- Services
- FAQ
- Case Study
- Related Services
- Support Documents
- Inquiry
What is Host Cell Residual DNA?
Host cell DNAs or residual DNAs (rDNAs) are trace/low quantity of DNA originating from the organisms used in the production process of biopharmaceutical products, which may be introduced into the final products. These DNA fragments originate from the host cells used in the production of therapeutic proteins, vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, and other biopharmaceuticals. Commonly used host cells include mammalian cell lines such as Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, bacterial systems, and yeast. While these cells are critical for the production of high-quality biologics, small amounts of their DNA can persist in the final product despite extensive purification processes.
Why to Analysis Host Cell Residual DNA?
The rDNAs may be able to transmit viral infections, cause a potential risk for oncogenesis or adverse reactions, etc. To assure the safety and potency, rDNAs in final biopharmaceutical products must be carefully monitored and quantitated, following the requirements established by World Health Organization (WHO), the European Pharmacopeia, the US Food and Drug Administration, and other regulatory agencies. The acceptable limits have been set between 100 pg/dose and 10 ng/dose depending on the cell line used, and the mode and frequency of dosing. Hence, the sensitive, accurate, and quantitative methods must be applied to ensure the rNDA is cleared to the limits.
Conducting thorough host cell residual DNA analysis ensures:
- Product Safety: Residual DNA may carry tumorigenic or infectious risks. Testing ensures that these impurities are effectively reduced to safe levels, safeguarding patient health.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting global regulatory standards is essential for bringing biopharmaceuticals to market. Host cell DNA testing ensures that your product adheres to the latest guidelines.
- Quality Assurance: Monitoring residual DNA at various stages of the manufacturing process allows for the optimization of purification steps, ensuring product purity and consistency.
Creative Proteomics provides a sensitive and accurate analysis to quantitate a broad range of rDNAs in various types of samples, including monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins, viral products, etc. Our experts will deploy optimal method to perform rDNAs tests during all stages of drug discovery, including real-time qPCR assay, Southern Blot-like hybridization and Threshold technique and PicoGreen method, etc.
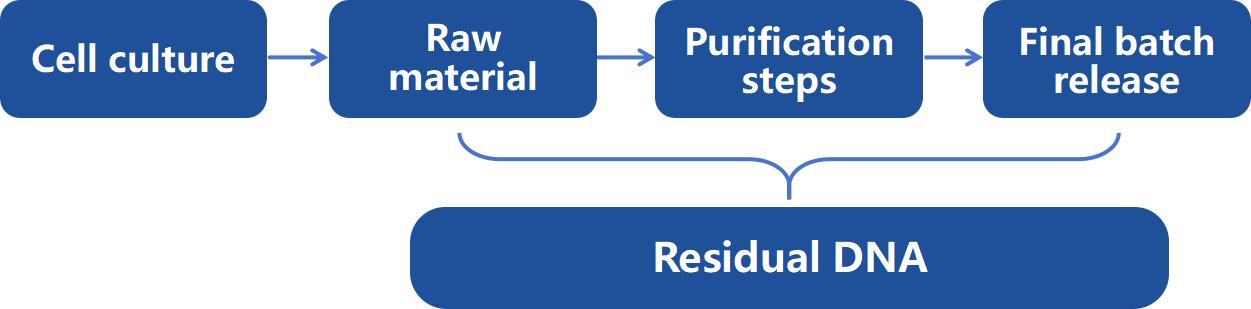 Figure 1: Typical residual DNA testing points in biopharmaceutical production.
Figure 1: Typical residual DNA testing points in biopharmaceutical production.We Provide but Not Limited to
- Sample preparation and DNA Extraction
- Ultra-sensitive detection of rDNAs from various species
- Quantification of total rDNAs
- Quantitation of specific rDNA
- DNA Sequencing of unknown rDNAs
Technology Platform of Host Cell Residual DNA Analysis
Creative Proteomics provides efficient and accurate rDNAs analysis to detect and quantitate rDNAs rapidly by optimized methods and protocols depending on your specific requirement, including PCR, real-time PCR, Southern Blot, DNA sequencing, Threshold assay, Hybridization assay, etc. Threshold assay can be conducted to nonspecifically quantify the total DNA by using DNA binding-proteins with high affinity for single-stranded DNA. The most commonly used standard for rDNAs quantification is based on real-time qPCR targeting specific repetitive DNA sequences. Besides, the treatment of the initial sample plays a critical role on successful rDNAs analysis. In order to ensure suitability with the assay and sample type, different pretreatment of samples will be considered, including organic extraction, magnetic beads, etc. To increase the efficiency, a digestion-free method will be conducted to rapidly extract DNA from the samples to following real-time qPCR analysis or PicoGreen assay of rDNAs. Based on your requirements, different protocols will be employed.
