Introduction to Enzyme
Enzymes are intricate proteins that function as biological catalysts, playing a pivotal role in myriad biological operations. By expediting chemical reactions within an organism without undergoing change themselves, enzymes serve as cornerstones for all metabolic activities. This spans across food digestion, DNA synthesis, and the translocation of ions across cell membranes.
In the case of each enzyme, it manifests as an extensive protein molecule that consists of an amino acid chain. Each enzyme harbors a unique structure and shape, thereby allowing its capacity to engage with a specific molecule or substrate to catalyze a distinct reaction. The fundamental principle behind enzymatic functions is their ability to reduce the energy barrier of a reaction, thereby facilitating the reaction's occurrence.
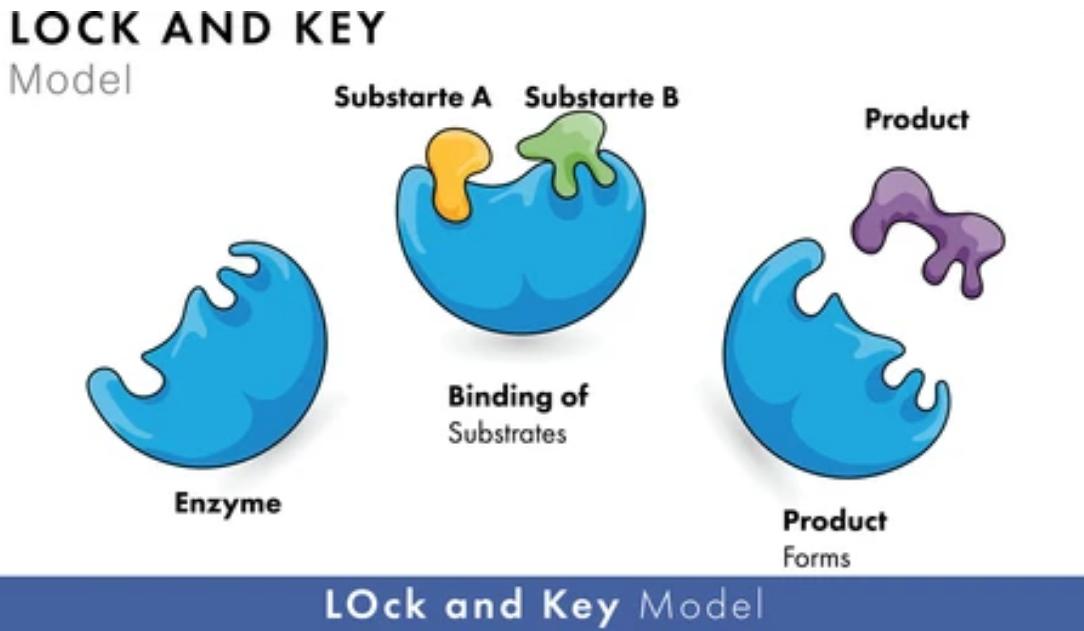
The hallmark of enzymes resides in their precise specificity. This applies both to the substrate they interact with and the reactions they catalyze. Such specificity emanates from the unique three-dimensional structure of every individual enzyme. This structure, in turn, results in an active site meticulously designed to align with its specific substrate.
What do Enzymes do?
Enzymes operate as critical facilitators in chemical reactions within biological entities or environmental ecosystems, functioning to expedite said reactions in a process known as catalysis. Of note is their ability to increase the rate of these reactions without themselves undergoing alteration, hence acting as biological catalysts. Their role also remarkably extends to facilitating normally impossible reactions under given conditions, such as at suboptimal temperatures.
While chemical and physical reactions may take place naturally, the addition of exogenous enzymes can significantly enhance the rate of these reactions. Given their crucial function, enzymes exert a broad impact on the overall health of natural ecosystems.
- Enzymes play a fundamental role in facilitating signal transduction. A notable enzyme involved in this process is protein kinase, responsible for catalyzing protein phosphorylation, making it the most commonly utilized enzyme in transduction processes.
- Enzymes also possess catabolic properties, where they decompose large chemical structures into minute constituents that can be seamlessly incorporated by the body.
- In terms of energy production, specific enzymes called ATP synthases play a crucial role. These enzymes govern the synthesis of ATP, thus managing the energy currency within the body.
- Enzymes function as regulatory agents in controlling ion transportation across the plasma membrane, thus ensuring proper cellular function and maintaining physiological stability.
- Biochemical detoxification processes involving enzymes include operations such as oxidation, reduction, and hydrolysis. These processes are vital for the removal of non-nutritious substances from the body.
- Furthermore, enzymes are entrusted with internal cellular reorganization, acting as arbiters that monitor and regulate cellular processes by adjusting the cell's internal structure. Such adjustments maintain the cell's functionality and adaptability, further underscoring the multifaceted roles of enzymes in overall biological systems.
What Can We Offer?
Why Choose Our Service

