IP-MS Absolute Quantification of Amyloid-β—Advanced Alzheimer's Disease Diagnostics
What Is IP-MS Absolute Quantification of Amyloid-β ?
Recent advancements in Alzheimer's disease (AD) diagnostics have introduced more accessible, efficient, and cost-effective methods, particularly through the detection of peripheral blood biomarkers. Among these biomarkers, Amyloid-β (Aβ) protein is a critical pathological indicator of AD. Historically, PET imaging and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis have been the gold standards for diagnosing Alzheimer's. However, these methods are limited by high costs, complex procedures, and patient non-compliance, making them less practical for large-scale screenings and clinical trials.
Revolutionizing Alzheimer's Diagnostics with IP-MS
While IP/MS dates back to the early 20th century, it gained significant traction in 2018 when Nakamura's Nature article confirmed its 90% accuracy in quantifying Aβ protein. Building on this foundation, Karikari et al. further optimized the technique. Today, IP/MS offers a less invasive, cost-effective alternative to PET scans. This not only democratizes Alzheimer's screening but also streamlines clinical trials by efficiently identifying eligible participants, proving essential for large-scale studies.
How IP-MS Works: Precision and Accuracy in Action
IP-MS combines immunoprecipitation (IP) to enrich Aβ peptides with the power of mass spectrometry (MS), typically LC-MS/MS, to deliver precise and absolute quantification of Aβ proteins in biological samples. This cutting-edge technology has become a leading tool in Alzheimer's research, offering unmatched accuracy and reliability for both diagnostic and prognostic applications.
Key steps in the IP-MS process:
- Antibody-Based Enrichment: Aβ proteins are captured from the sample using highly specific antibodies, followed by immunoprecipitation to isolate and enrich the target protein while removing unwanted contaminants.
- Internal Standard Addition: A known concentration of isotope-labeled Aβ (such as 13C/15N) is added to the enriched sample. Both the Aβ protein and the internal standard undergo mass spectrometric analysis.
- Absolute Quantification: The absolute concentration of Aβ in the sample is calculated by comparing the signal intensity of the target Aβ protein to that of the internal standard, allowing for highly accurate quantification.
Why Choose Aβ Protein IP-MS Absolute Quantification Analysis ?
- High Accuracy & Sensitivity: Achieves precise, absolute quantification of Aβ protein, ensuring reliable results.
- Non-Invasive: Detects Alzheimer's biomarkers from peripheral blood, offering a less invasive option compared to traditional CSF analysis or PET scans.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for expensive PET imaging and lowers clinical trial recruitment costs.
- Scalable & Accessible: Ideal for large-scale population screening and clinical research, improving accessibility for diverse patient groups.
IP-MS Absolute Quantification of Amyloid-β Service at Creative Proteomics
At Creative Proteomics, we offer comprehensive IP-MS-based absolute quantification services for Amyloid-β (Aβ) protein in plasma, serum, and cerebrospinal fluid, specifically designed for Alzheimer's disease research. Our service includes detailed bioinformatics reports, featuring key insights such as ROC curve analysis, suggested cut-off values, and correlation statistics with PET positivity rates. These reports are ready for direct use in research grant applications or publications, ensuring you have the necessary data for impactful scientific work.
Additionally, we provide fully customizable services tailored to your unique research needs. Our expertise covers the entire workflow, from sourcing critical reagents like magnetic bead-antibody conjugates and isotope-labeled internal standards to creating standard curve peptides. We manage all aspects of the immunoprecipitation process and mass spectrometry detection, ensuring the highest accuracy and sensitivity. Each service comes with a comprehensive bioinformatics report that includes ROC analysis, cut-off recommendations, and PET correlation statistics, giving you the tools you need to advance your Alzheimer's pre-clinical research.
Partner with us to take your research to the next level with reliable, high-quality data for your Alzheimer's studies.
We can provide the following testing services:
- Plasma and CSF Aβ Quantification
- Aβ42/Aβ40 Ratio Analysis
- Aβ Isoforms Quantification
- Aβ Oligomer and Aggregate Detection
- Aβ Quantification in Animal Models
- Cross-Platform Comparison and Standardization
IP-MS Absolute Quantification Platform

Workflow of IP-MS Absolute Quantification Service
Creative Proteomics utilizes state-of-the-art instruments to provide reliable analytical results for your projects.
