- Services
- FAQ
- Case Study
- Related Services
- Support Documents
- Inquiry
What is Sialic Acids?
Sialic acids are negatively charged monosaccharides, what are found on the non-reducing termini of glycans. The key role in product stability and efficacy, thus, sialic acids are often defined in glycoprotein therapeutic products. There exist two most common sialic acids in biopharmaceuticals, the one is N-acetyl-neuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) and the other one is N-glycolyl-neuraminic acid (Neu5Gc). The sialic acid mentioned above are both important to the firmness and 3D conformation of glycoproteins, they are involved in many biological interactions. Sialic acids often have a crucial functional collision, for example, sialylation of the N-glycans on IgG increases anti-inflammatory activity and by stopping uptake by the asialoglycoprotein-receptor located on liver cells, the presence of sialic acids enhances the serum half-life of glycoproteins. Sialic acids preserve the N-acetyl, N-glycolyl and O-acetylation are released from glycoproteins by mild acid hydrolysis using conditions.
Acetylation is the most commonly modification of sialic acids. O-acetylation decreases the kinetics of enzyme-catalysed desialylation of glycans. Since the wealth and type of sialylation influences the expression of therapeutic glycoproteins, for example, serum half-life, immunogenicity, activity. Under milder acid hydrolysis conditions, many LC-based methods start with the release of the targeted sialic acids. The most liable to change monosaccharides are the family of sialic acids, which are usually chain-terminating substituents. Thus, these are commonly released first by either mild acid hydrolysis or enzyme digestion and with detection of pulsed amperometric, it can be illustrated with great sensitivity by using high pH anion-exchange chromatography. The released sialic acids can be derivatized with DMB, the 1,2-diamino-4,5-methylenedioxybenzene-2HCl dye. High pH anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection is a frequently used method for accurate judgement of the two most common sialic acids found on glycoprotein oligosaccharides, N-acetylneuraminic acid and N-glycolylneuraminic acid. With more and more requires to quickly screen samples from expression cell line and growth condition optimization experiments, shorter analysis times are needed for all analyses, including sialic acid analysis.
Creative Proteomics' sialic acid analysis service is designed to provide unparalleled insights into the glycosylation profile of your biopharmaceutical products, ensuring optimal safety, efficacy, and regulatory compliance.
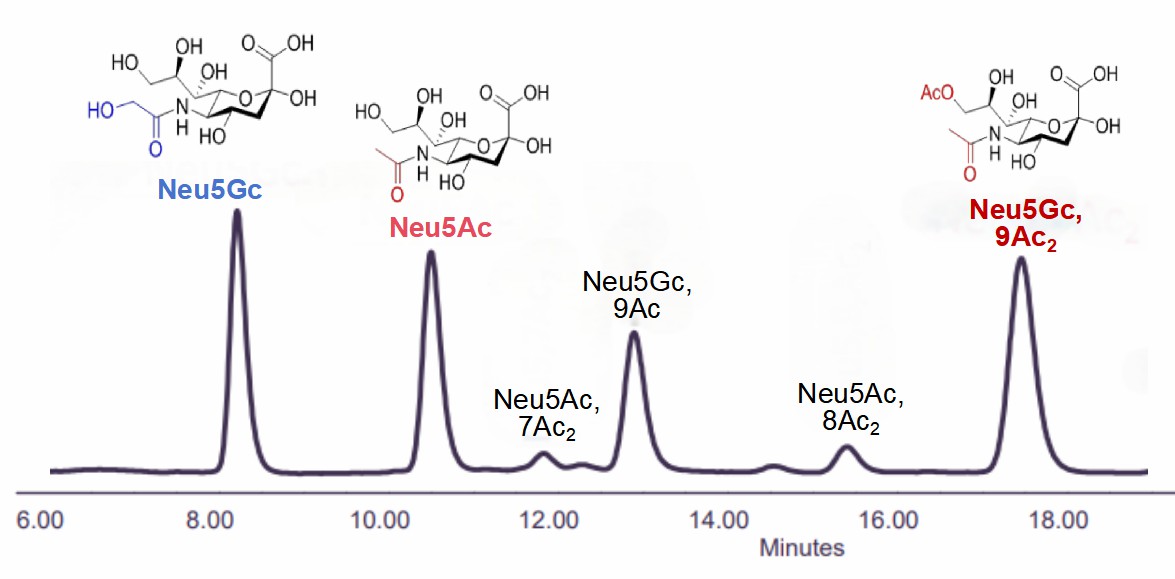 Figure 1. Sialic acid glycoanalysis.
Figure 1. Sialic acid glycoanalysis.We Can Provide (but not limited to):
- Sialic Acid Quantification: Accurate quantification of sialic acids in glycoproteins and glycan structures.
- Sialic Acid Structural Characterization: Determination of different forms of sialic acids, including Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc.
