Precise Quantification of Human Energy Metabolism Enzymes
What is precise quantification of human energy metabolism enzymes?
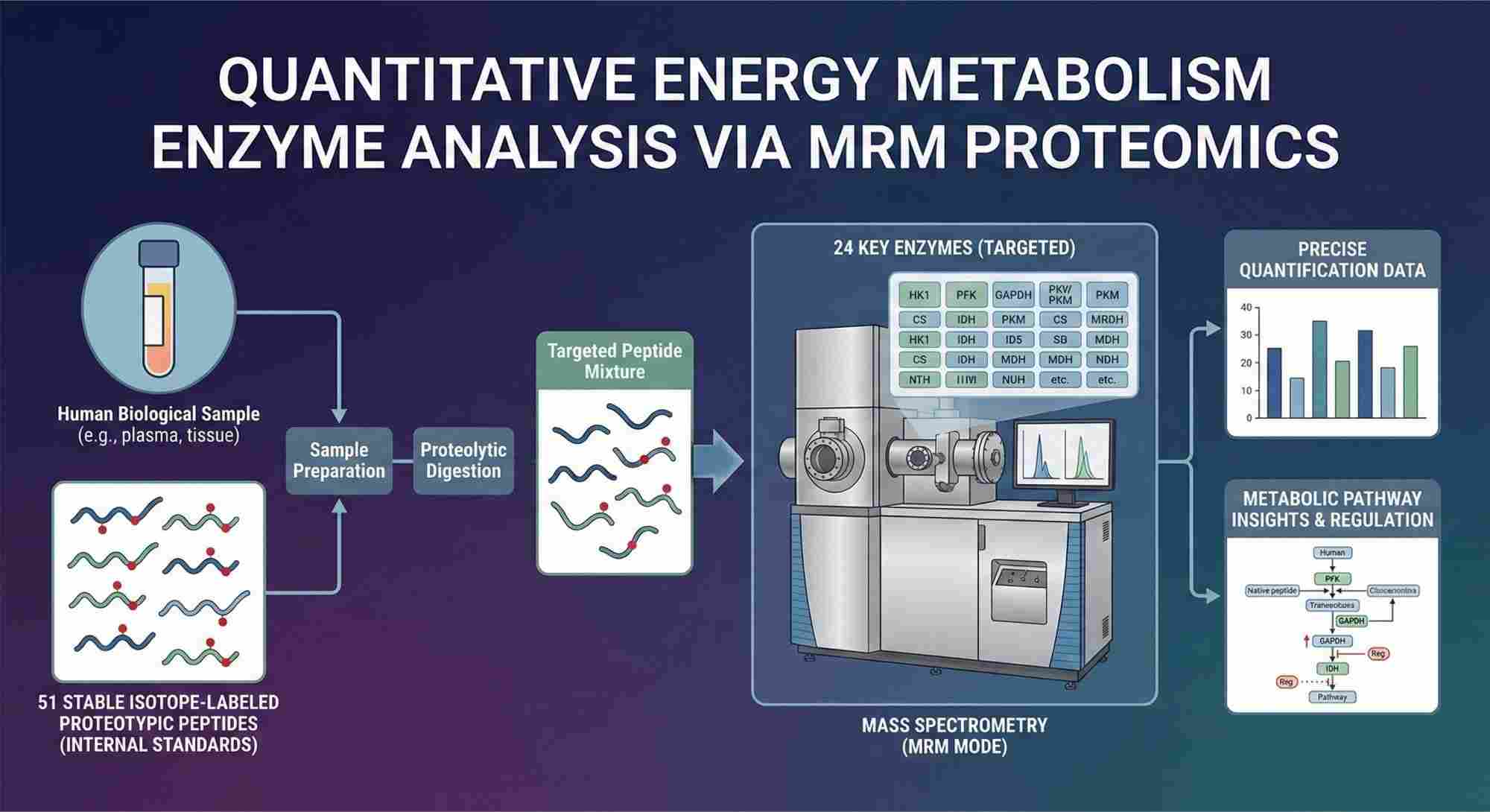
The precise quantification of human energy metabolism enzymes is achieved through a high-stringency targeted proteomics workflow utilizing Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) mass spectrometry. This analytical framework relies on the principle of stable isotope dilution, wherein 51 distinct, stable isotope-labeled proteotypic peptides are employed as internal standards to target 24 specific enzymes. By introducing these heavy-labeled standards—which are chemically identical to the endogenous peptides but distinguishable by mass—into the biological matrix, the methodology rigorously corrects for ionization suppression, matrix effects, and sample processing variability. This ensures that the mass spectral signal intensity correlates directly and linearly to the absolute abundance of the target proteins, offering a level of accuracy superior to traditional relative quantification methods.
From a functional biology perspective, this approach facilitates the stoichiometric mapping of the central energy metabolism network, encompassing glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Determining the absolute molar concentrations of these rate-limiting enzymes allows for the construction of accurate metabolic flux models and the assessment of bioenergetic capacity. This quantitative depth is essential for elucidating the kinetic constraints of cellular metabolism, enabling the precise characterization of metabolic phenotypes and the identification of regulatory bottlenecks underlying complex human biological states and disease pathologies.
Why choose precise quantification of human energy metabolism enzymes?
In systems biology, particularly within central carbon metabolism, the mere presence or relative upregulation of a protein does not equate to pathway throughput. Our precise quantification service addresses the limitations of semi-quantitative methods to provide data that is thermodynamically and kinetically relevant.
- Transitioning from Relative Expression to Absolute Stoichiometry
Traditional methods (Western Blotting, label-free proteomics) provide fold-change data, indicating only if a protein is "up" or "down" relative to a control. However, a twofold increase in a low-abundance enzyme may have a negligible effect on flux, while a minor fluctuation in a high-abundance, rate-limiting enzyme can drastically alter bioenergetics.
