Introduction to Peptide Hormones
Peptide hormones encompass a specific classification of hormones - biochemical effector molecules synthesized in the cellular environment to modulate physiological functions and processes. Principally constituted of brief amino acid sequences, or peptides, these hormones are biologically manufactured by diverse organs and glands within the organism, such as the pituitary, cardiac tissues, gastric system, and the intestines.
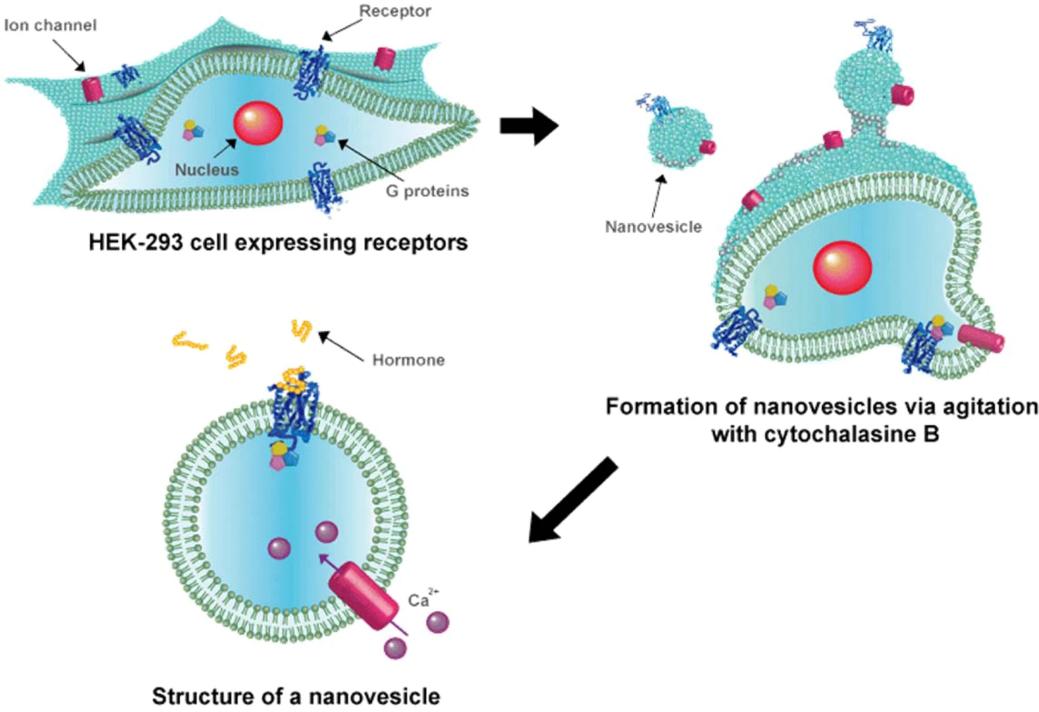 Fig 1. Schematic of the construction of human hormone receptors-carrying nanovesicles. (Ahn, Sae Ryun, et al. 2020)
Fig 1. Schematic of the construction of human hormone receptors-carrying nanovesicles. (Ahn, Sae Ryun, et al. 2020)
Their water-soluble property and particular molecular conformation prevent them from permeating cell membranes. Instead, they engage with distinct receptors situated on the cellular surfaces, instigating intracellular consequences via the initiation of signal transduction routes.
List of Peptide Hormones in Humans
Adropin, a crucial regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism, is composed of a peptide sequence of 76 amino acids as identified through microarray screening. The secretory signal peptide sequence is specifically encoded by the initial residues (1-33). A synthetic adropin version encompasses residues 34-76 and this isoform has been confirmed to be biologically active. This sequence is significantly conserved among mammalian species, with an identical sequence spotted in humans, horses, rats, and mice.
