Creative Proteomics is a leading organization in the field of proteomics research, offering exceptional services in detecting unusual toxicity of various substances. Owing to our deployment of advanced methodologies and state-of-the-art technological resources, we can identify proteins with an unprecedented level of precision and accuracy. Importantly, our endeavors continually align with the stipulations laid out in the ICH Q6B guidelines.
Introduction to Abnormal Toxicity Testing
Numerous quality control and safety measures have been implemented to ensure the maintenance and control of vaccine quality. Among these precautions, one stands out as a crucial component: the Abnormal Toxicity Test (ATT). This test, also commonly referred to as the general safety test, innocuity test or test for freedom from abnormal toxicity, was specifically designed to identify non-specific toxicity and contamination from exogenous substances. The World Health Organization firmly advocates for its incorporation within national vaccine control procedures.
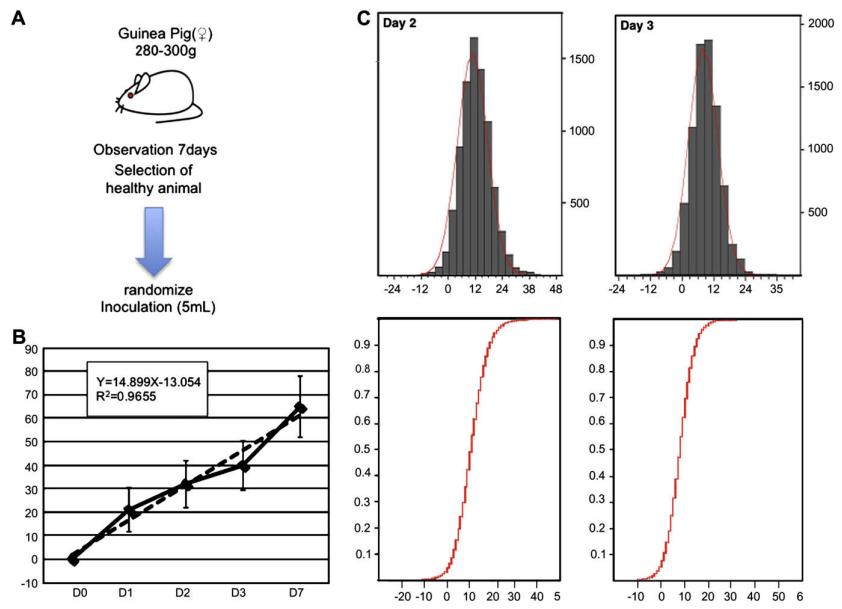 Fig 1. Preliminary phase of abnormal toxicty test. (Mizukami, T., et al.; 2009)
Fig 1. Preliminary phase of abnormal toxicty test. (Mizukami, T., et al.; 2009)
Countries such as Japan and the United States (specifically referenced under 21 CFR 610.11) necessitate the implementation of ATT for batch-release testing of vaccines, sera, and immunoglobulins using mice or guinea pigs. It should be noted that while European Union nations do not require this, the ATT is nonetheless encompassed in several European pharmacopeia monographs and remains a fundamental requirement for obtaining licensure and validating product processes within the EU.
Prior to Abnormal Toxicity Testing
Guinea pigs (clean grade and SPF grade) are continuously observed.Over the course of seven days, body weights were meticulously recorded. From the healthy contingents, individuals were randomly assigned to different injection groups, with each group constituting two specimens.

Hematological evaluation was conducted by obtaining 2 ml of peripheral blood extracted directly from the heart, which was immediately analyzed for peripheral blood leukocytes (PBL), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (HGB), red blood cells (RBC), hematocrit (HCT), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), and platelets (PLT) using a sophisticated automatic hematocytometer, the Celltac MEK-5254 from Nihon Kohden, Tokyo, Japan.