The Advantage: We provide absolute molar values (e.g., fmol/µg protein), enabling the determination of the system's true catalytic potential and the identification of thermodynamic bottlenecks.
- Accurate Reconstruction of Metabolic Flux
Metabolic pathways are tightly regulated networks defined by the ratios between enzymes, not just their individual abundance. To accurately model metabolic flux, one must understand the stoichiometric relationship between enzymes (e.g., the ratio of Hexokinase to Phosphofructokinase).
The Advantage: Precise quantification allows researchers to mathematically model how perturbations propagate through the network, distinguishing between compensatory mechanisms and true pathological drivers in metabolic diseases.
- Superior Specificity Over Antibody-Based Methods
Immunodetection relies on antibody binding, which is subject to cross-reactivity and batch-to-batch variability. In contrast, our MRM methodology utilizes mass-to-charge (m/z) ratios as intrinsic molecular barcodes.
The Advantage: By using heavy-labeled internal standards to correct for matrix effects and ionization suppression, we ensure the signal reflects biological reality rather than technical artifacts or non-specific binding.
- High-Throughput Multiplexing Efficiency
Investigating central energy metabolism requires a holistic view of interconnected nodes. Analyzing 24 distinct enzymes via traditional immunochemistry consumes significant time and sample volume.
The Advantage: Our targeted workflow analyzes the complete 24-enzyme panel in a single analytical run. This preserves valuable biological samples while delivering a comprehensive, simultaneous readout of the metabolic state.
Precise quantification service of human energy metabolism enzymes at Creative Proteomics
This service offers a specialized "sample-to-data" solution for the absolute quantification of 24 critical human metabolic enzymes. By leveraging our optimized MRM/PRM mass spectrometry workflow, we provide researchers with precise metabolic stoichiometry without the need for in-house instrumentation or assay development. This panel is specifically designed to capture the dynamic range of enzymes involved in central carbon metabolism and other key pathways, offering deep insights into cellular energetics and phenotypic changes.
The analysis is powered by a core mixture of 51 stable isotope-labeled proteotypic peptides, which are rigorously pre-quantified to serve as exact internal standards. Our dedicated facility handles the entire analytical pipeline—from protein extraction using proprietary lysis buffers to tryptic digestion and high-stringency LC-MS/MS acquisition. This end-to-end service delivers a comprehensive report detailing the absolute molar concentrations of the enzyme panel, alongside raw data files and QC validation. It is the ideal choice for clinical validation studies, high-throughput screenings, and research groups focused on biological interpretation rather than technical method optimization.
FAQs
-
How does absolute quantification via MRM differ from relative fold-change data provided by label-free proteomics?
Label-free proteomics and Western Blotting typically provide relative quantification (e.g., "Sample A has 2x more protein than Sample B"). While useful for discovery, these methods do not provide the molar concentrations required to understand stoichiometry. Our MRM-based service utilizes stable isotope-labeled internal standards to calculate the absolute concentration (e.g., fmol/mg total protein) of each target enzyme. This data is essential for mathematical modeling of metabolic flux and identifying rate-limiting steps in pathway kinetics.
-
What are the specific advantages of this method over antibody-based techniques like Western Blot or ELISA?
Antibody-based methods rely on the affinity and specificity of the antibody, which can suffer from cross-reactivity, non-specific binding, and batch-to-batch variability. Our targeted proteomics approach measures the mass-to-charge (m/z) ratio of proteotypic peptides, serving as a highly specific molecular barcode for each enzyme. Furthermore, the use of internal standards rigorously corrects for matrix effects and ionization suppression—factors that antibody methods cannot account for—resulting in superior reproducibility and dynamic range.
-
Which biological matrices are compatible with the CP 24 quantification service?
The assay is optimized for a wide range of human biological matrices, including cultured cell lines, fresh or frozen tissue samples (e.g., liver, muscle, tumor biopsies), and biofluids. Please refer to our Sample Preparation Guide for specific instructions regarding lysis buffers and minimum protein requirements to ensure optimal enzymatic stability and proteotypic peptide recovery.
-
Can the data obtained be used for metabolic flux analysis (MFA)?
Absolutely. The output of our service provides the stoichiometric abundance of enzymes, which serves as a critical parameter for constraining metabolic models. When combined with metabolite concentration data and isotope tracing, the absolute enzyme quantification allows for high-fidelity reconstruction of metabolic flux distributions and the assessment of maximum theoretical throughput (Vmax) in glycolysis and the TCA cycle.
-
What is the "Stable Isotope Dilution" (SID) strategy mentioned in the workflow?
Stable Isotope Dilution is the gold standard for quantitative mass spectrometry. We add a known amount of "heavy" peptides labeled with stable isotopes like 13C or 15N to your sample. These heavy peptides are chemically identical to the natural (endogenous) peptides but have a distinct mass. By comparing the signal intensity of the endogenous peptide to the heavy internal standard, we can calculate the exact amount of the endogenous protein, correcting for any loss during sample preparation or variability in instrument performance.
-
Which specific enzymes are included in the panel?
The panel targets 24 key enzymes covering the central energy metabolism backbone. This includes, but is not limited to:
- Glycolysis: Hexokinase (HK), Phosphofructokinase (PFK), Pyruvate Kinase (PKM).
- TCA Cycle: Citrate Synthase (CS), Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (IDH), Succinate Dehydrogenase (SDH).
- Oxidative Phosphorylation: Key subunits of the Electron Transport Chain complexes.
Please download the CP 24 Human Enzymes Quantification Service Target Peptide List.xlsx for the full target list.