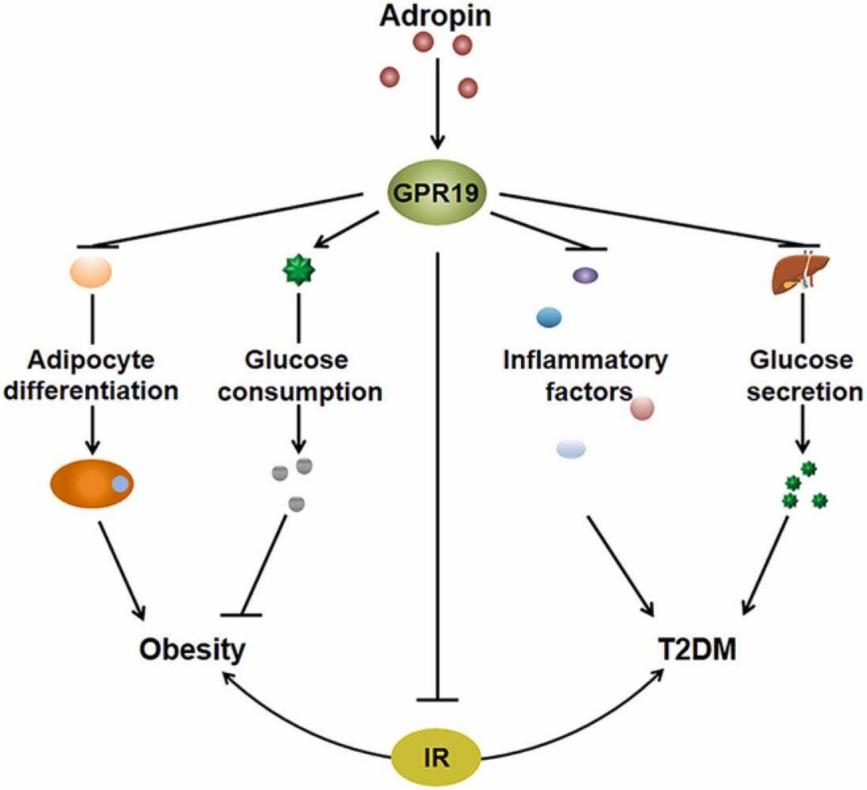 Fig 2. Adropin as an indicator of T2DM and its complications. (Zhang, Hu, and Ning Chen. 2022)
Fig 2. Adropin as an indicator of T2DM and its complications. (Zhang, Hu, and Ning Chen. 2022)
The energy homeostasis-associated gene (ENHO), located on chromosome 9 in humans and chromosome 4 in mice, is responsible for encoding Adropin. Enho mRNA is abundantly expressed in various brain areas and in the liver. The level of hepatic Adropin mRNA expression is influenced by the nutritional status.
The apelin gene in the human and mouse genomes is located on chromosome X and encodes a 77 amino acid prepropeptide, pre-pro-apelin. As a result of the post-translational processing of this precursor peptide, Apelin-17, Apelin-13, and [Pyr1]-Apelin-13 (with a pyroglutamate substitution at the N terminus of Apelin-13) are formed. All of these isoforms are biologically active. Previous studies showed that apelin and the APJ receptor are widely expressed in all mammalian peripheral tissues, such as the stomach, heart, lung, skeletal muscle, etc., as well as in some regions of CNS, e.g., in the brain, including the extrahypothalamic structures, such as the piriform cortex, the nucleus of the lateral olfactory tract, the central grey matter, the pars compacta of the substantia nigra, the dorsal raphe nucleus, and the entorhinal cortex.
