Alkylation analysis of proteins allows for the identification of conformational changes and functional alterations in proteins, as well as the improvement of protein stability and the protection of organisms from the external environment. Protein alkylation analysis is important in protein research and can provide a powerful tool for the protection of organisms and the study of disease mechanisms. Creative Proteomics offers a comprehensive range of protein alkylation analysis services that meet the ICH Q6B guidelines.
Protein Alkylation
Protein alkylation constitutes a fundamental chemical modification procedure in which the covalent bonding of an alkyl group - predominantly methyl, ethyl, or propyl - transpires on designated amino acid residues within a protein. This alteration occurs with the assistance of alkylating agents such as iodoacetamide or N-ethylmaleimide, interacting with the sulfhydryl (SH) groups of cysteine residues within the protein
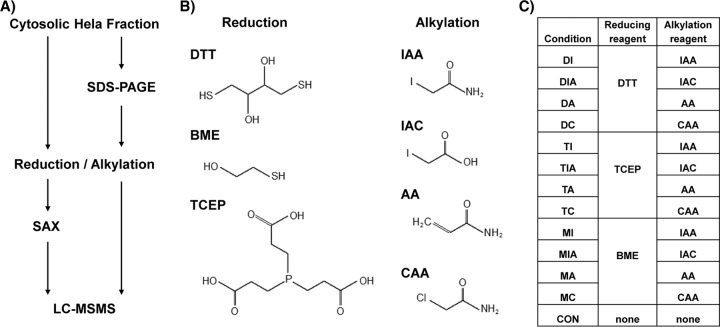 Fig 1. A, Experimental workflow for sample generation and analysis; B, reduction and alkylation reagents used; and C, combinations of reduction and alkylation reagents for generation of the different data sets. (Müller, T., & Winter, D.; 2017)
Fig 1. A, Experimental workflow for sample generation and analysis; B, reduction and alkylation reagents used; and C, combinations of reduction and alkylation reagents for generation of the different data sets. (Müller, T., & Winter, D.; 2017)
Evidence of protein alkylation's pervasive usage in protein chemistry and proteomic research reveals its role in probing the protein's structure, operations, and interactive disposition. Furthermore, it can be leveraged to adjust proteins for therapeutic objectives, encompassing enhancement of stability, activity modulations, or coupling conjugates for precision drug delivery.
Notably, alkylation of cysteine residues can alter their reactivity rates, hinder disulfide bonds, and impact the fold and stability of proteins. As such, protein alkylation frequently serves as part and parcel of denaturation and reduction regimens preceding the ensuing analysis or protein handling.
Experimental Procedures
How to Detect Protein Alkylation?

Mass spectrometry: Post-alkylation, proteolytic enzymes are used to break down the proteins into peptides for analysis via mass spectrometry. This sophisticated process delineates and locates alkylated residues in the protein sequence. By contrast analysis of the mass shifts associated with alkylated peptides, specific alkylation sites can be identified and, importantly, the extent of protein alkylation can be quantified.
Western blotting: The unique epitopes of alkylated proteins can be identified through the use of specific antibodies. The comparison of migration patterns between alkylated and non-alkylated proteins on a gel matrix post-SDS-PAGE based on molecular weight aids in detecting protein alkylation. Once separated on the gels, proteins are transferred to membranes to be analyzed with specialized antibodies.

Fluorescent labeling: Reaction of alkylated protein residues with specifically targeted fluorescent dyes leads to distinctive marking and illumination of alkylated proteins. The precise quantification of alkylated proteins is achievable with fluorometric assays, and identification is possible through fluorescence microscopy.
Biochemical assays: Precise identification of different protein alkylation can be achieved via specific biochemical tests, including specific methyltransferase assays or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) utilizing antibodies to detect protein methylation. These assays provide a valuable means of obtaining exact measurements of protein alkylation and provide a way to investigate the inhibition or activity of particular alkylating enzymes.
Our Advantages
- Ongoing and dedicated support from experienced scientists
- Availability of state-of-the-art sequencing platforms
- Extensive multiplexing flexibility
- Cost-effective service
Want to Learn More?
The protein alkylation service offered by Creative Proteomics offers our customers a cost-effective and practical option. Our protein alkylation services were developed to improve workflow by a team of experts with specialized training. Please get in touch with our technical support staff if you're interested in our services. We'd be pleased to collaborate with you on a unique project solution.
Reference
- Müller, T., & Winter, D. Systematic Evaluation of Protein Reduction and Alkylation Reveals Massive Unspecific Side Effects by Iodine-containing Reagents. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 2017, 16(7), 1173–1187.
Related Sections
Services
Applications
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.

 Fig 1. A, Experimental workflow for sample generation and analysis; B, reduction and alkylation reagents used; and C, combinations of reduction and alkylation reagents for generation of the different data sets. (Müller, T., & Winter, D.; 2017)
Fig 1. A, Experimental workflow for sample generation and analysis; B, reduction and alkylation reagents used; and C, combinations of reduction and alkylation reagents for generation of the different data sets. (Müller, T., & Winter, D.; 2017)




