- Services
- FAQ
- Demo
- Case Study
- Related Services
- Support Documents
- Inquiry
What is Isoelectrofocusing (IEF)?
Isoelectric point (pI) is the pH value at which the molecule carries no net electrical charges, which is one of important characters for zwitterionic molecules such as aimno acids, peptides, and proteins. Since pI can be a critical factor to affect the overall pharmacokinetic (PK) behavior, it is necessary to assess pI during drug development.
Isoelectrofocusing (IEF) is the most common and widely used electrophoretic technique to determine pI of a protein or separate proteins depending on their pI s. The net charges of proteins are determined by the overall pH of proteins' environment. When the acidic groups in a protein are more than the number of basic groups, the protein's pI is at a low pH value. In the contrary, the protein's pI is at a high pH value, if the number of basic groups exceeds the number of acidic groups of the protein. During electrophoresis, positively charged proteins, which are at pH values below the pI, will move toward the cathode on pH-gradient gel. Whereas, negatively charged proteins with pH values above the pI will migrate to the anode. Besides, protein at its pI has no net charge, and will not move during electrophoresis.
In IEF, proteins migrate to their respective pI and remain stabilized. To conduct successful IEF, stable and linear pH gradients are important. Creative Proteomics provides a high-resolution IEF capable of separating proteins with different pIs. Depending on your samples, different antibodies, antigens, and enzymes will be employed to ensure the successful fractionation. Buffers and ampholyte conditions will also be optimized to separate proteins across a broad range of pH.
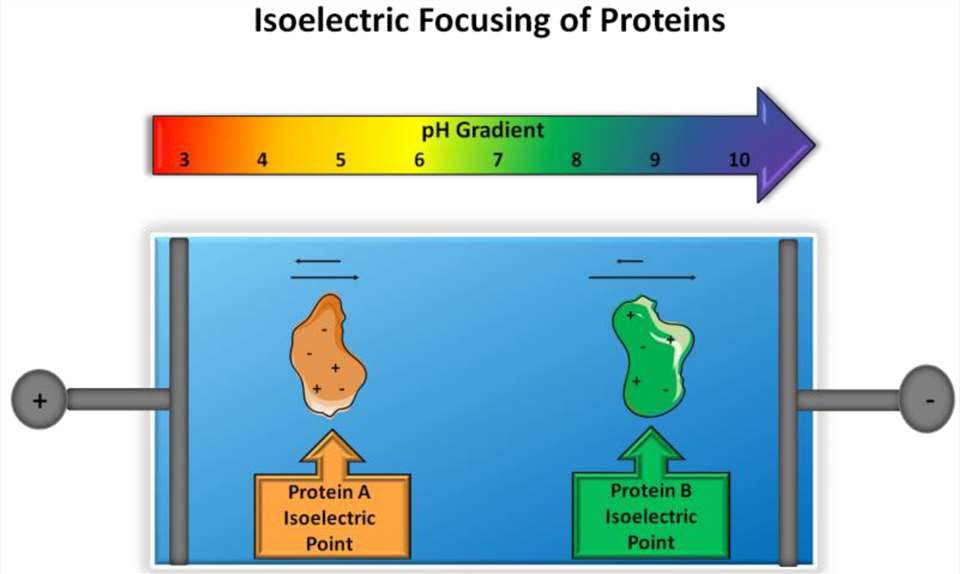 Figure 1. Principle of isoelectric focusing. (Schlattner U, et al.)
Figure 1. Principle of isoelectric focusing. (Schlattner U, et al.)Principle and Methodology of IEF
The principle of IEF is based on the migration of charged molecules in an electric field through a pH gradient. Here's how the IEF process works:
Creation of a pH Gradient: A stable pH gradient is established in a gel or capillary by applying an electric field. The pH gradient typically spans from acidic to basic conditions.
Protein Migration: Proteins are loaded into the gel or capillary, and an electric field is applied. The charged molecules migrate toward the electrode of opposite charge.
Focus at the pI: As proteins move through the pH gradient, they eventually reach a point where their net charge is zero — the pI. At this point, the proteins stop migrating and "focus," forming sharp bands corresponding to their pI values.
Analysis: The focused bands are then analyzed, and the pI of the proteins can be determined based on their position in the pH gradient.
