- Services
- Demo
- FAQ
- Case Study
- Related Services
- Support Documents
- Inquiry
What Is Protein Molecular Weight and Why Does It Matter?
Protein molecular weight refers to the mass of a protein molecule, typically measured in Daltons (Da). It reflects the number and type of amino acids in the polypeptide chain, along with post-translational modifications.
Why is it important?
Accurate protein molecular weight measurement plays a pivotal role in drug discovery and development. Whether confirming the identity of a recombinant protein or validating subunit structure, understanding a molecule's true size helps detect sequence errors, degradation, or post-translational modifications. For biologics developers, especially those working on monoclonal antibody production, reliable molecular weight data supports key decisions in formulation and regulatory submissions.
Overview of Methods Used to Determine Intact Mass
a. SDS-PAGE
Denatures proteins and coats them with SDS to standardize charge.
Separation by size using gel electrophoresis.
Pros: Cost-effective, visual.
Cons: Low resolution, can't resolve small MW differences.
b. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC/SEC)
Separates proteins based on size using porous beads.
Ideal for: Analyzing protein aggregates or multimers.
Limitations: Requires calibration standards and cannot identify mass precisely.
c. Light Scattering (DLS, MALS)
Measures scattered light to infer hydrodynamic size.
Best for: Observing protein aggregation.
Limitations: Sensitive to impurities; doesn't yield precise molecular weight.
d. Mass Spectrometry
Ionizes proteins to measure their mass-to-charge ratio.
Two dominant methods:
Why Mass Spectrometry Is the Gold Standard
Mass spectrometry offers unmatched sensitivity, accuracy, and versatility, especially when performed using high-resolution platforms.
At Creative Proteomics, we deliver fast, high-accuracy molecular weight analysis through two industry-leading technologies:
MALDI-TOF-MS (Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight):
Ideal for directly measuring intact protein mass, MALDI-TOF-MS is prized for its speed, sensitivity, and minimal sample prep requirements.
High-Resolution ESI-MS (Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry):
This method captures multiply charged protein ions, which are then deconvoluted to reveal precise molecular weights—making it a go-to solution for complex protein mixtures.
These complementary techniques enable detailed molecular assessments, such as:
- Detecting mutations or truncations in recombinant proteins
- Confirming isotope incorporation in labelled proteins
- Verifying subunit homogeneity
- Supporting peptide mass fingerprinting and protein identification workflows
Why It's Preferred:
- Detects post-translational modifications (PTMs)
- Handles complex mixtures
- Suitable for intact antibodies (e.g., LC-MS for Antibodies)
With both platforms integrated in our lab, Creative Proteomics offers flexible, project-specific testing packages. Let us help you accelerate your biologic development with protein molecular weight services you can trust.
We Can Provide but Not Limited to:
| ESI-Q TOF-MS Intact Mass Analysis Service | MALDI-TOF-MS Intact Mass Analysis Service | |
|---|---|---|
| Salt Impurities Tolerance | Better | Bad |
| Sample Condition | Liquid | Solid |
| Ionization | Continuous | Impulse |
| Protein Mixture Identification | Good | Bad |
| Combine with LC | Yes | No |
| Analysis Time | Long | Short |
| Data Information | Much | Less |
| Charge | +1.2.3. | +1 |
| Other Characteristics | It can also be combined with various quality analyzers. |
|
Workflow
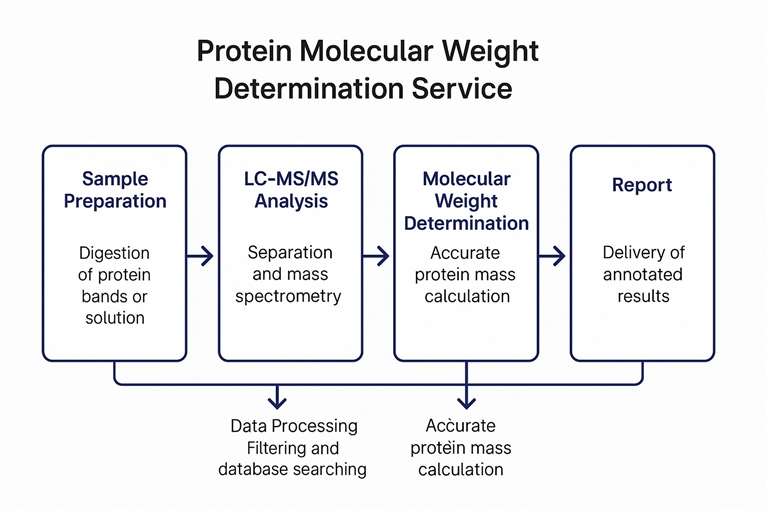
Applications of Molecular Weight Analysis
Protein MW analysis supports a wide range of research and QC goals:
- Verifying recombinant protein identity
- Detecting truncations, isoforms, and degradation products
- Studying protein subunit structures and oligomers
- Monitoring antibody aggregation
- Supporting proteomics discovery workflows
- Ensuring batch-to-batch consistency in biologics production
Why Choose Our Protein Molecular Weight Determination Service?