- Glycosylation Site Identification: Pinpointing the specific attachment sites of sialic acids on glycoproteins.
- Sialic Acid Linkage Analysis: Identification of glycosidic bonds between sialic acids and other sugar residues.
Technology Platform of Sialic Acid Analysis Service
At Creative Proteomics, we leverage state-of-the-art instrumentation and methodologies to deliver precise sialic acid analysis:
Mass Spectrometry (MS): Utilizing matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight (MALDI-TOF MS), electrospray ionization mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS), and Nano-ESI-MS/MS for high-resolution structural analysis.
Liquid Chromatography: Combining liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry for detailed glycan mapping and sialic acid quantification.
Enzymatic Cleavage and Hydrolysis: Mild acid hydrolysis (e.g., acetic acid) or enzyme treatment to release sialic acids from glycoproteins.
Why Choose Our Sialic Acid Analysis Service
- High Sensitivity and Specificity: Our advanced platforms allow for the detection of sialic acids in low-abundance samples, providing reliable results even for trace amounts.
- Comprehensive Analysis: We offer detailed characterizations of both N- and O-linked sialic acids, identifying their specific structures, attachments, and modifications.
- Customized Protocols: Our team customizes analysis protocols based on sample type, project scope, and specific customer needs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Our methodologies comply with global standards and regulations, including ICH Q6B, USP<1047>, and PharmEu guidelines.
Applications of Sialic Acid Analysis
- Biopharmaceutical Development: Monitoring glycosylation profiles and sialic acid content during the production of therapeutic glycoproteins to ensure product stability and immunogenicity.
- Vaccine Development: Sialic acid analysis plays a key role in understanding the glycosylation of viral glycoproteins and their interactions with the immune system.
- Cancer Immunotherapy: The presence of sialic acids in tumor-associated glycoproteins can be a target for immune-modulatory therapies.
- Inflammatory Disease Research: Sialylation is involved in regulating immune responses; analysis helps in understanding immune evasion mechanisms in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes.
- Quality Control: Ensuring batch-to-batch consistency of therapeutic proteins by monitoring sialic acid content and glycosylation patterns.
Sample Requirements
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Sample Type | Glycoprotein therapeutics, cell culture supernatants, or other biological matrices |
| Sample Volume | Minimum of 10 µL (adjustable based on project scope) |
| Concentration | ≥ 1 mg/mL preferred for optimal sensitivity |
| Buffer Composition | Samples should be in a neutral buffer; avoid detergents and high salt concentrations |
| Storage Conditions | Store samples at -20°C or lower; avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles |
FAQ
Q: What is the detection limit of your sialic acid analysis method, and can you detect sialic acids in complex biological matrices?
A: Our sialic acid analysis methods, including HPAEC-PAD and MALDI-TOF-MS, have a low detection limit, capable of identifying sialic acids even in complex biological matrices such as serum, plasma, or cell culture supernatants. The sensitivity of our techniques ensures that even trace amounts of sialic acids can be reliably quantified, making them ideal for studying low-abundance glycans in therapeutic samples.
Q: Are there any sample preparation steps required before submission, and can Creative Proteomics assist with these?
A: Yes, depending on the type of sample, there may be specific preparation steps required, such as deglycosylation of glycoproteins or acid hydrolysis for sialic acid release. We offer full sample preparation services, including enzymatic treatment (e.g., PNGase F for N-glycans) and acid hydrolysis, to ensure that your samples are properly prepared for analysis. We can guide you through the best preparation protocols for your specific research needs.
Q: Can you provide insights into the variability of sialic acid profiles across different cell lines or bioreactor conditions?
A: Yes, our glycosylation analysis services can provide valuable insights into the variability of sialic acid profiles when comparing different cell lines, bioreactor conditions, or culture media. We can analyze the impact of production variables on sialic acid content, including Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc levels, helping to optimize cell line selection and process conditions for more consistent and efficient glycoprotein production.
Case Study
Case: Determination of the Type and Quantity of Sialic Acid in the Egg Jelly Coat of the Sea Urchin Paracentrotus lividus Using Capillary LC-ESI-MS/MS
Background
Sialic acid plays a crucial role in numerous biological processes, particularly in fertilization, where it is involved in sperm-egg recognition and the acrosome reaction. However, the types and quantities of sialic acids present in the egg jelly coat of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus were not well-characterized. This study aimed to determine the sialic acid types and their distribution in the egg jelly coat using a highly sensitive technique, capillary liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (capLC-ESI-MS/MS). The findings are significant for understanding the role of sialic acids in fertilization and identifying potential receptors on sperm membranes.
Methods
- Sample Collection: Sea urchin eggs were collected from Paracentrotus lividus using an injection method, and the egg jelly coat was isolated for analysis.