What is the Difference Between IEF and cIEF?
| Characteristic | IEF | cIEF |
| Method | Typically performed in gels (e.g., polyacrylamide gels) | Performed in capillaries, typically using a liquid phase |
| Separation Medium | Gel-based (e.g., agarose or polyacrylamide gel) | Capillary column (often made of fused silica) |
| Resolution | High resolution with sharp protein bands | High resolution with improved separation efficiency |
| Sample Throughput | Low throughput, as it requires gel electrophoresis | Higher throughput, as it can be automated and used for multiple samples |
| Sensitivity | Excellent sensitivity, especially for large proteins or complex mixtures | High sensitivity, especially for small and medium-sized proteins |
| Flexibility | Can be adapted for multiple types of samples | Highly flexible, useful for small sample volumes and automation |
| Applications | Primarily used for protein analysis and fractionation | Used in quantitative pI determination, protein characterization, and diagnostics |
| Time Efficiency | Longer analysis time due to gel preparation and electrophoresis | Faster analysis with shorter run times |
Advantages of Our Isoelectric Point Determination with IEF Service:
- Rich experience in pI determination.
- High sensitivity and accuracy to detect proteins with different post-translational modifications.
- Rapid turnaround time to provide comprehensive report.
- Customized service: according to you sample type and sample size, optimized protocols will be deployed.
We Provide But Are Not Limited To
- Isoelectric point determination of proteins
- Separation of proteins and peptides
- Assessment of protein purity
- Quantitative pI profiling
- Isoform identification
Applications of pI Determination
- Protein Characterization: pI determination is crucial for understanding protein structure and charge properties, especially in therapeutic proteins and monoclonal antibodies.
- Quality Control in Biopharmaceuticals: pI determination is crucial in the production and quality control of therapeutic proteins, monoclonal antibodies, and biosimilars.
- Proteomics Research: Determining the pI of proteins is fundamental for proteomic profiling, especially when separating complex protein mixtures or identifying novel biomarkers..
- Drug Development: Understanding the pI of target proteins or therapeutic candidates can inform drug design and formulation, optimizing drug-target interactions and pharmacokinetics.
Sample Requirements
Sample Type: Pure protein, peptide, or protein mixtures, including recombinant proteins, antibodies, or therapeutic proteins.
Concentration: A minimum of 0.1 mg/mL.
Sample Volume: At least 50-100 µL.
Buffer Conditions: Provide samples in a buffer that is compatible with IEF, such as low ionic strength buffers or ampholyte solutions. Avoid detergents and high salt concentrations.
Storage: Samples should be stored at -80°C to preserve protein integrity.
FAQ
Q: How does your IEF service compare to other techniques, such as cIEF, in terms of resolution and throughput?
A: Our IEF service provides high resolution for a variety of protein samples, especially for larger-scale or preparative applications. While cIEF offers superior resolution for small volumes and is highly sensitive, our gel-based IEF system allows for larger sample volumes and can be better suited for high-throughput or routine analyses. Each method has its strengths, and we can guide you in selecting the best option depending on your sample type and experimental needs.
Q: What type of reporting do you provide for IEF results?
A: We provide detailed, comprehensive reports that include the pI values of your protein samples, along with visual representations such as pH gradient maps, protein profiles, and relevant data analysis. Reports are accompanied by interpretations and recommendations where necessary. You will also receive raw data, such as gel images or capillary electrophoresis results, depending on the technique used. We aim to make the results clear and accessible for further analysis or publication.
Q: Can I use this service to analyze proteins in complex biological samples, such as cell lysates or serum?
A: Yes, IEF can be used to analyze proteins in complex biological samples like cell lysates, serum, or tissue extracts. However, the complexity of the sample may require additional sample preparation steps to enrich the protein of interest or remove interfering substances. We can guide you on the best approaches for handling your specific sample type to ensure reliable results.
Q: What happens if the pI of a protein is outside the pH range of the gradient you provide?
A: If the pI of a protein is outside the typical pH range of the gradient, we can customize the pH gradient to suit the specific pI range of your protein. Our system is flexible, allowing us to adjust the gradient to better capture proteins with unusual or extreme pI values. We work with you to ensure the pH gradient covers the range necessary for your analysis.
Demo
Demo: A simple and rapid technique for detecting protein phosphorylation using one-dimensional isoelectric focusing gels and immunoblot analysis
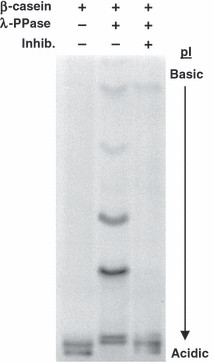 Figure 2. IEF gels can detect phosphorylation-dependent shifts in isoelectric point.
Figure 2. IEF gels can detect phosphorylation-dependent shifts in isoelectric point.Case Study
Case: Isoelectric point separations of peptides and proteins.
Background
The article investigates the biochemical properties of two human mitochondrial creatine kinase (MtCK) isoenzymes: ubiquitous MtCK (uMtCK) and sarcomeric MtCK (sMtCK). These enzymes are responsible for the synthesis and hydrolysis of phosphocreatine (PCr), a key energy reserve in muscles and other tissues. The study focuses on their kinetic behaviors, including pH dependence, enzyme activity, and substrate binding, which differ between the two isoenzymes. The work uses heterologous protein expression and purification methods to characterize these isoenzymes in detail, addressing the lack of previous studies due to contamination and purification difficulties.