At Creative Proteomics, we combine cutting-edge instrumentation with deep technical expertise to deliver protein mass analysis that's both precise and practical. From small peptide chains to complex biopharmaceutical proteins, our workflow is built to support biologics developers seeking high-confidence data at every stage of development.
Key Advantages:
- Comprehensive Technology Platform:
We integrate advanced mass spectrometers, protein-specific columns, curated databases, and validated analytical protocols to ensure accuracy from ionization to data reporting. - High Mass Accuracy for Large Proteins:
Our system can detect protein masses exceeding 100 kDa at low picomole concentrations, achieving <0.1% error—critical for analyzing recombinant proteins and engineered variants. - Isobaric Amino Acid Discrimination:
With ultra-high mass accuracy (5–10 ppm), we can resolve subtle 1 Da differences between structurally similar amino acids—such as Asp vs. Asn, or Glu vs. Gln—improving sequence verification. - Fast Turnaround:
Speed is essential in modern R&D. Our streamlined process delivers rapid results without compromising data integrity. - Custom Solutions Based on Your Needs:
Whether you're analysing a single construct or comparing multiple formulations, we tailor the method to your sample and research objectives.
Sample Submission Guidelines
To ensure optimal performance of the mass spectrometry analysis, please prepare your samples according to the following requirements:
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Sample Form | Dry powder or solution |
| Sample Amount | 10–50 µg |
| Sample Purity | Greater than 90% |
| Surfactants & Salts | Avoid SDS, Triton-X, and high Tris content if possible |
Demo
 ESI Mass Spectrum of Lac Permease
ESI Mass Spectrum of Lac PermeaseFAQ:
Q: How does SDS-PAGE help in estimating protein molecular weight?
A: SDS-PAGE separates denatured proteins by size. Migration distance is compared to standards for MW estimation.
Q: How long does the analysis take?
A: Turnaround time varies depending on the sample and analysis complexity. However, we strive to provide fast and reliable results.
Q: Can Creative Proteomics handle complex or modified proteins?
A: Yes, our advanced mass spectrometry platforms can analyze complex protein mixtures and detect various post-translational modifications, ensuring comprehensive molecular weight determination even for challenging samples.
Q: How do I submit a sample for analysis?
A: To submit a sample:
Contact our team through our online inquiry form to discuss your project and receive shipping instructions.
Ship the sample to our laboratory, ensuring it is properly labeled and packaged.
Q: What information will I receive in the final report?
A: Our comprehensive report includes:
- Detailed molecular weight measurements.
- Analysis of post-translational modifications, if applicable.
- Interpretation of results in the context of your research objectives.
- Recommendations for further analysis or validation, if necessary.
We also offer consultation services to discuss the findings and address any questions you may have.
Client Case Study: Protein Molecular Weight Analysis of SPB-Associated Proteins in Neurospora crassa
Authors: Madeira, D. et al.