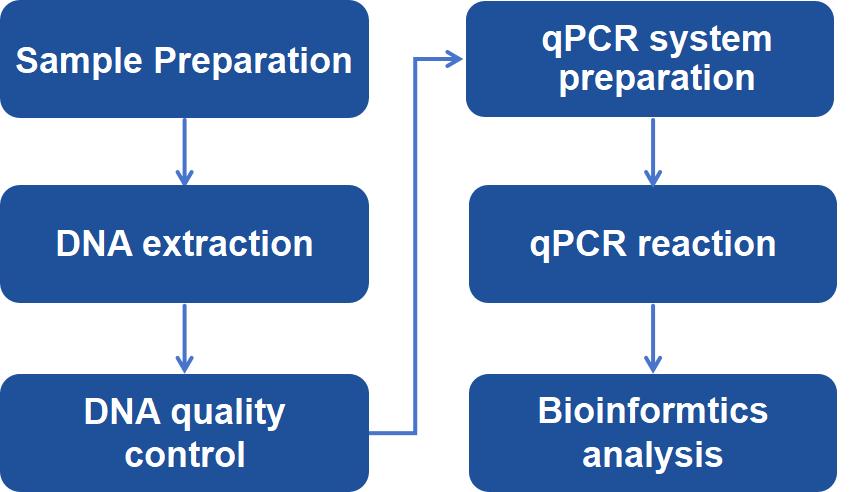
Why Choose Our Host Cell Residual DNA Analysis Service
- High sensitivity and accuracy: Detection of genomic DNA on picogram level and bacterial DNA on femtogram level, and DNA from viral origin.
- High specificity: No cross reactivity to unrelated DNA.
- Advanced system: The Applied Biosystems resDNASEQ™, etc.
- Customized service: Optimized methods will be customized based on your sample type and size.
Creative Proteomics's experienced scientists can provide extensive analysis of rDNAs, including detection, quantitation, sequencing, etc. Clear, comprehensive written reports, recommendations and protocols, and customized services will be provided to help customers solve analytical and technical problems.
Sample Requirements
| Sample Type | Required Volume | Sample Condition | Storage Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monoclonal Antibodies | 1 mL | Clear liquid, no visible particulates | 2-8°C for short-term, -20°C for long-term |
| Recombinant Proteins | 500 µL | Clear liquid; ideally free from aggregates | 2-8°C for short-term, -20°C for long-term |
| Viral Products | 1 mL | Clear liquid, no visible particulates | 2-8°C for short-term, -20°C for long-term |
| Cell Culture Supernatants | 1 mL | Clear liquid; centrifuged to remove cells | 2-8°C for short-term, -20°C for long-term |
| Cell Lysates | 100 µL | Homogeneous solution, free of aggregates | -80°C |
| Cell Harvests (e.g., pellets) | 10-50 mg | Dry or frozen pellets | -80°C |
FAQ
Q: How do you handle samples that contain high levels of residual DNA?
A: For samples with high levels of residual DNA, we take several approaches to ensure accurate analysis:
Dilution Techniques: We may dilute the sample to bring the DNA concentration within the detection range of our assays.
Optimized Sample Preparation: Specialized protocols are used to reduce the sample volume while concentrating the residual DNA, enhancing the sensitivity of the analysis.
Protocol Adjustments: Depending on the nature of the sample, we may adjust the assay protocols to accommodate higher concentrations and maintain accuracy.
Q: What specific types of host cell residual DNA can you detect?
A: Creative Proteomics can detect various types of host cell residual DNA, including:
Mammalian Cell Line DNA: Commonly derived from Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells and other mammalian cell lines used in biopharmaceutical production.
Bacterial DNA: Residual DNA from bacterial expression systems, such as E. coli.
Yeast DNA: DNA remnants from yeast-based production systems.
Viral DNA: Potentially harmful viral DNA that could originate from the host cells.
Q: How to determine which method is most suitable for my analysis needs?
A: The selection of the most suitable method for host cell residual DNA analysis depends on several factors, including:
Sample Type: Different sample types may require specific methods to optimize sensitivity and accuracy.
Expected DNA Concentration: For samples with high DNA concentrations, we may choose methods that can accommodate this without compromising accuracy.
Regulatory Requirements: We take into account the specific regulatory guidelines relevant to your product and its intended use.
Case Study
Case: Quantitative Detection of Residual E. coli Host Cell DNA by Real-Time PCR
Background
The detection and quantification of residual E. coli host cell DNA in biopharmaceutical products are essential due to the potential risks associated with these contaminants. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA mandate strict quality control and validation procedures to ensure that DNA contamination remains within acceptable limits throughout the manufacturing process. Traditionally, Slot Blot Hybridization and Threshold assays have been used for this purpose, but they are relatively time-consuming, expensive, and less sensitive. To address these shortcomings, this study focuses on validating real-time PCR as a more efficient, accurate, and sensitive method for detecting residual host cell DNA. The real-time PCR method, based on SYBR Green chemistry, aims to overcome the limitations of previous assays, offering improved sensitivity and precision for routine testing in the biopharmaceutical industry.
Methods
The study validated and compared three different assays: real-time PCR, Slot Blot Hybridization, and Threshold assays. The validation was based on four key parameters:
- Precision: Measured by assessing the concentration of spiked DNA standards (62.5 pg and 125 pg) over six independent runs.
- Accuracy: Evaluated by calculating the percentage of recovery at different concentrations (31.25 pg, 62.5 pg, and 125 pg) for the three methods.