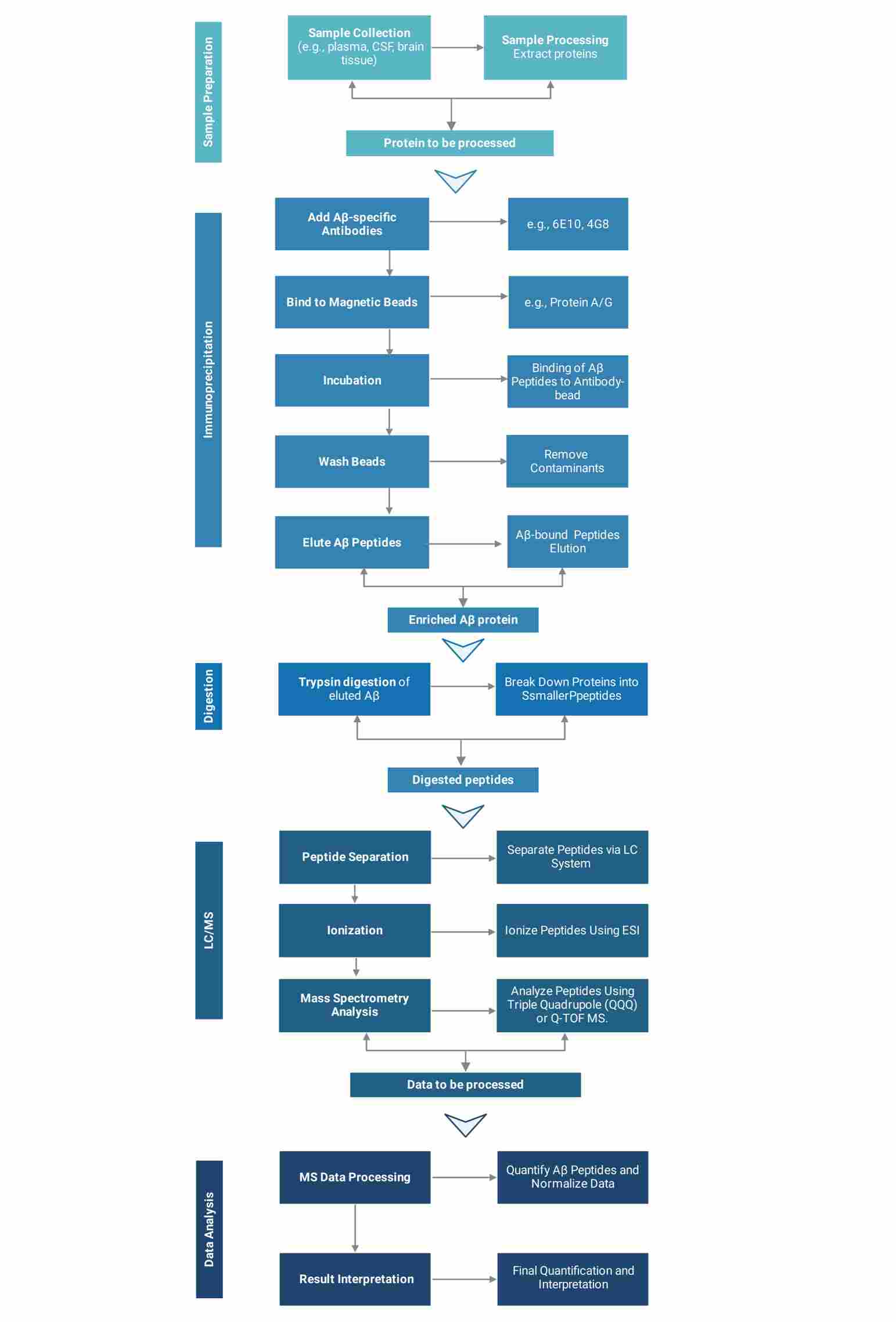
Advantages of Our IP-MS Absolute Quantification Service
- Unmatched Accuracy and Sensitivity: Achieve precise, reliable quantification of Amyloid-β (Aβ) proteins, even in complex samples, for the most accurate results in Alzheimer's diagnostics and research.
- Comprehensive Bioinformatics Support: Our service includes detailed bioinformatics reports featuring ROC curve analysis, suggested cut-off values, and PET correlation statistics, ready for use in research publications and grant applications.
- Non-Invasive and Cost-Effective: Offering testing in plasma, serum, and cerebrospinal fluid, our service provides a less invasive and more affordable alternative to traditional diagnostic methods, such as PET imaging and CSF analysis.
- Customizable Solutions for Your Research: We offer fully tailored services, from providing key reagents (e.g., magnetic bead-antibody conjugates) to optimizing the process for your specific research needs, ensuring the best fit for your project.
