To help customers more accurately quantify proteins by understanding the absorbance of protein solutions at particular wavelengths, Creative Proteomics provides protein extinction coefficient determination service as required by the ICH Q6B guidelines.
Overview
The extinction coefficient of a protein, alternatively referred to as molar absorptivity or absorption coefficient, is a measure tabulating the strength of absorption of light at a defined wavelength by that protein. This property is intrinsic to each protein, rendering it unique for every protein molecule. This coefficient plays a fundamental role in quantifying protein concentrations in a solution through the measurement of light absorption at a predefined wavelength, which is then interpreted using the Beer-Lambert's law.
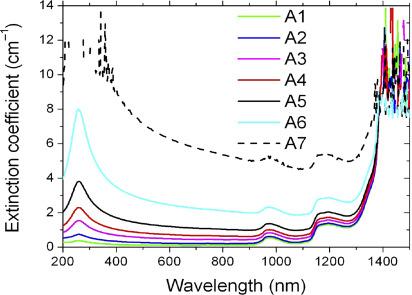 Fig 1. Spectral extinction coefficient for the various samples. (Sani, E., et al.; 2010)
Fig 1. Spectral extinction coefficient for the various samples. (Sani, E., et al.; 2010)
How to find Molar Extinction Coefficient?
For the determination of the molar absorption coefficient of a substance, it generally involves the quantification of the substance's absorbance at a predetermined wavelength. The concentration of the substance needs to be known beforehand:
E = A / (c * l)
Where: E = molar extinction coefficient (in L·mol−1·cm−1) A = measured absorbance c = concentration of the compound (in mol·L−1) l = path length of the cuvette (in cm)
By rearranging the equation, you can solve for E:
E = A / (c * l)
The molar extinction coefficient is specific for each compound and depends on factors such as the structure, molecular weight, and the wavelength of light used for measurement.
Note that the molar extinction coefficient can also be reported in units of cm-1·M-1, where the concentration is in Molar (M), and the path length is in centimeters (cm).
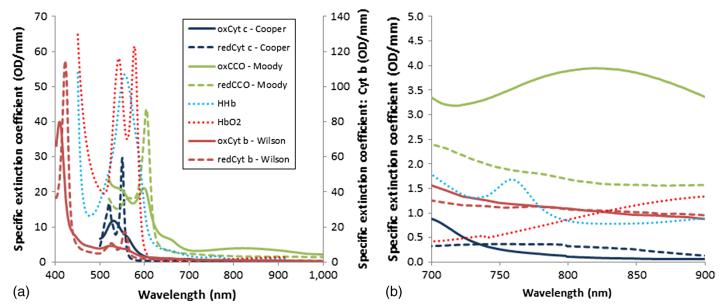 Fig 2. The extinction spectra of the absorbing cytochromes in the electron transport chain in the visible and NIR. (Bale, G., et al.; 2016)
Fig 2. The extinction spectra of the absorbing cytochromes in the electron transport chain in the visible and NIR. (Bale, G., et al.; 2016)
Importance of Molar Extinction Coefficient
- The molar extinction coefficient, a property that is intrinsic to a chemical substance, governs the extent to which a given compound absorbs light at a specific wavelength.
- This property is contingent on the distinct composition and structure of the chemical, but remains independent of concentration. Through absorbance measurement, we are able to swiftly ascertain the concentration of a particular chemical.
- The concentration of a chemical can be quickly determined by measuring absorbance, but the specific chemical species in solution must be known.
- Certain techniques of concentration measurement, such as titration, necessitate longer duration and greater quantities of chemicals compared to other methods.
- The International System of Units prescribes that the molar extinction coefficient is expressed in square meters per mole (m2/mol), although in practice, the unit used more commonly is inverse molarity-centimeter (M-1cm-1).
- Utilizing the molar extinction coefficient, it is possible to deduce a solution's molar concentration from the absorbance measured.
Application of Molar Extinction Coefficient

Protein Concentration Determination: Leveraging the Beer-Lambert's law, the molar extinction coefficient plays a crucial role in identifying the concentration levels of proteins present in a solution, this is achieved through their absorbance correlation. By gauging a protein sample's absorbance at a distinct wavelength and cognizant of the molar extinction coefficient, the determination of protein content is feasible.
Kinetic Studies: The molar extinction coefficient is instrumental in observing enzyme-driven processes or potential protein-protein interactions - this is accomplished by monitoring fluctuations in absorbance periodically. This practice enables the estimation of binding constants, enzymatic kinetics, and reaction rates.
Protein Purity Determination: The computation of the molar extinction coefficient aids in verifying the purity of protein samples. Identification of any absorbing species contaminants is possible by contrasting the absorbance of the protein solution at a range of wavelengths against the anticipated values derived from the molar extinction coefficient.
Why Us?
- Quick and economical workflow
- Complete solution for extinction coefficient determination
- Takes a variety of sample types
- High-quality data and prompt turnaround
Service Process
Want to Learn More?
Creative Proteomics offers reliable assistance for biomedical research and drug development, as well as efficient, accurate, and professional protein characterization services in strict accordance with ICH Q6B guidelines. This is done to help our customers better understand the structure, composition, and function of proteins. Please feel free to get in touch with us if you have any specific requests for our extinction coefficient determination service.
References
- Sani, E., et al.; Carbon nanohorns-based nanofluids as direct sunlight absorbers. Optics Express. 2010, 18(5), 5179.
- Bale, G., et al.; From Jöbsis to the present day: a review of clinical near-infrared spectroscopy measurements of cerebral cytochrome-c-oxidase. Journal of Biomedical Optics. 2016, 21(9), 091307.
Related Sections
Services
Applications
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.

 Fig 1. Spectral extinction coefficient for the various samples. (Sani, E., et al.; 2010)
Fig 1. Spectral extinction coefficient for the various samples. (Sani, E., et al.; 2010) Fig 2. The extinction spectra of the absorbing cytochromes in the electron transport chain in the visible and NIR. (Bale, G., et al.; 2016)
Fig 2. The extinction spectra of the absorbing cytochromes in the electron transport chain in the visible and NIR. (Bale, G., et al.; 2016)



