- Services
- FAQ
- Case Study
- Related Services
- Support Documents
- Inquiry
What is Deamidation and Oxidation
Therapeutic proteins products have been proven effective against various diseases. Complex post-translational modifications (PTMs) are required by most therapeutic proteins. Common PTMs include glycosylation, phosphorylation, oxidation, deamidation, acetylation, methylation, proteolysis, and so forth. These PTMS not only affect efficient secretion, drug efficacy and stability of therapeutic proteins, but also may influence safety, immunogenicity, serum clearance, pharmacokinetics, etc. Deamidation is the process of converting asparagine and glutamine into aspartic and glutamic acids, respectively, which frequently happens during purification of natural and recombinant proteins. Deamidation might result in changes to protein hydrophobicity, charge, mass, and a reduction/loss of biological activity.
Oxidation is a major degradation pathway in protein and peptide formulation and storage, and might cause potential problem in protein production, isolation, and purification. Several amino acids are susceptible to oxidation, including methionine, cysteine, histidine, tyrosine, tryptophan and phenylalanine. Besides, oxidation of certain amino acids can cause changes of conformation, binding affinity, stability, lifespan, immunogenicity, which consequently affect the safety and efficacy of therapeutic proteins.
Since deamidation and oxidation are typical degradation for therapeutic proteins, deamidation and oxidation are critical quality attributes (CQAs) and must be presented during drug discovery.
Creative Proteomics provides a high-sensitivity deamidation and oxidation analysis service to identification and quantification of deamidation and oxidation in accordance with relevant guidelines (ICH Q6B, PharmEu and USP<1047>). Our experienced scientists and professional analytic team will deploy different approaches to help you with deamidation and oxidation analyses, and meet the requirements of every stage of drug discovery.

We Can Provide but Not Limited to
- Asparagine Deamidation analysis
- Glutamine Deamidation analysis
- Deamidation sites identification
- Deamidation products quantification
- Oxidation analysis
- Oxidation sites identification
- Oxidation product quantification
- Glucose Unit (GU) values determination
Technology Platform of Deamidation and Oxidation Analysis Service
Creative Proteomics provides efficient and accurate deamidation and oxidation analysis services through several techniques, including ion exchange chromatography (IEC), capillary isoelectric focusing (cIEF), hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC), liquid-chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), etc.
Both asparagine and glutamine deamidation can be rapidly analyzed by ion IEC and LC-MS/MS. And identification of oxidation sites can be determined by HIC, reverse phase-HPLC coupled with Fabricator digestion, and mixed mode size exclusion chromatography (SEC). Creative Proteomics offers simultaneous identification and quantification of deamidation and oxidation by bottom-up LC-MS with ultrafast tryptic digestion. Pharmaceutical products will be digested into peptides by a 5 min tryptic digestion method. Then the peptides will be separated with nano-LC before subject to mass spectrometer.

Advantages of Deamidation and Oxidation Analysis Service
- High sensitivity: deamidation and oxidation can be identified for low mass ones.
- High accuracy: deamidation and oxidation results can be consistent and accurate.
- Experienced scientists and professional analytic team: professional assistance to identify deamidation and oxidation will be provided throughout drug discovery.
- Advanced equipment: Thermo Scientific™ UltiMate™ 3000 RSLCnano System.
- Optimized analysis platform: The current technology uses automatic chromatographic instruments designed for analysis, which can reduce the scale of analysis and greatly improve the flexibility and effectiveness of analysis.
- Customized service: Optimal buffers and protocols will be customized based on your project and sample type.
Creative Proteomics's analytical scientists can provide complete analysis of deamidation and oxidation, as well as quantification of deamidation and oxidation at specific sites. Quick turnover, clear and concise written reports and protocols, and customized services to will be provided to help customers solve analytical and technical problems.
Sample Requirements
- Sample Type: Purified proteins/peptides, Biological fluids (e.g., serum, plasma)
- Sample Volume: Minimum of 50 µL
- Storage Conditions: Store at -80°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles)
- Buffer Composition: Use compatible buffers (e.g., phosphate-buffered saline) and avoid reducing agents unless required
FAQ
Q: Can you provide customized deamidation and oxidation analysis services based on specific project requirements?