- End-to-End Service: From immunoprecipitation to mass spectrometry analysis, we handle the entire process, ensuring a seamless workflow and high-quality results.
- Scalable for Large-Scale Studies: Our service is suitable for both small-scale research projects and large clinical trials, making it an ideal solution for a wide range of research environments.
- Publication-Ready Results: Bioinformatics reports are prepared for immediate inclusion in scientific publications, minimizing the effort required to integrate results into your research.
- Efficient Clinical Trial Support: Our service simplifies participant recruitment and reduces the costs associated with clinical trials, enhancing the feasibility and speed of your study.
Applications of IP-MS Absolute Quantification of Amyloid-β
At Creative Proteomics, we utilize Immunoprecipitation-Mass Spectrometry (IP-MS) for the absolute quantification of Amyloid-β (Aβ), a key biomarker in Alzheimer's disease (AD). This advanced technique offers highly sensitive, specific, and reproducible measurements of Aβ peptides, enabling researchers and clinicians to gain deeper insights into AD pathology. Below are the primary applications of IP-MS in Alzheimer's disease research and diagnostics:
- Early Diagnosis and Detection of Alzheimer's Disease
IP-MS allows for precise Aβ quantification in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), providing valuable information for the early detection of Alzheimer's disease. Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio is a key diagnostic marker for Alzheimer's disease, a lower Aβ42/40 ratio is associated with amyloid plaque formation in the brain.
- Monitoring Disease Progression and Treatment Response
IP-MS can be used to track Aβ levels over time, making it a valuable tool for monitoring disease progression and assessing the effectiveness of treatments. Tracking changes in Aβ aggregation or clearance can evaluate the biological effects of potential therapies aimed at slowing or halting AD progression.
- Identification of Novel Biomarkers and Aβ Isoforms
Through IP-MS, we can identify and quantify new Aβ-related biomarkers and isoforms, including pyroglutamate-Aβ and oligomeric forms that may be more closely linked to disease pathology. Quantifying specific Aβ isoforms and modified peptides can enhance early diagnosis and monitoring, especially in individuals with atypical Alzheimer's pathology.
- Differentiating Alzheimer's Disease from Other Neurodegenerative Disorders
IP-MS enables the differentiation of Alzheimer's disease from other neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson's disease, frontotemporal dementia, and vascular dementia. By analyzing the Aβ42/40 ratio and other biomarkers, we provide a more accurate method for differential diagnosis, ensuring that individuals receive the correct diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Preclinical Research and Animal Models
