In order to meet the requirements of the ICH Q6B guidelines for the identification of modifications in biological products, Creative Proteomics provides protein methylation analysis services to help our global customers gain a deeper understanding of the physiological state of organisms and biological processes, which is of great importance for the study of epigenetics, biosignaling, physiology and other fields.
Why do Protein Methylation?
Protein methylation is a post-translational modification process that involves the addition of a methyl group (-CH3) to specific amino acid residues of proteins. Methylation can occur on amino acids such as lysine, arginine, and histidine.
Enzymes called protein methyltransferases catalyze the transfer of the methyl group from a methyl donor molecule, typically S-adenosyl methionine (SAM), to the target amino acid residue on the protein. Different protein methyltransferases have substrate specificity for specific amino acids and can add one or multiple methyl groups.
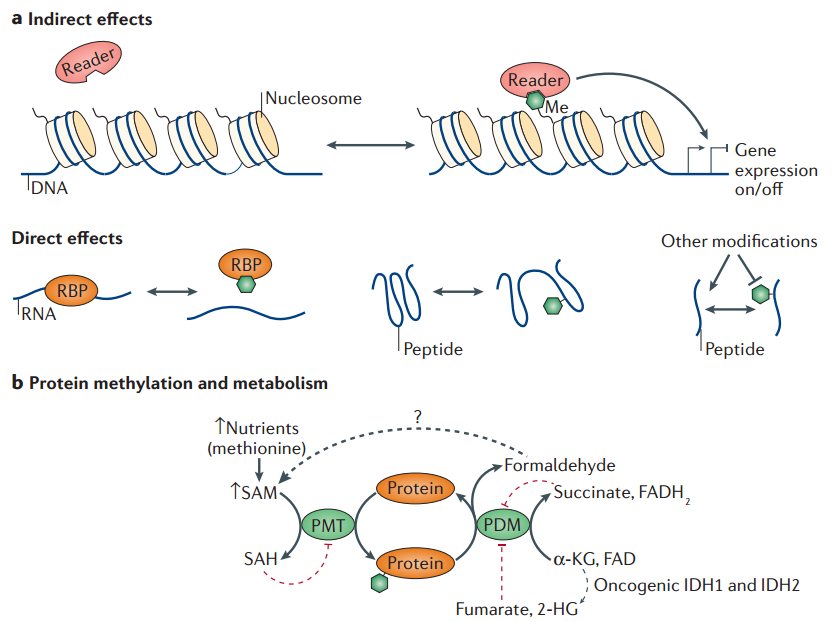 Fig 1. Interfaces between protein methylation and biological processes. (Murn, J., & Shi, Y.; 2017)
Fig 1. Interfaces between protein methylation and biological processes. (Murn, J., & Shi, Y.; 2017)
Protein methylation can have diverse functional outcomes, depending on the specific protein, amino acid residue, and the number of methyl groups added. It can affect protein-protein interactions by altering the charge or shape of the modified residue, leading to changes in protein conformation and function. Methylation can also serve as a binding site for specific effector molecules or promote the recruitment of other proteins.
Protein methylation is a dynamic and reversible process similar to other post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation and acetylation. It is tightly regulated by a balance between methylation and demethylation activities performed by protein methyltransferases and demethylases, respectively.
Protein Methylation Future Prospects
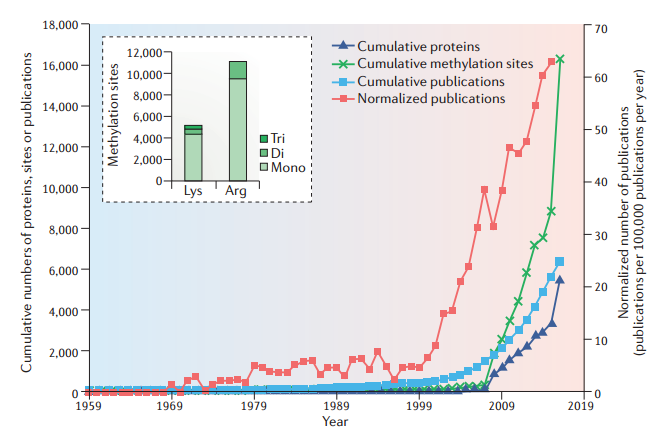 Fig 2. Protein methylation in numbers. (Murn, J., & Shi, Y.; 2017)
Fig 2. Protein methylation in numbers. (Murn, J., & Shi, Y.; 2017)
Determining the proteome-wide substrate specificity of specific PMTs and PDMs is a crucial task for the future. Although a rising number of papers (including a recent proteome-wide analysis on PMT-specific enzymes) reveal that a significant number of non-histone substrates also exist, the majority of these enzymes are primarily known for their histone methylation activity. If PMT and PDM are to be employed as therapeutic targets for the treatment of people, it will be crucial to identify the full targeting complex of each enzyme.
Characterizing Protein Methylation Analysis
- Using techniques such as immunoblotting (Western blotting) and immunoprecipitation, specific antibodies recognize methylated protein epitopes, thus providing valuable information about the extent and localization of protein methylation.
- Mass spectrometry can accurately determine the methylation status of individual amino acid residues in proteins. By observing specific mass shifts associated with methylated amino acids, researchers can identify and quantify protein methylation at the level of specific residues and understand the pattern of methylation within a protein.
- The use of chemical markers represents a paramount strategy in our understanding of protein methylation. By exclusively tagging or concentrating methylated proteins or corresponding peptides from complex protein aggregations, we are able to shed light on the varying methylation statuses of proteins.
- Fluorophores, diminutive molecular agents, exhibit the phenomenon of fluorescence upon binding to methylated proteins or affiliated amino acids. This distinct capability enables the deployment of practices such as imaging science, microscopy and flow cytometry. These methodologies facilitate the detection of protein methylation occurrences within actively functioning cells or fixated tissue samples.
Fluorescence-based methods
- The creation of enzyme-oriented assays presents a reliable course in monitoring protein methylation. These assays provide a meticulous observation of the migration of methyl groups towards proteins, further offering a comprehensive understanding of the enzymatic operations and regulatory aspects of protein methylation.
Service Process
Why Us?
Creative Proteomics offers clients cutting-edge, effective, personalized, and high-quality protein methylation analysis services. We pledge to provide timely and high-quality results and goods. We are devoted to supporting researchers all across the world. Please get in touch with us if you'd like additional information.
Reference
- Murn, J., & Shi, Y. The winding path of protein methylation research: milestones and new frontiers. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2017, 18(8), 517–527.
Related Sections
Services
Applications
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.

 Fig 1. Interfaces between protein methylation and biological processes. (Murn, J., & Shi, Y.; 2017)
Fig 1. Interfaces between protein methylation and biological processes. (Murn, J., & Shi, Y.; 2017) Fig 2. Protein methylation in numbers. (Murn, J., & Shi, Y.; 2017)
Fig 2. Protein methylation in numbers. (Murn, J., & Shi, Y.; 2017)