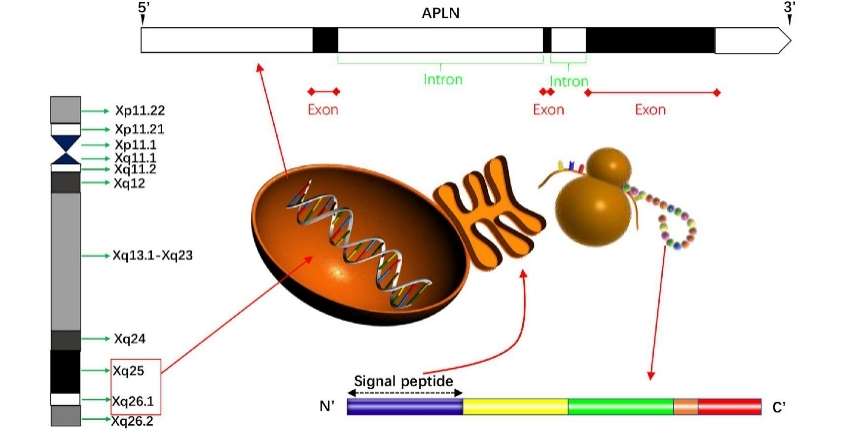 Fig 3. Schematically presentation of apelin in gene and protein. (Hu, Gonghui, et al. 2021)
Fig 3. Schematically presentation of apelin in gene and protein. (Hu, Gonghui, et al. 2021)
Relaxin is a hormone primarily synthesized within the ovary and placenta, holding significant influence over the female reproductive system and governing several physiological processes during gestation. This hormone manifests its action preeminently in preparation for parturition, where it induces the relaxation of the pelvic ligaments and facilitates the softening and dilating of the cervix.
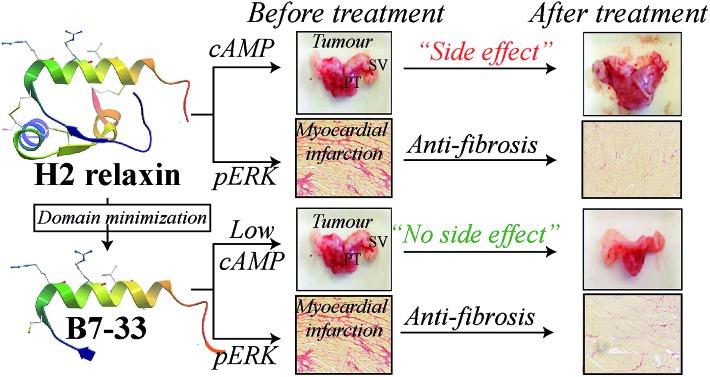 Fig 4. A single-chain derivative of the relaxin hormone ameliorates fibrosis without side-effects. (Hossain, Mohammed Akhter, et al. 2016)
Fig 4. A single-chain derivative of the relaxin hormone ameliorates fibrosis without side-effects. (Hossain, Mohammed Akhter, et al. 2016)
In addition to the aforementioned functionalities, relaxin acts as an inhibitor of uterine contractions, potentially contributing to the precise scheduling of birth. While the implications of relaxin are most prominent during pregnancy, its roles extend beyond this scope. Indeed, our understanding constantly expands to encompass its impact on a myriad of other biological processes, such as bone remodeling, regulation of cardiovascular function, and the exertion of anti-fibrotic actions.
What Can We Offer?
Why Choose Our Service
Recognized as a leader in the field of biotechnology, Creative Proteomics offers a wide range of services specializing in the complex arena of protein pharmaceutical characterization. Please do not hesitate to reach out to us for further dialogue or to request more information.
References
- Ahn, Sae Ryun, et al. Peptide hormone sensors using human hormone receptor-carrying nanovesicles and graphene FETs. Scientific Reports. 2020, 10.1: 388.
- Zhang, Hu, and Ning Chen. Adropin as an indicator of T2DM and its complications. Food Science and Human Wellness. 2022, 11.6: 1455-1463.
- Hu, Gonghui, et al. The role of apelin/apelin receptor in energy metabolism and water homeostasis: a comprehensive narrative review. Frontiers in physiology. 2021, 12: 632886.
- Hossain, Mohammed Akhter, et al. A single-chain derivative of the relaxin hormone is a functionally selective agonist of the G protein-coupled receptor, RXFP1. Chemical science. 2016, 7.6: 3805-3819.