In preclinical Alzheimer's research, IP-MS is used to study Aβ aggregation, clearance, and toxicity in animal models, helping researchers understand disease progression at the molecular level.
- Exploring Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
We apply IP-MS to study how lifestyle and environmental factors (e.g., diet, exercise, stress) influence Aβ metabolism and contribute to Alzheimer's disease risk.
- Cross-Platform Validation and Standardization
We leverage IP-MS to validate and standardize diagnostic methods across different platforms, such as Simoa or ELISA, for more consistent and reliable Alzheimer's disease diagnostics.
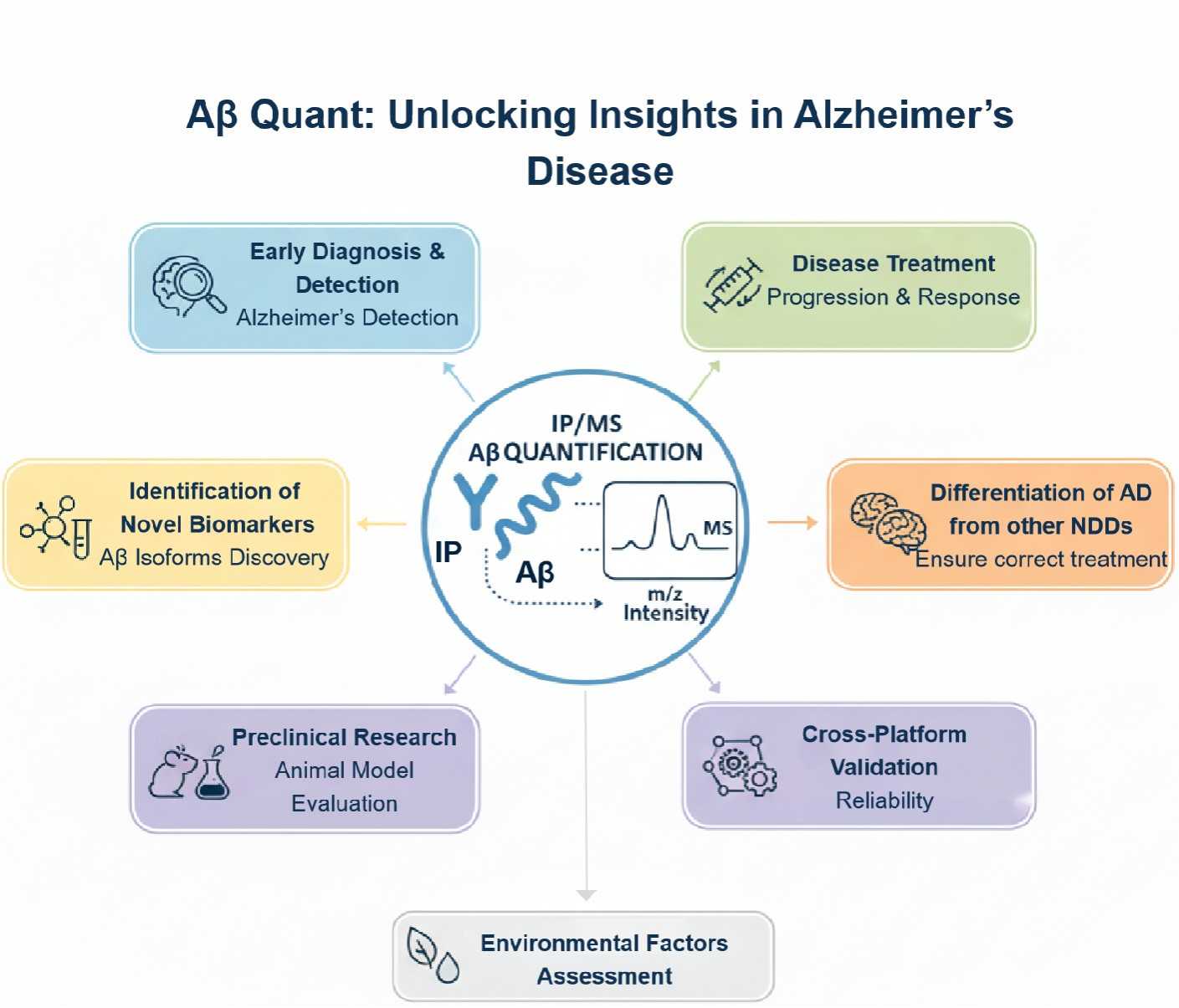
Demo Reports
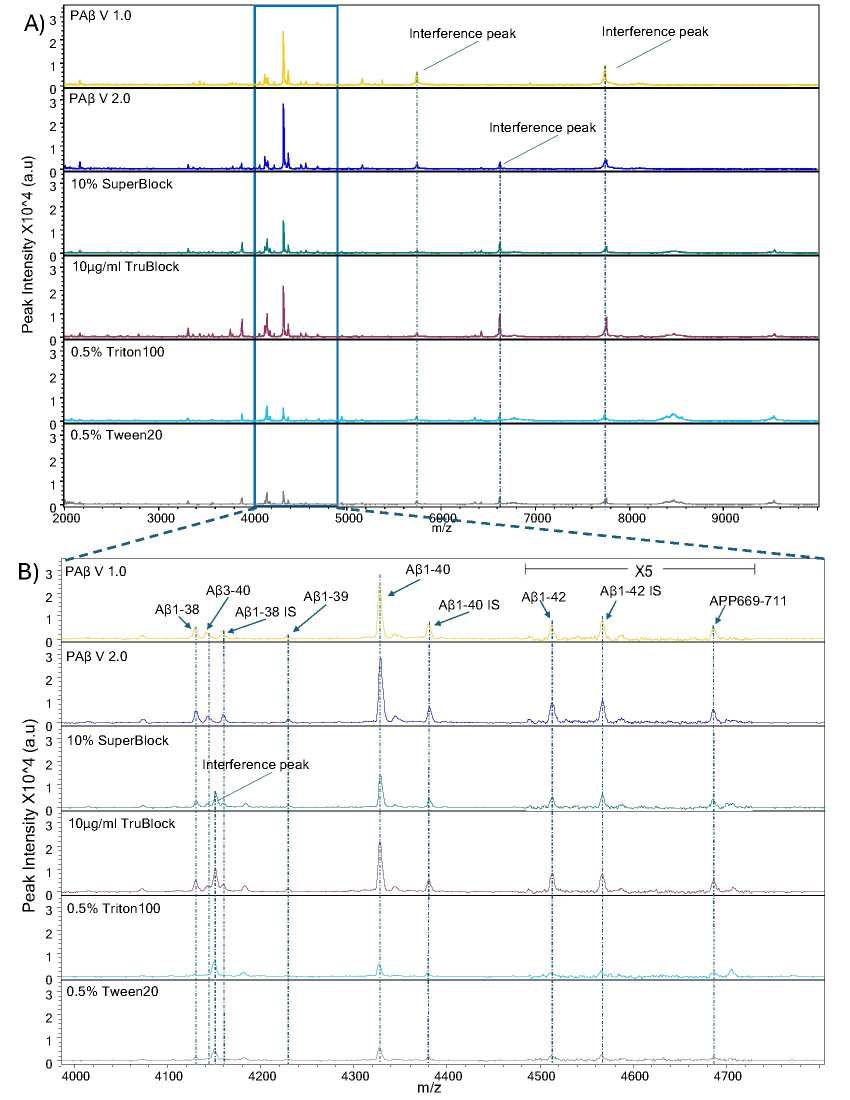
Mass spectra representative of Aβ peptides over multiple reagents and blocking buffers
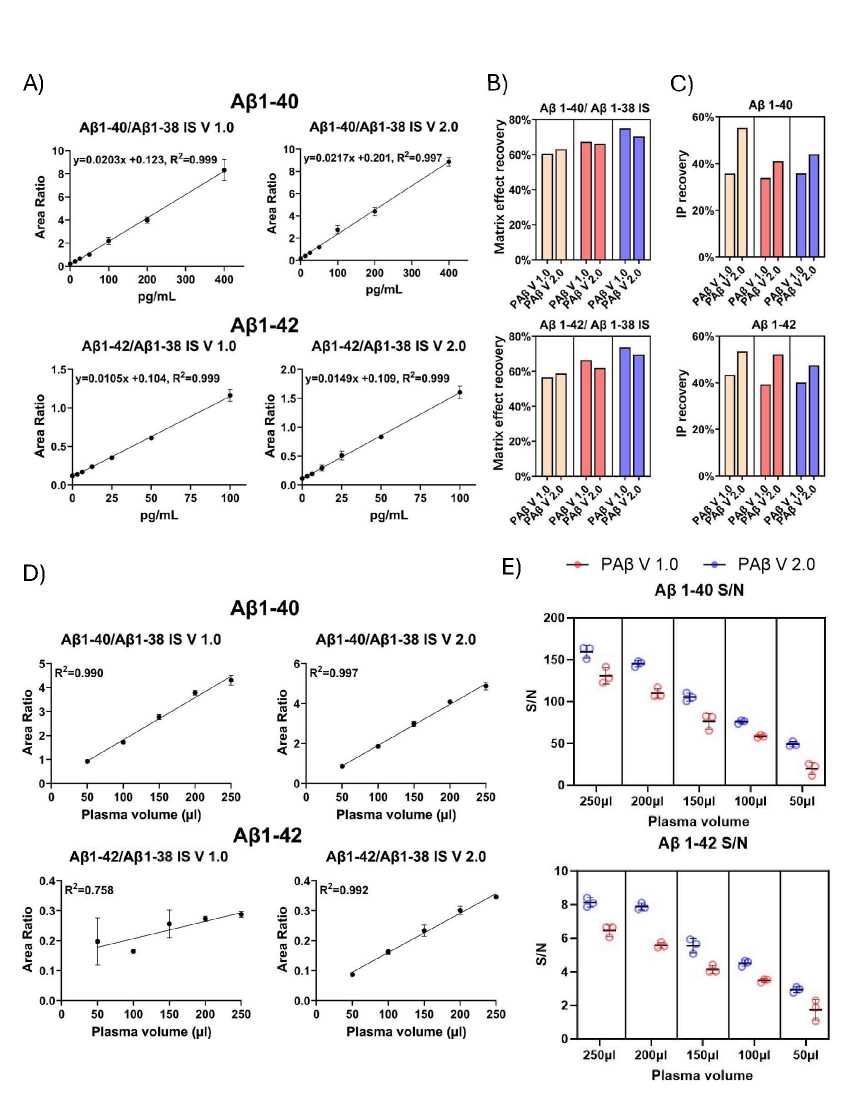
Analytical performance assessment of the IP-MS assays
FAQs of IP-MS Absolute Quantification of Amyloid-β
-
What is the ideal sample type for IP-MS Aβ quantification?
The most common sample types for IP-MS Aβ analysis are:
Plasma: A non-invasive sample that can be collected easily. Plasma Aβ quantification is often used in large cohort studies or for initial screenings.