Expertise

Collaborative Approach

Accuracy and Reliability
Recognized globally for our pioneering role in the biotechnology sector, we at Creative Proteomics offer a wide range of specialized services tailored to address intricate issues in protein pharmaceutical characterization. If you require additional insights or more comprehensive information, we cordially encourage you to initiate dialogues or inquiries with us.
Related Sections
Services
Applications
Creative Proteomics specializes in protein drug characterization, and we offer a range of services to help our clients understand and optimize their protein drug products. Our services include, but are not limited to:
|
Protein Drug characterization
|
Reaearch Project
|
Method
|
Application
|
|
Protein Structure Confirmation Service
|
Primary Structure Analysis
|
X-ray crystal diffraction,
nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy,
ellman's assay,
ion exchange chromatography (IEC),
edman degradation,
mass spectrometry (MS), etc.
|
Protein functions, disease mechanisms, and drug design, etc.
|
|
Higher-Order Structure Analysis
|
|
Post-Translational Modification (PTM) Analysis Service
|
Protein Glycan Analysis
|
Mass spectrometry (MS),
nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy,
lectin affinity chromatography,
liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), etc.
|
Disease mechanism research, drug discovery and development, regulation of biological processes, clinical diagnostic, bioinformatics, etc.
|
|
Protein Acetylation Analysis
|
|
Protein Phosphorylation Analysis
|
|
Protein Ubiquitination Analysis
|
|
Protein Deamidation Analysis
|
|
Protein Oxidation Analysis
|
|
Protein Methylation Analysis
|
|
Protein Alkylation Analysis
|
|
Protein Sulfation Analysis
|
|
Proteolysis Analysis
|
|
Protein Truncation Analysis
|
|
Protein Physicochemical Property Determination Service
|
Isoelectric Point (PI) Determination
|
Isoelectric focusing (IEF),
thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence assay,
western blotting,
ultraviolet-visible spectrometry,
fluorescence spectrometry, etc.
|
Protein structure study, protein interaction study, protein modification study, protein purity and quantitative analysis, clinical diagnosis, etc.
|
|
Charge Variant Analysis
|
|
Extinction Coefficient Determination
|
|
Protein Aggregation Analysis
|
|
Protein Degradation Analysis
|
|
Thermal (Tm) Stability Analysis
|
|
Protein Quantitation
|
|
Protein Purity Service
|
/
|
Composition-based and activity-based analyses,
mass spectrometry (MS),
high performance liquid chromatography,
capillary electrophoresis, etc.
|
Biomedical research, biological research, clinical diagnostics, etc.
|
|
Protein Impurities Service
|
Host Cell Protein (HCP) Analysis
|
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC),
mass spectrometry (MS),
size-exclusion chromatography (SEC),
capillary electrophoresis, etc.
|
Quality control, safety assessment, clinical diagnostics, bioprocess research, etc.
|
|
Residual Host Cell DNA (HCD) Analysis
|
|
Residual Protein A Analysis
|
|
Process Related Impurities and Residual Analysis
|
|
Protein Biosafety Analysis Service
|
Bacterial Endotoxins Testing
|
Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL),
membrane filtration,
PCR,
nucleic acid testing (NAT),
massively parallel sequencing (MPS), etc.
|
Biomedical research, food safety testing, environmental science, industrial production, etc.
|
| Bioburden Testing |
| Sterility Testing |
| Abnormal Toxicity Testing |
| Mycoplasma Testing |
| Subvisible Particles Analysis |
| Visible Particles Analysis |
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.