Related Sections
Services
Applications
Creative Proteomics specializes in protein drug characterization, and we offer a range of services to help our clients understand and optimize their protein drug products. Our services include, but are not limited to:
|
Protein Drug characterization
|
Reaearch Project
|
Method
|
Application
|
|
Protein Structure Confirmation Service
|
Primary Structure Analysis
|
X-ray crystal diffraction,
nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy,
ellman's assay,
ion exchange chromatography (IEC),
edman degradation,
mass spectrometry (MS), etc.
|
Protein functions, disease mechanisms, and drug design, etc.
|
|
Higher-Order Structure Analysis
|
|
Post-Translational Modification (PTM) Analysis Service
|
Protein Glycan Analysis
|
Mass spectrometry (MS),
nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy,
lectin affinity chromatography,
liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), etc.
|
Disease mechanism research, drug discovery and development, regulation of biological processes, clinical diagnostic, bioinformatics, etc.
|
|
Protein Acetylation Analysis
|
|
Protein Phosphorylation Analysis
|
|
Protein Ubiquitination Analysis
|
|
Protein Deamidation Analysis
|
|
Protein Oxidation Analysis
|
|
Protein Methylation Analysis
|
|
Protein Alkylation Analysis
|
|
Protein Sulfation Analysis
|
|
Proteolysis Analysis
|
|
Protein Truncation Analysis
|
|
Protein Physicochemical Property Determination Service
|
Isoelectric Point (PI) Determination
|
Isoelectric focusing (IEF),
thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence assay,
western blotting,
ultraviolet-visible spectrometry,
fluorescence spectrometry, etc.
|
Protein structure study, protein interaction study, protein modification study, protein purity and quantitative analysis, clinical diagnosis, etc.
|
|
Charge Variant Analysis
|
|
Extinction Coefficient Determination
|
|
Protein Aggregation Analysis
|
|
Protein Degradation Analysis
|
|
Thermal (Tm) Stability Analysis
|
|
Protein Quantitation
|
|
Protein Purity Service
|
/
|
Composition-based and activity-based analyses,
mass spectrometry (MS),
high performance liquid chromatography,
capillary electrophoresis, etc.
|
Biomedical research, biological research, clinical diagnostics, etc.
|
|
Protein Impurities Service
|
Host Cell Protein (HCP) Analysis
|
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC),
mass spectrometry (MS),
size-exclusion chromatography (SEC),
capillary electrophoresis, etc.
|
Quality control, safety assessment, clinical diagnostics, bioprocess research, etc.
|
|
Residual Host Cell DNA (HCD) Analysis
|
|
Residual Protein A Analysis
|
|
Process Related Impurities and Residual Analysis
|
|
Protein Biosafety Analysis Service
|
Bacterial Endotoxins Testing
|
Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL),
membrane filtration,
PCR,
nucleic acid testing (NAT),
massively parallel sequencing (MPS), etc.
|
Biomedical research, food safety testing, environmental science, industrial production, etc.
|
| Bioburden Testing |
| Sterility Testing |
| Abnormal Toxicity Testing |
| Mycoplasma Testing |
| Subvisible Particles Analysis |
| Visible Particles Analysis |
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.

 Fig 1. Schematic of the construction of human hormone receptors-carrying nanovesicles. (Ahn, Sae Ryun, et al. 2020)
Fig 1. Schematic of the construction of human hormone receptors-carrying nanovesicles. (Ahn, Sae Ryun, et al. 2020) Fig 2. Adropin as an indicator of T2DM and its complications. (Zhang, Hu, and Ning Chen. 2022)
Fig 2. Adropin as an indicator of T2DM and its complications. (Zhang, Hu, and Ning Chen. 2022) Fig 3. Schematically presentation of apelin in gene and protein. (Hu, Gonghui, et al. 2021)
Fig 3. Schematically presentation of apelin in gene and protein. (Hu, Gonghui, et al. 2021) Fig 4. A single-chain derivative of the relaxin hormone ameliorates fibrosis without side-effects. (Hossain, Mohammed Akhter, et al. 2016)
Fig 4. A single-chain derivative of the relaxin hormone ameliorates fibrosis without side-effects. (Hossain, Mohammed Akhter, et al. 2016)
