ICH Q6B states "Such monographs, applicable to biotechnological and biological products, generally include, but are not limited to tests for sterility, endotoxins, microbial limits, volume in container, uniformity of dosage units and particulate matter." Creative Proteomics is a distinguished company offering a broad spectrum of research services, with a special focus on sterility testing services.
Background
The notion of sterility, as it pertains to biological systems, is unequivocal: an entity is either sterile or not. However, the sterility criteria for pharmaceuticals deviate from this hard biological definition, pivoting away from a requirement for 'complete absence of viable life'. Instead, the sterility testing protocol for these products centers around the detection of specific fungal and bacterial strains, those that possess the ability to proliferate under the distinctive culture conditions of the test.
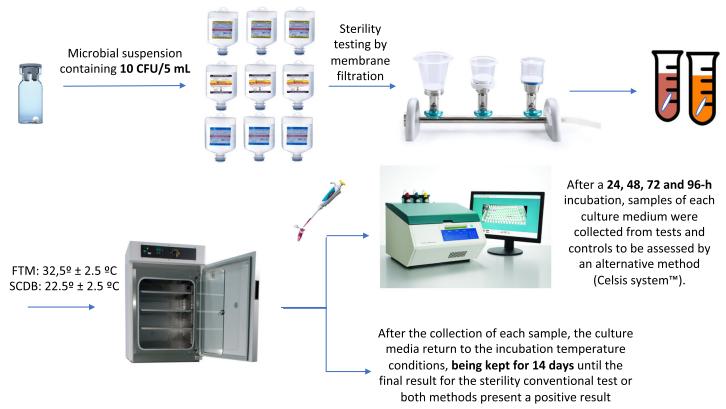 Fig 1. Graphical representation of the first experiment. (Bugno, A., et al.; 2018)
Fig 1. Graphical representation of the first experiment. (Bugno, A., et al.; 2018)
While there is currently a contingent of specialists who are skeptical about the necessity of sterility testing for batches that have been exposed to validated levels of heat or irradiation sterilization, a strong consensus still exists endorsing the need for rigorous testing and release of batches processed aseptically, as well as those sterilized using gas - particularly due to the challenging nature of controlling this process.
Sterility Test Methods
In the realm of pharmacopoeias, sterility testing fundamentally operates on two main methodologies:
a) Membrane filtration
 Fig 2. Dr. Tim Sandle inspecting a membrane filtration test chamber. (Tim S.; 2014)
Fig 2. Dr. Tim Sandle inspecting a membrane filtration test chamber. (Tim S.; 2014)
The sterility testing membrane filtration technique can provide enhanced sensitivity compared to alternative methods. This is because it allows the entirety of a sample, or a composite subset, to be examined via a solitary filter. Additionally, filtration offers the opportunity to eliminate certain components of the sample that could instigate turbidity or obstruct growth, such as antibiotics or preservatives. This makes it a reliable method for detecting contaminants and ensuring the purity of pharmaceutical products.
b) Direct inoculation
In the process of direct inoculation, the extraction of a minuscule quantity of the sample is executed aseptically from the sample module and instantaneously inoculated into an appropriate quantity of culture medium prior to incubation. The application of this method confines the inoculation to minor volumes of the product into the culture medium, thereby restricting testing sensitivity.
Test environment
The sterility examination necessitates execution in a contamination-free environment to prevent the risk of false positive outcomes. Ideal conditions for such tests may entail a unidirectional airflow apparatus located within a cleanroom setting, or an isolator. It is imperative to consistently monitor the environment during every testing session to ensure that the conditions remain precisely controlled and regulated.
Sterility Testing Workflow

Alternative and Rapid Methods
ATP-bioluminescence
The most widely accepted accelerated methodology that uses enzymes to degrade microbial ATP in proliferating cells and produce measurable luminescence is ATPlite bioluminescence detection. This technique is acknowledged for its sensitivity and ability to avail results equivalent to that of the conventional monograph procedure within a shorter time frame of fewer than 7 days.
Colorimetric growth detection
The given methodology utilizes highly sensitive chromogenic systems capable of detecting carbon dioxide produced by proliferating microbial cells. According to various reports, this procedure can yield results within a span of three days.
Cytometry systems
Cytometric quantification employs fluorescence-based cellular tagging approaches rather than relying upon cellular growth. The typical process involves labeling microbial cells with a fluorescent dye or a non-fluorescent substrate, which is subsequently converted into a flourochrome in viable cells. Detection ensues via laser scanning, which may occur within a flow cell or on a solid phase like a membrane filter.
Service Process
Our Goals
Creative Proteomics, a global leader in the biotech industry, proudly offers a specialized sterility testing service. This essential service works to confirm the absence of harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses in a wide range of items including biological substances, drugs, and medical devices. Please feel free to contact us.
References
- Bugno, A., et al.; Evaluation of an Amplified ATP Bioluminescence Method for Rapid Sterility Testing of Large Volume Parenteral. Journal of Pharmaceutical Innovation. 2018.
- Tim S. The Test for Sterility of Medicinal Products. International Journal of Microbiology and Allied Sciences. 2014.
Related Sections
Services
Applications
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.

 Fig 1. Graphical representation of the first experiment. (Bugno, A., et al.; 2018)
Fig 1. Graphical representation of the first experiment. (Bugno, A., et al.; 2018) Fig 2. Dr. Tim Sandle inspecting a membrane filtration test chamber. (Tim S.; 2014)
Fig 2. Dr. Tim Sandle inspecting a membrane filtration test chamber. (Tim S.; 2014)