The experiment was considered successful if the animal subjects exhibited no abnormal histopathological modifications. Furthermore, if the body weight distribution between the guinea pigs injected with the trial vaccine and the reference population was not significantly divergent (P < 0.01), the animals were adjudged to have successfully passed the test.
How to Detect Abnormal Toxicity Testing?
In Vivo testing, undertaken in living organisms, allows for the comprehensive evaluation of drug substances. Assorted parameters are measured, encompassing alterations in behavior, physiological reactions, and the rates of mortality.
In Vitro testing, on the other hand, replicates the human body's milieu in a laboratory environment, facilitating the observation of the cytotoxic impacts of substances on cells, tissues, or organ analogues.
Abnormal Toxicity Testing Workflow
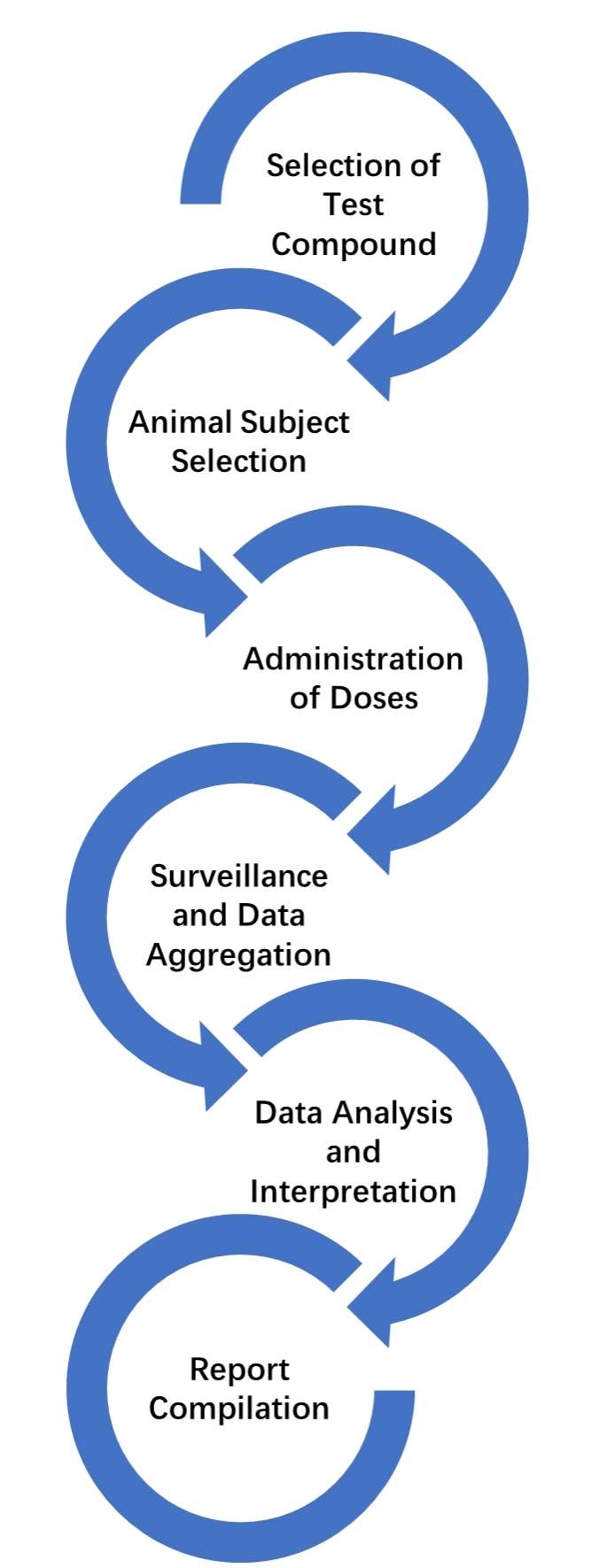
Selection of Test Compound: The chosen compound undergoes rigorous toxicity screening to discern if it poses any deleterious effects to the physiological system.
Animal Subject Selection: The majority of acute toxicity assessments are performed on diminutive mammals. Rabbits and guinea pigs are predominantly employed, however, the choice of the animal model is contingent upon the nature of the product under testing.
Administration of Doses: The test compound is typically administered in more than a single dose under strictly controlled environments to the animal subjects. The dosage volume and the number of injections differ in accordance to the specific testing protocol being employed.
Surveillance and Data Aggregation: The animal subjects are stringently monitored for any manifestation of toxicity. Any indications of sickness, aberrant behavior, or mortality are meticulously documented.
Data Analysis and Interpretation: The collated empirical data undergoes comprehensive review and analysis. Any resultant adverse effects observed in the test animals are scrutinized to ascertain if these impacts are correlated to toxicity.
Report Compilation: A thorough report encapsulating the administration methods, monitoring outcomes, data dissection, and interpretation of findings is composed.
Why Us?

Our Goals
Using advanced technologies and analytical methodologies, the skilled team at Creative Proteomics can thoroughly explore and determine the toxic qualities or potential risks of these substances. It's also an invaluable tool in new drug development, as it allows researchers to pinpoint potential toxic effects early in the development trajectory, thereby ensuring the eventual safety and efficacy of the drug. We welcome your inquiries.
Reference
- Mizukami, T., et al.; An improved abnormal toxicity test by using reference vaccine-specific body weight curves and histopathological data for monitoring vaccine quality and safety in Japan. Biologicals. 2009, 37(1), 8–17.
Related Sections
Services
Applications
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.

 Fig 1. Preliminary phase of abnormal toxicty test. (Mizukami, T., et al.; 2009)
Fig 1. Preliminary phase of abnormal toxicty test. (Mizukami, T., et al.; 2009)