Journal: Environmental Research (2021)
DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.110885
Background
In filamentous fungi such as Neurospora crassa, the spindle pole body (SPB) serves as a microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) critical for nuclear division and cellular organization. Despite its importance, the protein network surrounding the SPB and related septal components remains under-characterized.
To address this, researchers from CICESE (Mexico) and KIT (Germany) used a mass spectrometry-driven approach to map protein-protein interactions of four MTOC components:
- γ-Tubulin-sGFP
- MZT-1-sGFP
- APS-2-dRFP
- SPA-10-sGFP
The aim was to identify novel interactors and clarify the architecture of SPB and septal structures in N. crassa.
Our Contribution: Protein Identification and Molecular Weight Determination
Creative Proteomics supported this project through our Protein Molecular Weight Determination and Identification Service, which included:
- Sample digestion from Co-IP gel bands
- Nano LC-MS/MS analysis using high-resolution Orbitrap technology
- Accurate molecular weight profiling and database annotation against the N. crassa proteome
- Filtering of high-confidence interactors using internal controls (WT and cytosolic sGFP)
We received SDS-PAGE-separated bands corresponding to the bound protein fractions of each tagged strain (γ-Tubulin, MZT-1, APS-2, and SPA-10). Using in-gel digestion followed by LC-MS/MS, we enabled the detection of over 500 unique interactors per experiment (after background subtraction).
Key Results
- Protein interactors confirmed for each target (γ-Tubulin, MZT-1, APS-2, and SPA-10)
- High-confidence protein IDs (score > 50) delivered with molecular weight and abundance
- Functional annotation enabled hypothesis generation for novel SPB-associated roles
- Validated molecular mass detection of fluorescent-tagged fusion proteins (~40–80 kDa)
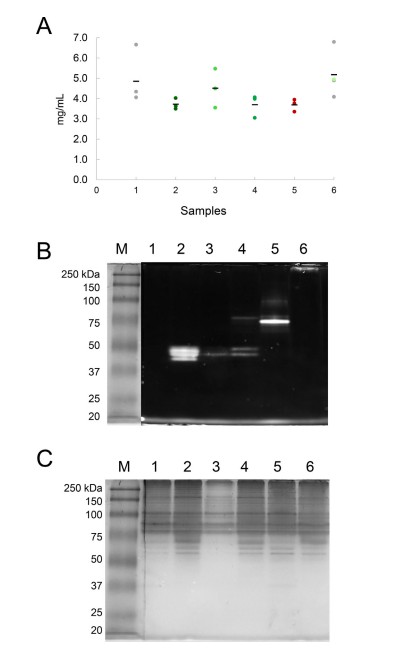 Fig. 1. Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE showing protein profiles
Fig. 1. Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE showing protein profiles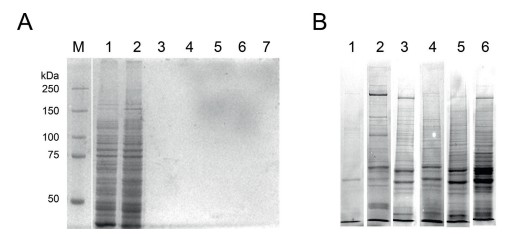 Fig. 2. Protein Interaction Map
Fig. 2. Protein Interaction MapWorkflow Summary
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Co-IP | Magnetic bead enrichment using anti-GFP agarose |
| SDS-PAGE | Protein separation and band excision |
| In-gel Digestion | Trypsin digestion and desalting |
| LC-MS/MS | High-resolution MS/MS analysis |
| Data Processing | Background subtraction, ID scoring, and protein annotation |
Reference
- Nadler W M, Waidelich D, et al. MALDI versus ESI: the impact of the ion source on peptide identification. Journal of proteome research, 2017, 16(3): 1207-1215. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00805
Related Services
Support Documents
KNOWLEDGE CENTER
Molecular Weight Characterization - Comparison of MALDI and ESI











