Creative Proteomics provides protein truncation analysis services to detect and characterize protein truncations due to mutations or other causes, in order to further study the function and disease relationships of the proteins involved. In addition, protein truncation analysis can help customers discover novel protein degradation chaperone proteins or enzymes, as well as develop novel drugs to regulate the protein degradation process for the treatment of related diseases.
Why do Protein Truncation Analysis?
The in vitro protein synthesis (IVPS) assay, also known as the protein truncation test (PTT), was initially developed as a technique to identify mutations that result in premature translation termination in the dystrophin gene. The coding region of a gene is examined for the existence of mutations that result in premature translation termination, or that result in shortened proteins, using in vitro transcription/translation from amplified RNA.
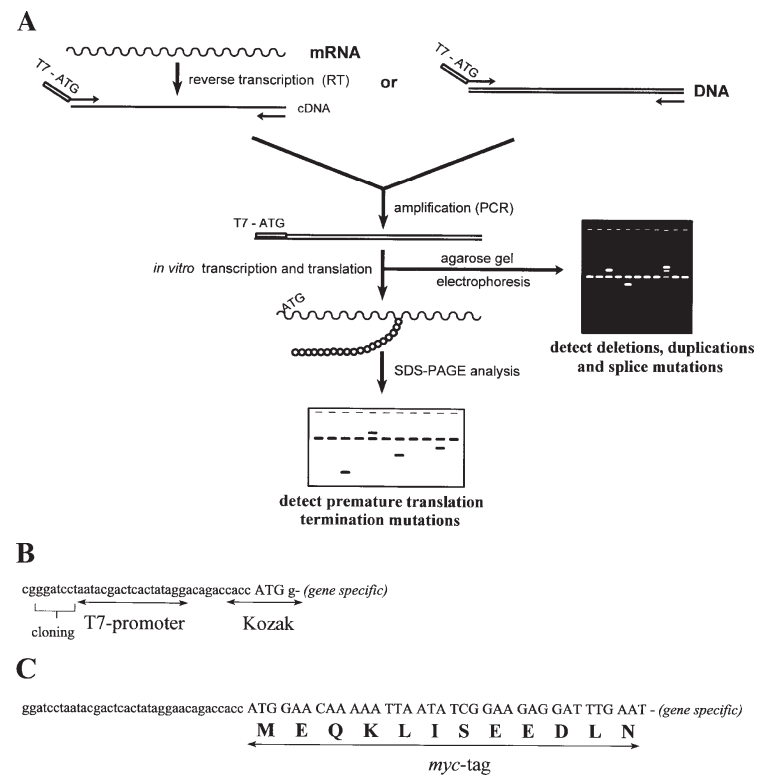 Fig 1. The protein truncation test (PTT). (Den Dunnen, J. T., & Van Ommen, G.-J. B.; 1999)
Fig 1. The protein truncation test (PTT). (Den Dunnen, J. T., & Van Ommen, G.-J. B.; 1999)
There are identified three crucial steps:
- Reverse transcription (RT) is used to copy the target's coding sequences from a patient's RNA sample, and then a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used to amplify the result.
- Creating RNA and then protein in vitro using the amplification products as a template.
- Conducting an analysis of the synthetic protein, such as utilizing SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis).
Shorter proteins, which may be easily distinguished from completely translated run-off products, are products resulting from truncating modifications, i.e., the mutant alleles, with their size pointing to the site of the mutation.
Protein Truncation Test in Practice
PTT is most frequently used to identify tumor suppressor gene mutations that lead to a variety of cancers, including colon cancer (FAP, HNPCC), breast cancer (BRCA1 and BRCA2), tuberous sclerosis (TSC1 and TSC2), and neurofibromatosis (NF1 and NF2) (Table 1 and the references therein). PTT is a particularly sensitive and effective approach for mutation identification because the majority, and in some cases all, reported mutations in these genes result in premature translation termination and are easily detectable by PTT. PTT is also very effective at scanning (or pre-scanning) disease genes for conditions like ataxia telangiectasia (ATM), Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy, Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, and polycystic kidney disease type 2 (PKD), in which a sizable portion of the mutations are caused by truncating mutations.
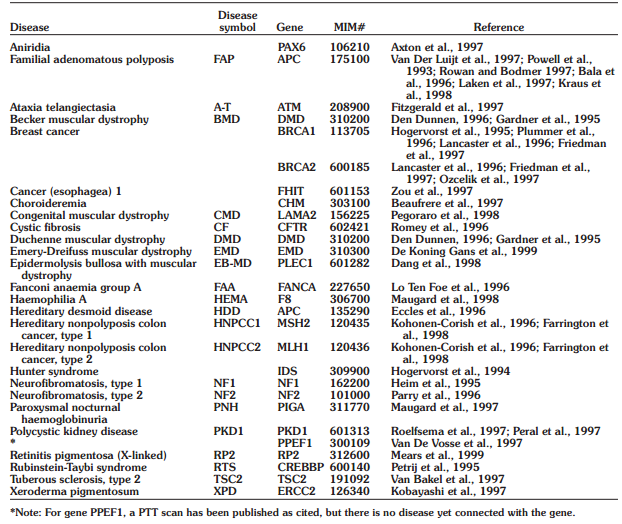 Fig 2. Genes for Which PTT Scans Have Been Published. (Den Dunnen, J. T., & Van Ommen, G.-J. B.; 1999)
Fig 2. Genes for Which PTT Scans Have Been Published. (Den Dunnen, J. T., & Van Ommen, G.-J. B.; 1999)
Our Service

SDS-PAGE: Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is a commonly used technique to separate proteins based on their molecular weight. By comparing the migration of the truncated protein with the full-length protein on the gel, one can determine if truncation has occurred.

Western blotting: This technique involves transferring the separated proteins from an SDS-PAGE gel onto a membrane and then detecting the protein of interest using specific antibodies. By comparing the sizes of the truncated and full-length proteins detected on the blot, truncation can be identified.

Mass spectrometry: This technique can be used to identify and characterize protein truncations by analyzing the mass-to-charge ratio of protein fragments generated through enzymatic digestion. Truncated proteins may produce distinct fragmentation patterns compared to full-length proteins.

Immunoprecipitation: This technique involves using antibodies to specifically isolate the protein of interest from a mixture. By comparing the size of the truncated protein with the full-length protein in the immunoprecipitated fraction, truncation can be determined.
Service Workflow
Our Goals
The mission of Creative Proteomics, a rapidly expanding, preeminent global provider of scientific research services and solutions, is to assist our clients in meeting the escalating and constantly shifting demands for protein drug characterization. We provide a wide range of services for protein drug characterisation. If you are interested in our offerings or have any other questions, don't hesitate to get in touch with us. We look forward to working with you.
Reference
- Den Dunnen, J. T., & Van Ommen, G.-J. B. The protein truncation test: A review. Human Mutation. 1999, 14(2), 95–102.
Related Sections
Services
Applications
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.

 Fig 1. The protein truncation test (PTT). (Den Dunnen, J. T., & Van Ommen, G.-J. B.; 1999)
Fig 1. The protein truncation test (PTT). (Den Dunnen, J. T., & Van Ommen, G.-J. B.; 1999) Fig 2. Genes for Which PTT Scans Have Been Published. (Den Dunnen, J. T., & Van Ommen, G.-J. B.; 1999)
Fig 2. Genes for Which PTT Scans Have Been Published. (Den Dunnen, J. T., & Van Ommen, G.-J. B.; 1999)