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): More invasive but provides a closer reflection of brain amyloid burden. CSF Aβ levels are particularly useful for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease in more advanced stages.
IP-MS can also be applied to serum, saliva, and other body fluids, though plasma and CSF are the most frequently studied in relation to Alzheimer's.
-
What is the significance of the Aβ42/40 ratio in diagnosing Alzheimer's disease?
The Aβ42/40 ratio is a widely used metric in Alzheimer's diagnostics.
- Aβ42: More prone to aggregation and is the main component of amyloid plaques in the brain.
- Aβ40: The most abundant form of Aβ, less likely to aggregate into plaques.
The reduced Aβ42/40 ratio reflects early amyloid deposition in the brain and is often observed in individuals with Alzheimer's disease. This ratio serves as an early biomarker and is often used in combination with cognitive testing and brain imaging (e.g., amyloid PET) to confirm a diagnosis.
-
Can IP-MS detect Aβ oligomers?
Yes, one of the advantages of IP-MS is its ability to selectively isolate and quantify soluble Aβ oligomers (which are believed to be neurotoxic intermediates in Alzheimer's disease).
Oligomers are thought to accumulate earlier in the disease process and can induce synaptic dysfunction before amyloid plaques form. Using antibodies like OC antibody (specific for Aβ oligomers), IP-MS can detect different Aβ species, including monomers, oligomers, and aggregates, providing a more detailed picture of amyloid pathology.
-
What is the sensitivity of IP-MS for detecting low levels of Aβ in plasma?
IP-MS is highly sensitive and can detect Aβ peptides at sub-picogram levels, depending on the sample type and the instrument used. The sensitivity is further enhanced by the immunoprecipitation step, which concentrates the Aβ peptides from plasma, a complex biological matrix, before they are analyzed by mass spectrometry.
-
How do you ensure specificity when detecting different forms of Aβ (monomers, oligomers, aggregates)?
Specificity is achieved by using highly selective antibodies that bind only to the target Aβ species. For example, 6E10 targets the first 16 amino acids of Aβ (Aβ1–16), while OC antibody specifically detects Aβ oligomers. Additionally, mass spectrometry allows for the precise detection of different molecular species based on their unique mass-to-charge ratio (m/z), ensuring that only the targeted Aβ forms are measured.
-
How does the choice of bead (Protein A/G vs. Dynabeads) affect the results?
Both Protein A/G beads and Dynabeads are commonly used for immunoprecipitation. Protein A/G beads are ideal for higher affinity antibody binding, but may require more washing steps to reduce non-specific binding. Dynabeads, on the other hand, offer high stability, uniformity, and are easier to handle for high-throughput workflows. The bead type might affect yield and specificity, so the choice depends on the experimental needs and sample type.
-
How do you quantify Aβ using IP-MS? Do you use internal standards?
Absolute quantification is performed by spiking samples with stable isotope-labeled (SIL) Aβ peptides before immunoprecipitation. After MS analysis, the amount of Aβ in the sample is compared to the SIL standard to determine the concentration of the endogenous peptides. This allows for precise and reproducible quantification, even in complex biological matrices.
-
What mass spectrometry methods are used to analyze the Aβ peptides after IP?
The analysis is typically performed using LC-MS/MS (Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry). Specifically, methods like Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) or Parallel Reaction Monitoring (PRM) are used to target specific Aβ peptides (e.g., Aβ40, Aβ42) based on their unique mass-to-charge ratios. These techniques allow for highly sensitive and specific detection of endogenous Aβ peptides in complex biological samples.
-
Case Study
IP-MS Absolute Quantification of Amyloid-β Service Case Study
Title: Blood-based biomarkers and plasma Aβ assays in the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and behavioral-variant frontotemporal dementia
Journal: Alzheimer's Research & Therapy
Published: 2024
Background
The formation of neurotoxic amyloid beta (Ab) oligomers and plaques in specific brain regions is a key event in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The 42-amino acid isoform of Ab (Ab1-42) is thought to initiate plaque formation and AD progression. Various isoforms of Ab, such as Ab1-42, Ab1-40, and pGluAb3-42, have been detected in both sporadic AD (SAD) and familial AD (FAD) brains, but the relative importance of these isoforms in disease development is not fully understood. A study using immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry analyzed Ab isoform patterns in the cerebellum, cortex, and hippocampus of AD subjects, including those with presenilin (M146V) or amyloid precursor protein (KM670/671NL) mutations, SAD patients, and non-demented controls. The results revealed that the dominant Ab isoforms in all brain regions were Ab1-42, pGluAb3-42, Ab4-42, and Ab1-40, with Ab1-42 and Ab4-42 being the primary isoforms in the hippocampus and cortex across all groups, including controls. There were no significant differences in Ab isoform patterns between FAD and SAD patients, suggesting similar amyloid pathology in both forms of AD.