Methods
The full-length cDNAs for human uMtCK and sMtCK were cloned into expression vectors and expressed in E. coli using a T7-based expression system. Purification involved a two-step chromatography procedure, including Blue Sepharose and strong cation exchange chromatography, followed by gel filtration to obtain highly pure enzyme samples. Various assays, including a photometric assay, were used to measure enzyme activity and kinetic parameters. Lineweaver-Burk plots and Cleland algorithms were employed to calculate Michaelis-Menten parameters, such as the dissociation constants (Kd) and Michaelis constants (Km). Enzyme activity was tested across different pH ranges to assess the pH-dependence of both isoenzymes.
Results
- Enzymatic Activity: Human sMtCK exhibited higher specific activity in both the forward (PCr synthesis) and reverse (ATP synthesis) reactions compared to uMtCK. The forward/reverse activity ratio was 0.85 for sMtCK and 0.65 for uMtCK. In the pH stat assay, uMtCK showed greater pH sensitivity, with a significant increase in activity in the forward reaction (PCr synthesis) at pH 7 to 8, while sMtCK showed a smaller increase.
- Enzyme Kinetics: Both isoenzymes followed Michaelis-Menten kinetics, with the sequential reaction mechanism suggesting a rapid equilibrium random mechanism. uMtCK demonstrated a more pronounced substrate synergism in the forward reaction, with Km values for ATP and Cr significantly lower than sMtCK.
- Structural Properties: Both isoenzymes showed octameric structures, but uMtCK was more resistant to dissociation compared to sMtCK. This higher stability of uMtCK octamers may have physiological relevance, particularly for mitochondrial membrane interactions. Structural differences between uMtCK and sMtCK were observed through electron microscopy, where uMtCK octamers maintained stability on cardiolipin surfaces, while sMtCK octamers appeared to flatten upon binding.
- pI and Molecular Structure: The isoelectric point (pI) values for human MtCK isoenzymes were consistent with previously published data, but a slight variation was noted. Human MtCK had a lower pI compared to other species' MtCKs, with a less pronounced pH difference between its octameric and dimeric forms.
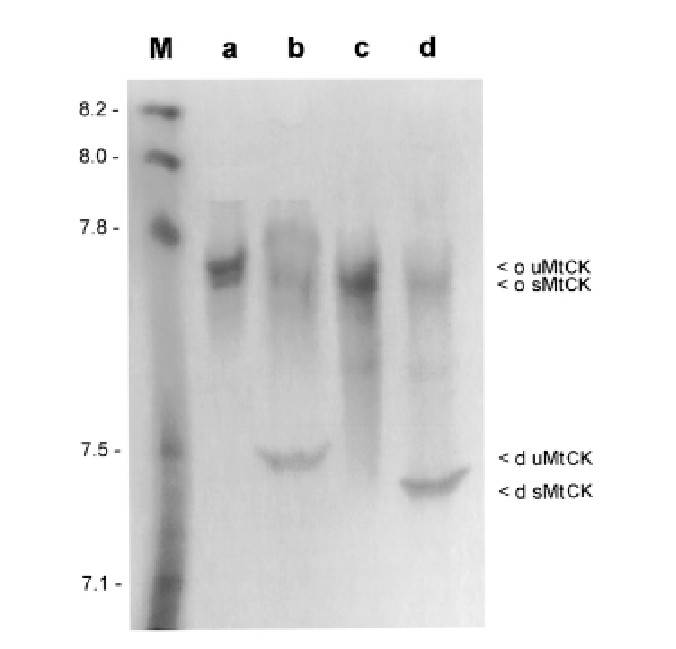 Figure 3. Isoelectric Point Determination of Human MtCK with Agarose-IEF.
Figure 3. Isoelectric Point Determination of Human MtCK with Agarose-IEF.References
- Pergande M R, Cologna S M. Isoelectric point separations of peptides and proteins. Proteomes, 2017, 5(1): 4. DOI: 10.3390/proteomes5010004
- Anderson J C, Peck S C. A simple and rapid technique for detecting protein phosphorylation using one‐dimensional isoelectric focusing gels and immunoblot analysis. The Plant Journal, 2008, 55(5): 881-885. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-
- Schlattner U, et al. Divergent enzyme kinetics and structural properties of the two human mitochondrial creatine kinase isoenzymes. Biological Chemistry, 2000, 381: 1063-1070. DOI: 10.1515/bc.2000.131
Related Services
Support Documents
KNOWLEDGE CENTER
KNOWLEDGE CENTER













