Creative Proteomics provides protein acetylation analysis services to understand the acetylation modifications of proteins, helping customers gain insights into physiological and pathological processes in organisms while meeting ICH Topic Q6B: Test Procedures and Acceptance Criteria for Biotechnological/Biological Products.
Overview
A post-translational modification (PTM) known as protein acetylation occurs when an acetyltransferase is present and an acetyl group is covalently attached to the -amino group of a lysine residue in a protein. Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs), which add or remove acetyl groups, respectively, control this change.
Protein acetylation is reversible, allowing it to be dynamically added or withdrawn in response to cellular signals and circumstances. Numerous biological factors, including food availability, stress reactions, and cell signaling pathways, control acetylation.
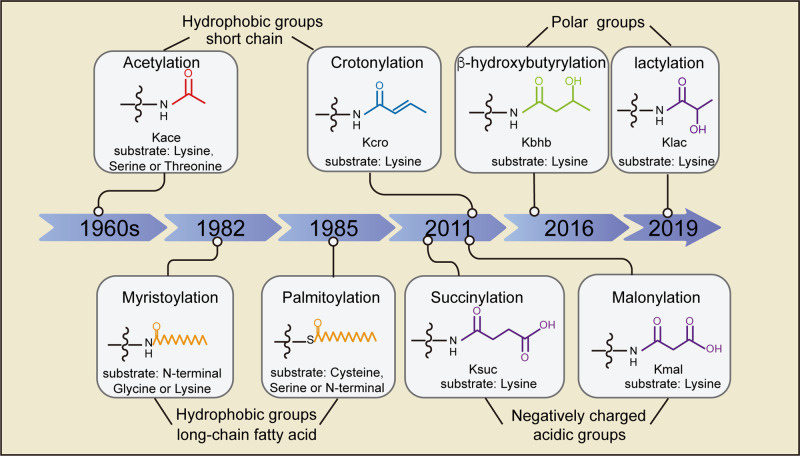 Fig 1. Timeline of the historical milestone for the discovery of protein acylation, and the chemical structures of acyl groups. (Shuang, S., et al.; 2022)
Fig 1. Timeline of the historical milestone for the discovery of protein acylation, and the chemical structures of acyl groups. (Shuang, S., et al.; 2022)
How to Detect Protein Acetylation?
- By subjecting a protein mixture to electrophoresis and transferring it onto a PVDF membrane, this method allows for the specific detection of acetylated proteins using antibodies that recognize acetylated lysine residues.
- Mass spectrometry measures the mass-to-charge ratios of acetylated proteins, enabling the determination of acetylation modifications and the identification of specific acetylation sites. This technique offers a deeper understanding of the diverse functionality of acetylated proteins.
- By utilizing specific antibodies that recognize acetylated residues, acetylated proteins can be selectively precipitated from a solution. Further analysis through techniques like immunoblotting or mass spectrometry allows a comprehensive characterization of the acetylated proteins, unraveling their involvement in various biological processes.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and enzyme immunoassays (EIA) are widely used antibody-based assays for detecting and quantifying acetylated proteins. Specific antibodies that recognize acetylated lysine residues allow for the efficient detection of these modified proteins.
- Fluorescent assays, such as immunofluorescence or fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), offer an opportunity to visualize acetylated proteins within cells and tissues. Antibodies or probes to fluorophores that specifically bind to acetylated proteins can be utilized, allowing for the localization and spatial understanding of acetylated protein distribution.
Application of Protein Acetylation
Epigenetics
Protein acetylation, particularly the acetylation of histone proteins, serves as a crucial player in epigenetic regulation. Histones are responsible for packaging DNA into a condensed structure called chromatin. The acetylation of histones can modulate the accessibility of DNA to transcription factors and other regulatory proteins, thereby influencing gene expression patterns.

Gene Regulation
Transcription factors, key players in controlling gene expression, can undergo acetylation, affecting their ability to bind DNA and regulate transcription. The tumor suppressor protein p53, for example, enhances its transcriptional activity upon acetylation, leading to increased expression of genes involved in cell cycle arrest and DNA repair.
Protein Function and Stability
Acetylation of lysine residues in enzymes can modify their enzymatic activity, protein-protein interactions, and subcellular localization. Additionally, acetylation protects certain proteins from being degraded by proteasomes, thereby increasing their stability and abundance within the cell.

Cellular Signaling Pathways
Protein acetylation has emerged as a crucial player in these signaling cascades. By modulating the activity of signaling molecules, acetylation can influence downstream cellular responses. For instance, acetylation of proteins involved in the insulin signaling pathway impacts insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, shedding light on the connection between protein acetylation and metabolic diseases.
Disease Mechanisms and Therapeutics
The dysregulation of protein acetylation has been implicated in the development and progression of various diseases, offering potential therapeutic targets. Enzymes involved in acetylation, such as histone deacetylases (HDACs), have emerged as promising candidates for drug development, exhibiting the potential to restore normal acetylation patterns and mitigate disease-associated dysfunctions.
Service Workflow
Want to Learn More?
Creative Proteomics is your trustworthy ally if you're looking for unmatched knowledge in protein drug characterisation. Our sector-leading offerings and breadth of knowledge can speed up your medication development process and guarantee the success of your protein drug. To find out more about our offerings and how we can help you make the most of your protein medications, get in touch with us. Let's work together to open the door to creative and potent therapeutic approaches.
Reference
- Shuang, S., et al.; Protein acylation: mechanisms, biological functions and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. 2022; 7: 396.
Related Sections
Services
Applications
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.

 Fig 1. Timeline of the historical milestone for the discovery of protein acylation, and the chemical structures of acyl groups. (Shuang, S., et al.; 2022)
Fig 1. Timeline of the historical milestone for the discovery of protein acylation, and the chemical structures of acyl groups. (Shuang, S., et al.; 2022)