- Linearity: Determined using a standard curve of the DNA concentration and calculating the correlation coefficient for each method.
- Detection Limit: The minimum detectable concentration of DNA was compared across the three methods. Additionally, the study optimized real-time PCR conditions, including primer design, Mg²⁺ concentrations, and primer concentrations to maximize the specificity and sensitivity of the assay.
Results
- Precision: The real-time PCR assay exhibited significantly better precision, with lower coefficients of variation (1.86% and 1.22% for the 62.5 pg and 125 pg standards, respectively) compared to Slot Blot and Threshold assays.
- Accuracy: The real-time PCR assay also had more consistent accuracy, with percentage recovery closer to 100% and lower standard deviations than the other two methods.
- Linearity: Real-time PCR demonstrated superior linearity, with a correlation coefficient of 0.996, higher than Slot Blot (0.976) and Threshold assays (0.986), indicating better performance in quantifying DNA across different concentrations.
- Detection Limit: The detection limit for real-time PCR (0.042 pg of DNA) was significantly lower than Slot Blot (2.42 pg) and Threshold assays (3.73 pg), proving real-time PCR's greater sensitivity. The real-time PCR assay also had a broader dynamic range, with a calibration curve spanning from 0.042 to 42,000 pg of DNA.
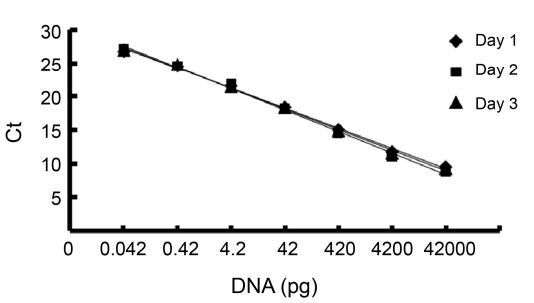 Figure 2. Sensitivity of real-time PCR assay for the quantitative detection of E. coli host cell DNA. A) Amplification plots obtained with 10-fold serial dilutions of E. coli host cell DNA. B) Melting curve analysis of the amplification plot.
Figure 2. Sensitivity of real-time PCR assay for the quantitative detection of E. coli host cell DNA. A) Amplification plots obtained with 10-fold serial dilutions of E. coli host cell DNA. B) Melting curve analysis of the amplification plot.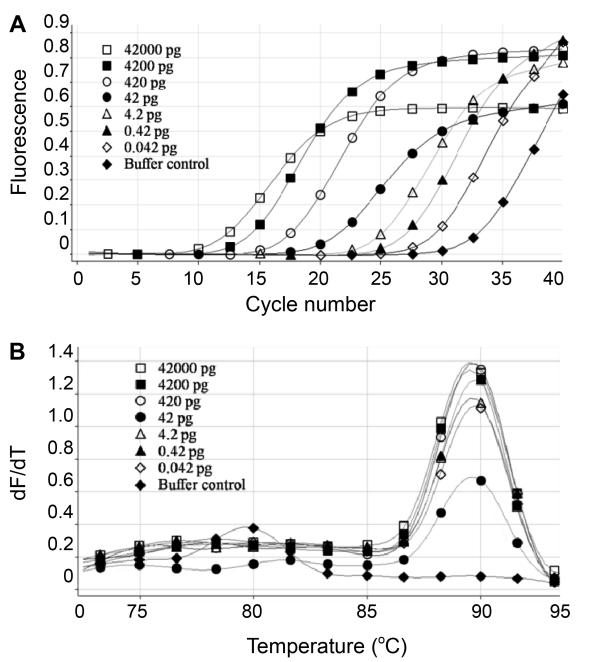 Figure 3. Reproducibility of the real-time PCR assay for quantitative detection of E. coli host cell DNA.
Figure 3. Reproducibility of the real-time PCR assay for quantitative detection of E. coli host cell DNA.References
- Lee D H, et al. Quantitative detection of residual E. coli host cell DNA by real-time PCR. Journal of microbiology and biotechnology, 2010, 20(10): 1463-1470. DOI: 10.4014/jmb.1004.04035
- Vernay O., et al. Comparative analysis of the performance of residual host cell DNA assays for viral vaccines produced in Vero Cells. Journal of Virological Methods, 268 (2019) 9-16. DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2019.01.001
- Wang Y., et al. A digestion-free method for quantification of residual host cell DNA in rAAV gene therapy products. Molecular Therapy: Methods & Clinical Development. Vol. 13 June 2019. DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2019.05.005
- Rathore A.S., et al. Analysis of residual host cell proteins and DNA in process streams of a recombinant protein product expressed in Escherichia coli cells. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 32 (2003) 1199-1211. DOI: 10.1016/s0731-7085(03)00157-2
- Ikeda Y., Iwakiri S. and Yoshimori T. Development and characterization of novel host cell DNA assay using ultra-sensitive fluorescent nucleic acid stain "PicoGreen". J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2009 May 1;49(4):997-1002. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2009.01.022
Related Services
Support Documents
KNOWLEDGE CENTER
KNOWLEDGE CENTER
What is Residual DNA Testing and How to Determine Residual DNA












