provide you with the optimal solution for your research requirements. In addition, we provide protein-protein interaction analysis service, protein-metabolite interaction analysis service and protein-RNA interaction analysis service.
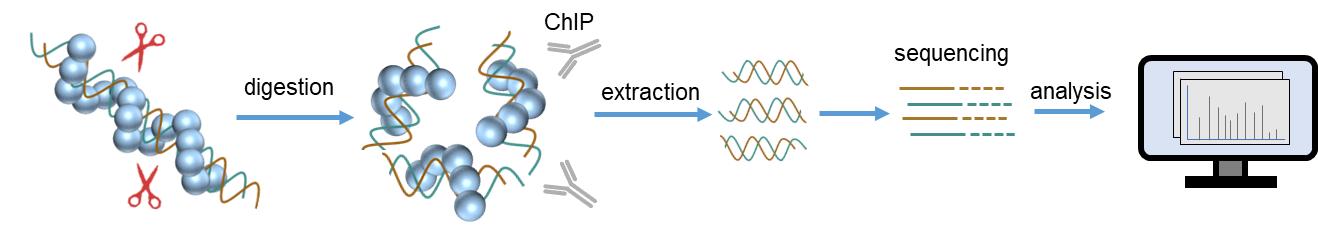
Fig. 2. Protein-DNA interaction analysis workflow by ChIP-Seq
Applications of Protein-DNA Interaction
Analysis of protein-DNA interactions contributes to a clear understanding of the overall properties of DNA-protein complexes. It allows the analysis of DNA conformation and the exact sequence of bases that bind to proteins, the identification of binding proteins based on specific DNA sequences, the identification of proteins on the surface of DNA, and, in addition, the study of the tertiary structure of proteins and their conformational changes in complexes, etc.
Advantages of Protein-DNA Interaction Analysis
- Determine histone modification sites within genome-wide regions.
- Compare the distribution of different types of histone modifications in the genome.
- Identify new promoters and enhancers.
- Can be used for nucleosome localization analysis.
Creative Proteomics provides comprehensive and high-quality proteomics analysis services. If you are interested in protein-DNA interaction analysis, please contact us for more details.
References
- Orlov, Y.; et al. Computer and Statistical Analysis of Transcription Factor Binding and Chromatin Modifications by ChIP-seq data in Embryonic Stem Cell. Journal of Integrative Bioinformatics. 2012, 9: 211.
- Nakato, R. Sakata, T. Methods for ChIP-seq analysis: A practical workflow and advanced applications. Methods. 2021, 187: 44-53