Materials & Methods
IP-MS measurement of Aβ38, Aβ40 and Aβ42 in plasma samples (Ulm)
EDTA plasma samples, calibrators and QC samples (490μL each) were mixed with 15N-Aβ38, 15N-Aβ40 and 15N-Aβ42 (rPeptide, Watkinsville, GA, USA) as internal standards, with triethylammonium bicarbonate (TEAB, final 120mM) and Tween 20 (final 0.05%). Magnetic beads (0.5 mg per sample, Thermo 14302D) covalently coupled with 6E10 antibody (Biolegend, 2 μg/mg beads) were added to each sample and incubated on a rotator over night at 4 °C. Beads were washed three times with 500μL 50mM TEAB/0.1% n-Dodecyl-β-D-maltoside and eluted with 25μL 50mM glycine HCl (pH 2.5). The eluted Aβ peptides were digested with 10μL of a TrypN working solution (12.5ng/μL, Protifi, Fairport, NY, USA) for 2.5 h at 37 °C and stopped with 10μL of 0.5% TFA in acetonitrile and stored in the autosampler at 4 °C. A volume of 20μL was injected into a QTRAP6500 mass spectrometer (Sciex) coupled to an Eksigent MicroLC200 and Agilent 1260 pump. Peptides were loaded on an Acclaim PepMap100, C18 trap column (5 μm, 0.3×5 mm, Thermo) using mobile phase A: 0.05% TFA and mobile phase B: 90% acetonitrile, 0.1% ammonium hydroxide and a flow rate of 200μL/min. Separation of peptides was performed on a HALO Fused-Core C18, 100×0.5 mm analytical column (Eksigent, Framingham, MA, USA) at 60 °C and a gradient time of 9.85 min (5–35%B, total run time 17.5 min) with mobile A: 4% DMSO, 0.1% formic acid and mobile phase B: 4% DMSO, 96% acetonitrile, 0.1% formic acid. Peptides were infused into the QTRAP6500 mass spectrometer by electrospray ionization and measured in MRM mode using the following transitions: Aβ38 (aa28-38, 508.3→784.5 (b8+), 508.3→883.5 (b9+), 508.3→653.4 (b7+)); Aβ40 (aa28-40, 607.4→997.6 (b11+), 607.4→548.8 (b12++), 607.4→499.3 (b11++)); Aβ42 (aa28-42, 699.4→598.4 (b13++), 699.4→548.8 (b12++), 699.4→1096.7 (b12+)). Data were analysed using Skyline software v23.1 and for quantification, external calibration curves were generated using the light-to-heavy peak area ratios of calibrator samples and a quadratic function with 1/x² weighting. Calibrator samples (8-point calibration) were prepared in a surrogate matrix (3% bovine serum albumin in PBS) using synthetic Aβ38, Aβ40 and Aβ42 (Sigma) in the range of 1-100pg/mL (Aβ38, Aβ42) and 10-1000pg/mL (Aβ40). Plasma QC samples were included in all runs to monitor performance of measurements. The method was validated in terms of intraassay (1.2–10.5%) and interassay CV (3.4–7.4%), dilution stability (tested for 2- and 4-fold dilution, accuracy 89.9-110.7%), spike-in recovery (20pg/mL for Aβ38 and Aβ42, 200pg for Aβ40, recovery 93.1-100.4%) and stability at room temperature for 2h and up to 3 freeze-thaw-cycles (accuracy 80.2-108.1%). Intraassay CV of QC samples during measurement of patient samples was 1.2–10.5%.
Results
A strong correlation was observed between Aβ40 concentrations in patient samples, as determined by various assays (Fig. 1). The novel assay, referred to as "ULM," performed with IP-MS using ESI-MRM, demonstrated good correlation, with Spearman's rho values of 0.74 (P≤0.0001) when compared to the Shimadzu assay and 0.80 (P≤0.0001) when compared to the Simoa assay. For Aβ42 concentrations, a moderate to good correlation was seen, with Spearman's rho values of 0.61 (P≤0.0001) for the Shimadzu assay and 0.71 (P≤0.0001) for the Simoa platform. In contrast, the correlation for the Aβ42/40 ratio between the ULM assay and the Shimadzu assay was weak, with a Spearman's rho of 0.30 (P≤0.05), and a weak to moderate correlation of 0.46 (P≤0.001) with the Simoa platform's Aβ42/40 ratio. Comparatively, the correlations between the Shimadzu assay and the Simoa platform were modest but slightly lower, with Spearman's rho values of 0.68 (P≤0.0001) for Aβ40, 0.57 (P≤0.0001) for Aβ42, and 0.28 for the Aβ42/40 ratio. However, the latter correlation remained above the threshold of statistical significance (P>0.05).
