Creative Proteomics has strategically designed its bioburden testing service to procure precise, reliable, and expedient results, ensuring it is optimally tailored to meet the necessities of our clientele and adhere to industry stipulations.
What is Bioburden?
Bioburden, also referred to as the biological burden, is a term used to describe the total count of bacteria and other viable microorganisms present on a surface prior to sterilization or disinfection. This concept is pertinent in several fields, especially those related to health care, pharmaceuticals, and food safety, where the absence of harmful microbes is a prime concern to maintain product integrity and consumer safety. Bioburden testing measures the amount of microbial contamination on a product or surface, thereby determining the sterilization process needed for effective decontamination. Accurate bioburden assessment is imperative as it forms the basis for sterilization validation and helps in analyzing the overall safety and acceptability of the end product.
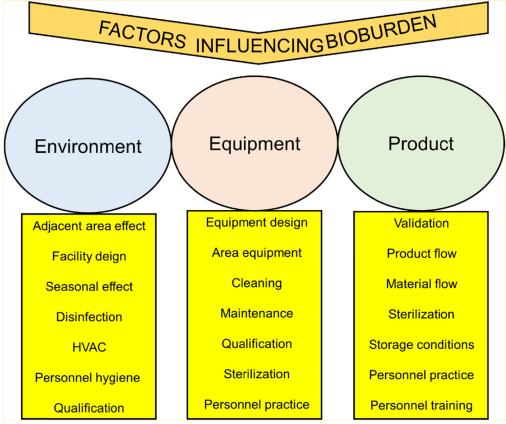 Fig 1. Factors affecting bioburden. (Moondra, S., et al.; 2018)
Fig 1. Factors affecting bioburden. (Moondra, S., et al.; 2018)
Bioburden Control Trial
The Bioburden Test is a meticulous methodology established specifically to enumerate the quantity of microorganisms, represented as colony-forming units (CFU) in materials or products that are initially non-sterile. This comprehensive testing is initiated utilizing a wide range of culture mediums that foster the robust growth of bacteria and fungi.
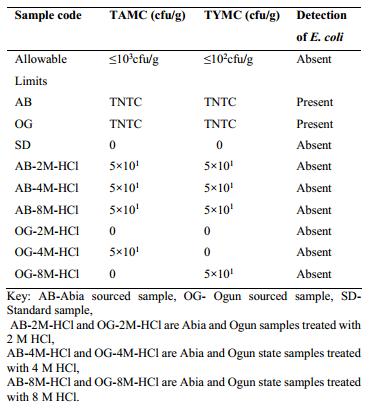 Fig 2. TAMC, TYMC and Test for specific micro-organism. (Adebowale O. A., et al.; 2018)
Fig 2. TAMC, TYMC and Test for specific micro-organism. (Adebowale O. A., et al.; 2018)
The test can be implemented by either one or both of the compendial procedures - Total Aerobic Microbial Count (TAMC) or Total Yeast and Mold Count (TYMC), or alternatively, utilized a different method altogether.
TAMC is an empirical approximation of the viable aerobic mesophilic microorganisms achievable from a universally-adopted medium. The Pharmacopoeia advocates the implementation of a soy casein digest medium for TAMC. TYMC targets the viable aerobic mesophilic fungi - inclusive of yeast-like, filamentous, and dimorphic fungi. When conducting a TYMC test, a fungal medium such as a Saboraud Dextrose Agar, is used to condone a comprehensive fungal growth.
Steps in Estimating Bioburden
The quantification of the bioburden associated with a medical apparatus is essentially a sequential progression of four separate procedures:
Step 1: A representative specimen of the object intended for examination is meticulously fabricated, with careful consideration given to its unique physical traits.
Step 2: An isolation phase is conducted, typically utilizing methods of membrane filtration, to extricate microorganisms from this sample, followed by their cultivation.
Step 3: The following step involves the enumeration of the gathered specimen, which encapsulates the retrieved microorganisms.
Step 4: There is an in-depth characterization of the microbial load present. The findings from these procedures are thoroughly documented, and a comprehensive report is compiled detailing each step of the test results.
Nonsterile Products and Microbial Limits Testing
In the realm of microbiological control, the guidelines for non-sterile products typically prescribe the employment of two major methodologies: the membrane filtration method or the plate count method. Utilizing the most probable number method is generally an exception, and is only enlisted when the execution of microbial counts via the two primary methodologies is impeded, often due to the fat content inherent in the product or the suspected abundance of organic matter.
Membrane filtration
The optimal methodology for analyzing samples containing antimicrobial agents involves the utilization of a membrane filtration approach with a pore size of 0.45 μm or smaller. The function of the membrane is critical as it acts as a barricade, collecting microbes that exceed the membrane's pore size.
Direct plating methods
Bioburden testing involves the use of direct plating methods that include the pour plate technique and the spread plate technique. The pour plate method is generally favored due to its superior theoretical precision.
Most probable number method
The Most Probable Number (MPN) methodology is a quantitative technique utilized by experts in the biological sciences to ascertain an estimation of bacterial concentration within a given sample. This approach necessitates subdividing the initial sample or solution by orders of magnitude (often utilizing factors such as 10× or 2×) within a broth culture. Subsequent to this, the presence or absence of microorganisms is then gauged across these subdivisions.
Our Advantages
Our Commitment and Future Goals
As an established player in life scientific research, Creative Proteomics provides an exhaustive and dependable bioburden examination service to support multiple sectors in upholding the security and quality of their items. Through the implementation of advanced methodologies and strict observance of regulatory guidelines, we effectively pinpoint and measure diverse types of microorganisms—thus aiding our clients in meeting industry regulations and ultimately securing public health. Do not hesitate to reach out to us for further information.
References
- Moondra, S., et al.; Sterilization of Pharmaceuticals. Dosage Form Design Parameters. 2018, 467–519.
- Adebowale O. A., et al.; Processing and Evaluation of Locally Sourced Kaolin for Pharmaceutical Production. Tropical Journal of Natural Product Research. 2018, 2(8):388-395.
Related Sections
Services
Applications
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.

 Fig 1. Factors affecting bioburden. (Moondra, S., et al.; 2018)
Fig 1. Factors affecting bioburden. (Moondra, S., et al.; 2018) Fig 2. TAMC, TYMC and Test for specific micro-organism. (Adebowale O. A., et al.; 2018)
Fig 2. TAMC, TYMC and Test for specific micro-organism. (Adebowale O. A., et al.; 2018)