A: Yes, Creative Proteomics offers fully customized deamidation and oxidation analysis services tailored to the specific needs of your project. We understand that different therapeutic proteins, formulations, and stages of drug development may require unique approaches.
Sample Handling: We can accommodate a variety of sample types, from purified proteins and peptides to biological fluids. Additionally, we offer flexibility in buffer composition and concentration based on the characteristics of your sample.
Analytical Approach: Depending on your project's goals, we can adjust the analytical techniques used, such as prioritizing specific modifications (e.g., methionine oxidation) or employing targeted methods to study degradation patterns under stress conditions.
Protocol Optimization: Our team will work closely with you to develop or modify protocols that suit your experimental conditions, ensuring that the analysis aligns with your research and regulatory needs.
Reporting and Consultation: We provide detailed, easy-to-interpret reports that summarize the findings of the analysis. Furthermore, our scientists are available for consultation to discuss the results and offer insights into how they may impact your drug development process.
Whether you need comprehensive analysis or targeted investigations, our flexible service platform ensures that your specific requirements are met efficiently and accurately.
Q: What types of proteins can be analyzed for deamidation and oxidation?
A: Creative Proteomics can analyze a wide variety of proteins for deamidation and oxidation, including:
Monoclonal Antibodies: These therapeutic proteins are commonly subject to deamidation and oxidation due to their complex structure and prolonged storage.
Recombinant Proteins: Proteins produced via recombinant DNA technology can exhibit various PTMs, making them suitable for analysis.
Peptides: Shorter peptide sequences can also undergo modifications, and we can analyze these for both deamidation and oxidation.
Enzymes and Hormones: Therapeutic enzymes and hormones may also be assessed for modifications that could impact their functionality.
Our analytical techniques are adaptable to a range of protein types, ensuring comprehensive analysis across diverse applications.
Q: What types of modifications are specifically detected during the analysis?
A: During the deamidation and oxidation analysis, several specific modifications can be detected, including:
Deamidation: Conversion of asparagine (Asn) to aspartic acid (Asp) and glutamine (Gln) to glutamic acid (Glu).
Oxidation: Modifications of specific amino acids, including: Methionine (Met) to methionine sulfoxide, cysteine (Cys) to cysteine sulfenic acid or disulfides, tyrosine (Tyr) to 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) or other oxidized forms, and tryptophan (Trp) and phenylalanine (Phe) to various oxidized derivatives.
Detection of these modifications provides insights into the stability and functional characteristics of the therapeutic protein, which can be crucial for its development and application.
Case Study
Case: Development of a rapid RP-UHPLC–MS method for analysis of modifications in therapeutic monoclonal antibodies
Background
The article focuses on the development and optimization of a rapid method for analyzing monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), specifically targeting critical quality attributes (CQAs) such as oxidation, deamidation, and fragmentation. Monoclonal antibodies are sensitive to various stress conditions during production, which can affect their stability and efficacy. Accurate characterization of these modifications is essential for ensuring product quality and safety.
Methods
- Optimization of Flow Rate and Gradient: The study compared different flow rates and gradient conditions in reversed-phase ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-UHPLC) to determine the best setup for separating MAb fragments.
- Online Coupling of UHPLC–MS: The RP-UHPLC system was coupled with a time-of-flight (TOF) mass spectrometer to enhance molecular detail retrieval. Key strategies included minimizing dead volume between the UV and MS detectors to improve peak resolution.
- Characterization of MAb Fragments: The separated MAb fragments were analyzed to identify structural variants using mass spectrometry techniques, including the Agilent MassHunter maximum entropy algorithm for mass deconvolution.
- Stress Panel Testing: The MAb was subjected to various stress conditions (oxidative, thermal, and pH stress) to assess degradation patterns, using both the IdeS-UHPLC method and traditional peptide mapping LC-MS for comparison.
- Correlation Studies: The performance of the IdeS-UHPLC method was correlated with results from peptide mapping to validate its effectiveness in monitoring oxidation.
Results
- Optimization Findings: The 0.6 mL/min flow rate provided better reproducibility and lower back pressure than the higher flow rate. A shallower gradient yielded improved resolution in chromatographic profiles.
- Improved Peak Resolution: The optimized UHPLC–MS setup demonstrated improved peak shapes and resolution, allowing for the identification of various glycosylation forms and degradation products.