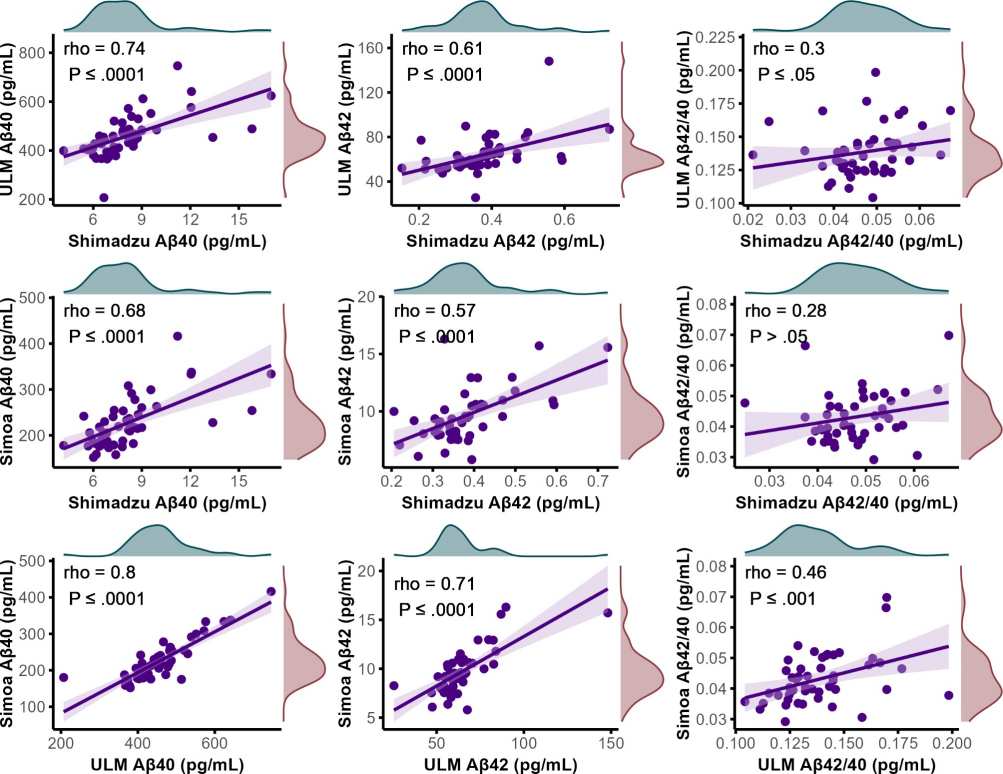
Figure 1. Scatter plots visualizing the correlations between plasma concentrations of Aβ40 and Aβ42, along with the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio, across various as says.
Conclusion
To summarize, this study developed an IP-MS assay for Aβ42/40, which showed comparable accuracy to the Shimadzu composite score in distinguishing Alzheimer's disease (AD) from control groups. This new assay outperformed both the Shimadzu Aβ42/40 ratio and the Simoa Aβ42/40 assay. The results indicate that Aβ levels alone do not offer additional diagnostic value when differentiating AD from behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD). Importantly, the combination of pTau181 and GFAP proves to be a powerful tool for the blood-based differential diagnosis of AD and bvFTD.
References
- Nakamura, Akinori et al. "High performance plasma amyloid-β biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease." Nature vol. 554,7691 (2018): 249-254. doi:10.1038/nature25456
- Karikari, Thomas et al. "A streamlined, resource-efficient immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry method for quantifying plasma amyloid-β biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease." Research square rs.3.rs-4947448. 2 Sep. 2024, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4947448/v1. Preprint.
- Bros, Pauline et al. "Quantitative detection of amyloid-β peptides by mass spectrometry: state of the art and clinical applications." Clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine vol. 53,10 (2015): 1483-93. doi:10.1515/cclm-2014-1048
- Yamashita, Kazuto et al. "Fully automated chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassays showing high correlation with immunoprecipitation mass spectrometry assays for β-amyloid (1-40) and (1-42) in plasma samples." Biochemical and biophysical research communications vol. 576 (2021): 22-26. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.08.066


