As a distinguished enterprise operating at the pinnacle of proteomics and other related scientific research fields, Creative Proteomics bring forth a state-of-the-art, comprehensive service to evaluate process-related impurities and residual constituents. The significance of these services lies in their concrete contributions to both comprehensive understanding and stringent control of manufacturing operations, predominantly within the realms of pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors.
Process Related Impurities and Residual
Process related impurities and residual, commonly referred to as impurities and residuals, represent inadvertent substances birthed or utilized within the confines of product fabrication. Such may encompass initial precursors, intermediary substances, degradation byproducts, reactants, and catalytic substances within fields relating predominantly to the manufacture of chemical or pharmaceutical products. Despite refinement processes, these impurities and residuals may persist within the final output.
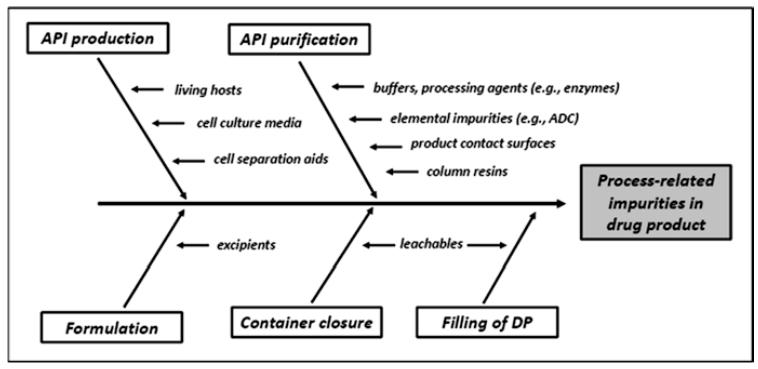 Fig 1. Sources contributing to biopharmaceutical process-related impurities. (Geigert, J.; 2019)
Fig 1. Sources contributing to biopharmaceutical process-related impurities. (Geigert, J.; 2019)
Their presence can critically impact key parameters including the safety, efficacy, and quality of the end product. Within the pharmaceutical realm, these impurities could potentially stimulate adverse drug responses or attenuate the therapeutic potency of medicaments. It's critical to understand and minimize these impurities to ensure the overall safety and effectiveness of the product.
Sources of Process-Related Impurities in Biopharmaceuticals
1. Impurities from API Production
Biopharmaceuticals are prone to process-related impurities, predominantly originating from the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) manufacturing procedures. It's vital to critically examine any upstream impurities that could potentially arise from cell culture media, living hosts, or cell separation aids.
2. Impurities from API Purification
We consider unique challenges in creating custom API purification methods. Various chromatographic techniques are used to purify culture media and biological elements in standard cell culture proceedings. For recombinant proteins from transgenic organisms, we meticulously remove milk-linked immunogenic proteins.
3. Impurities from Formulations
We carefully consider each unique biosystem production process when devising API purification techniques. We use a variety of chromatographic strategies to purify biopharmaceutical culture media and biosystem components. The purification process for recombinant proteins from transgenic animals is designed to remove immunogenic milk-associated proteins.
4. Impurities from Filling of the Drug Product
The integrity of a biopharmaceutical product can potentially be influenced by the nature of the container closure system employed, in terms of its process-related impurities. It is therefore incumbent upon researchers to undertake a comprehensive evaluation of potential contaminants that could arise from leachable at the product contact surfaces, or as a result of interactions between the formulated biopharmaceutical entity and the container closure mechanism.
Process Related Impurities and Residual Analysis Methodology
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
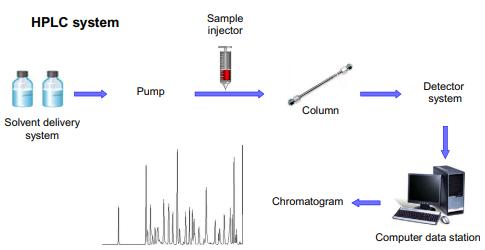 Fig 2. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) instrument. (Lozano-Sánchez, J., et al.; 2018)
Fig 2. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) instrument. (Lozano-Sánchez, J., et al.; 2018)
HPLC's reliable precision makes it crucial in pharmaceutical labs, not just for identifying impurities but also for separating and measuring individual chemical elements within mixtures, thereby enhancing quality control and understanding of complex chemical reactions.