- Degradation Observations: Stress conditions led to oxidation of methionine residues, deamidation, and other structural modifications. The IdeS-UHPLC method effectively captured these changes, with good correlation to site-specific results obtained from peptide mapping.
- Validation of the Method: The IdeS-UHPLC method proved to be a reliable and rapid alternative for monitoring CQA like Fc oxidation, showing high correlation with peptide mapping results, thereby supporting its application in routine analyses during clinical development and post-commercialization.
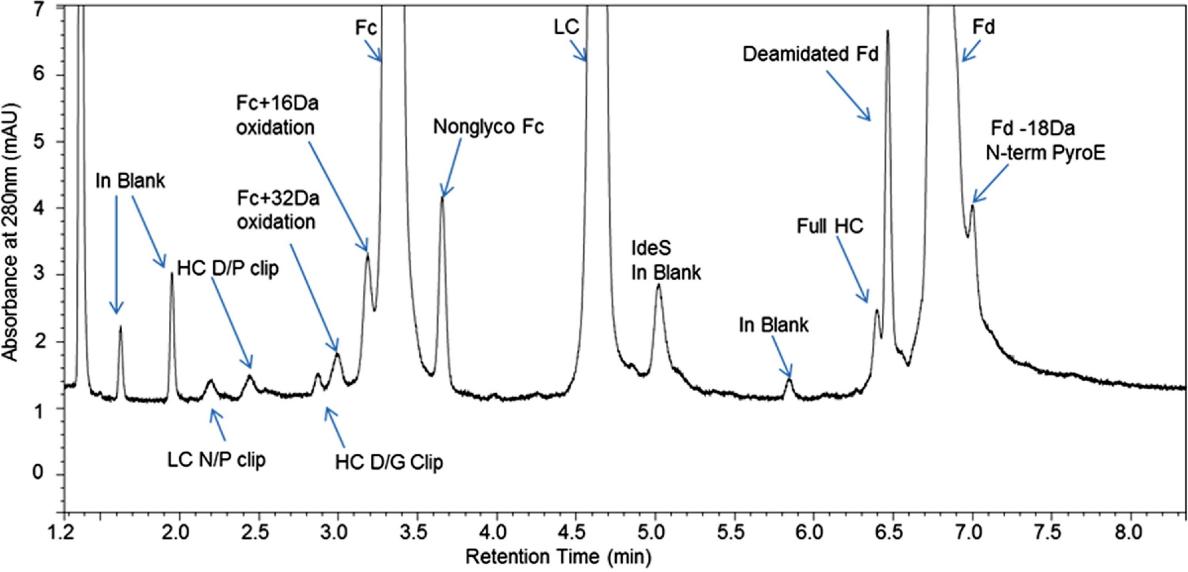 Figure 1. Peak identification by on-line LC-MS. Minor peak mass identifications included N-terminal pyroglutamate, deamidation, oxidation, and aglycosylation.
Figure 1. Peak identification by on-line LC-MS. Minor peak mass identifications included N-terminal pyroglutamate, deamidation, oxidation, and aglycosylation.References
- Jenkins N. Modifications of therapeutic proteins: challenges and prospects. Cytotechnology. 2007, 53:121–125.
- Wang Y, et al. Simultaneous monitoring of oxidation, deamidation, isomerization, and glycosylation of monoclonal antibodies by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method with ultrafast tryptic digestion. MAbs. Taylor & Francis, 2016, 8(8): 1477-1486.
- Nepomuceno A.I., et al. Accurate identification of deamidated peptides in global proteomics using a quadrupole orbitrap mass spectrometer. J Proteome Res. 2014, 13(2): 777-785.
- Riggs D.L., et al. Analysis of glutamine deamidation: products, pathways and kinetics. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 13032−13038.
- Zhang B, et al. Development of a rapid RP-UHPLC–MS method for analysis of modifications in therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Journal of Chromatography B, 2016, 1032: 172-181.
Related Services
Support Documents
KNOWLEDGE CENTER
PTMs of Monoclonal Antibodies and Their Druggability Evaluation
KNOWLEDGE CENTER
KNOWLEDGE CENTER