- Sialic Acid Release: The sialic acids were released from the egg jelly by acid treatment (using 4 M acetic acid at 80°C for 3 hours) to avoid the destruction of substitutions present on the sialic acid molecules.
- Derivatization: The released sialic acids were derivatized with DMB (1,2-diamino-4,5-methylenedioxybenzene dihydrochloride) to enhance detection sensitivity.
- Analysis: The derivatized sialic acids were analyzed using capLC-ESI-MS/MS. Mass spectrometric data, including collision-induced dissociation (CID) fragments, were used to identify the different sialic acid types based on their retention times and fragmentation patterns.
- Confirmation: Standards of Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc were used for comparison and to confirm the molecular types of sialic acids.
Results
- Sialic Acid Types Identified: The analysis identified twelve distinct sialic acid types in the egg jelly coat. Neu5Gc was the most abundant sialic acid, accounting for 66% of the total sialic acids, followed by Neu5Ac (11%) and other derivatives such as Neu5GcS, Neu5AcS, and Neu5Gc7,9Ac2.
- Mass Spectral Data: The tandem mass spectrometry data revealed the presence of both mono- and di-acetylated forms of Neu5Gc and Neu5Ac. The sulfated forms (Neu5GcS and Neu5AcS) were also detected and identified using characteristic fragment ions.
- Quantification: The quantity of each sialic acid derivative was determined by measuring the peak areas in the extracted ion chromatograms, with Neu5Gc being the most prevalent.
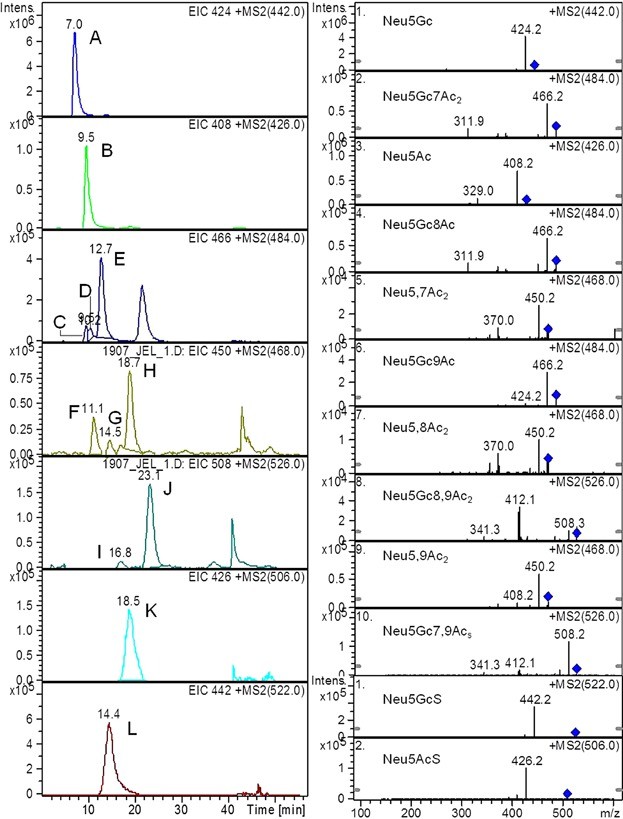 Figure 3. CapLC-ESI-MS/MS mass spectra and chromatograms of the DMB-sialic acids (twelve types) found in isolated egg jelly.
Figure 3. CapLC-ESI-MS/MS mass spectra and chromatograms of the DMB-sialic acids (twelve types) found in isolated egg jelly.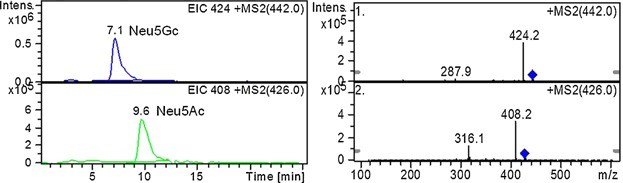 Figure 4. CapLC-ESI-MS/MS mass spectra and chromatograms of the DMB-standard sialic acids (Neu5Gc and Neu5Ac).
Figure 4. CapLC-ESI-MS/MS mass spectra and chromatograms of the DMB-standard sialic acids (Neu5Gc and Neu5Ac).References
- Yeşilyurt B, Şahar U, Deveci R. Determination of the type and quantity of sialic acid in the egg jelly coat of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus using capillary LC‐ESI‐MS/MS. Molecular Reproduction and Development, 2015, 82(2): 115-122. DOI: 10.1002/mrd.22448
- Cheeseman J, et al. Assays for the identification and quantification of sialic acids: challenges, opportunities and future perspectives. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 30: 115882. DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115882
Related Services
Support Documents
KNOWLEDGE CENTER
KNOWLEDGE CENTER
Molecular Weight Characterization - Comparison of MALDI and ESI