- Capillary Electrophoresis (CE)
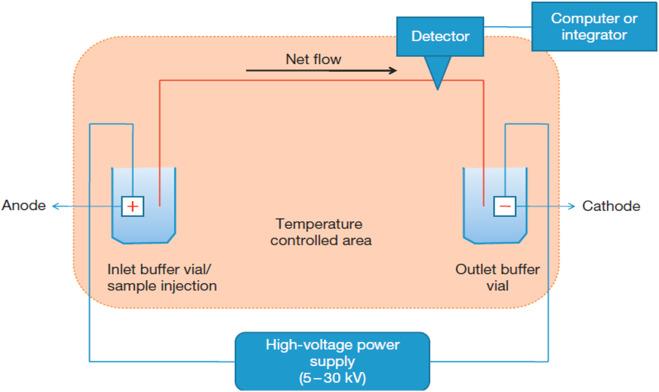 Fig 3. Basic capillary electrophoresis instrumentation. (Mostafa A. A., et al.; 2023)
Fig 3. Basic capillary electrophoresis instrumentation. (Mostafa A. A., et al.; 2023)
Capillary Electrophoresis (CE) uses ionic species' properties to separate constituents in a sample, generates charge particles with an electric field, and analyzes migration patterns to provide insights into their molecular weights and sizes.
- Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
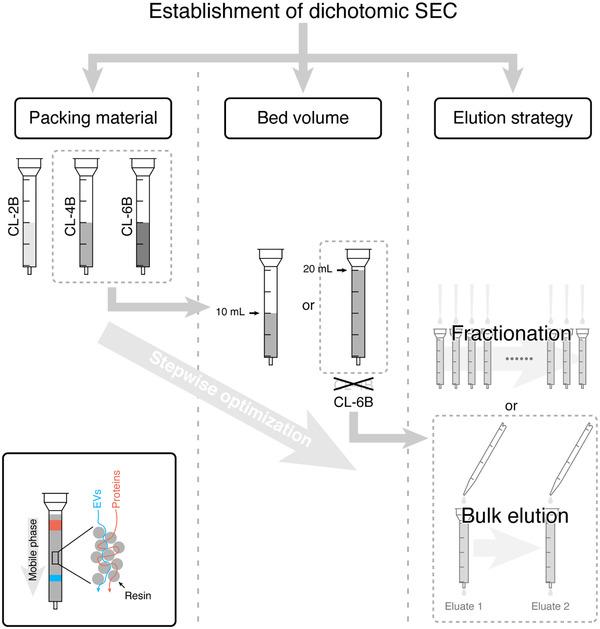 Fig 4. Basic capillary electrophoresis instrumentation. (Guo, J., et al.; 2021)
Fig 4. Basic capillary electrophoresis instrumentation. (Guo, J., et al.; 2021)
Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) is a scientific technique often used in biological and polymer studies. It's known for its ability to assess molecular weight and composition in polymer solutions, making it valuable in molecular biology. This method's effectiveness lies in its principle that particles filter through porous materials at different rates based on their sizes and shapes.
Service Process
Our Goals
Creative Proteomics offers impurity profiling and residual analysis services to ensure quality and safety in manufactured goods. We aim to enhance the efficiency of operational processes. Our service identifies potential hazards, providing detailed analysis to help clients make informed decisions and adjustments. We welcome inquiries about our service.
References
- Geigert, J. Complex Process-Related Impurity Profiles. The Challenge of CMC Regulatory Compliance for Biopharmaceuticals. 2019, 231–260.
- Lozano-Sánchez, J., et al.; Chromatographic Technique: High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Modern Techniques for Food Authentication. 2018, 459–526.
- Mostafa A. A., et al.; Capillary Electrophoresis. Encyclopedia of Forensic Sciences, Third Edition. 2023.
- Guo, J., et al.; Establishment of a simplified dichotomic size‐exclusion chromatography for isolating extracellular vesicles toward clinical applications. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 2021, 10(11).
Related Sections
Services
Applications
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.

 Fig 1. Sources contributing to biopharmaceutical process-related impurities. (Geigert, J.; 2019)
Fig 1. Sources contributing to biopharmaceutical process-related impurities. (Geigert, J.; 2019) Fig 2. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) instrument. (Lozano-Sánchez, J., et al.; 2018)
Fig 2. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) instrument. (Lozano-Sánchez, J., et al.; 2018) Fig 3. Basic capillary electrophoresis instrumentation. (Mostafa A. A., et al.; 2023)
Fig 3. Basic capillary electrophoresis instrumentation. (Mostafa A. A., et al.; 2023) Fig 4. Basic capillary electrophoresis instrumentation. (Guo, J., et al.; 2021)
Fig 4. Basic capillary electrophoresis instrumentation. (Guo, J., et al.; 2021)
