Regulations like ICH Q6B demand the analysis of charged variations in biotherapeutic proteins as a regulatory obligation.The motivated and knowledgeable scientific team at Creative Proteomics is committed to offering protein charge variant analysis services to aid in the thorough understanding of protein medication characterisation.
Charge Variant
Protein charge variants are distinct versions of a protein with variable charge characteristics. Post-translational modifications (PTMs) or genetic variation can cause these variances.
- PTMs: Phosphorylation, glycosylation, acetylation, and methylation are examples of post-translational modifications that can put different charged groups onto the protein molecule and hence affect its total charge. These changes can occur after the protein has been produced and impact its biological activity, stability, or function.
- Genetic Variation: Charge variances can also be caused by genetic variation or mutations in the protein-coding gene. These alterations can change the amino acid sequence, which affects the charge distribution and total charge of the protein. Protein folding, stability, protein-protein interactions, and enzymatic activity can all be affected by genetic alterations.
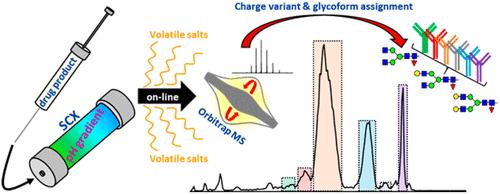 Fig 1. Charge variant analysis (CVA) of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). (Füssl, F., et al.; 2018)
Fig 1. Charge variant analysis (CVA) of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). (Füssl, F., et al.; 2018)
Gold Standard Method for Characterizing Protein Charge Variants
The gold standard approach for defining charge variations of proteins is ion exchange chromatography (IEX), and during the past ten years, numerous studies have detailed the charge profiles of mAbs. The majority of these research have discussed how the charge variations of mAbs are impacted by high temperature or alkaline pH-enforced stress degradation. The main sign of degradation under such conditions is a rise in acidity, which is a result of the protein demanding or oxidizing. After collecting the IEX fractions, the identification of these various species is often carried out utilizing a bottom-up method that includes enzymatic digestion and LC-MS/MS analysis.
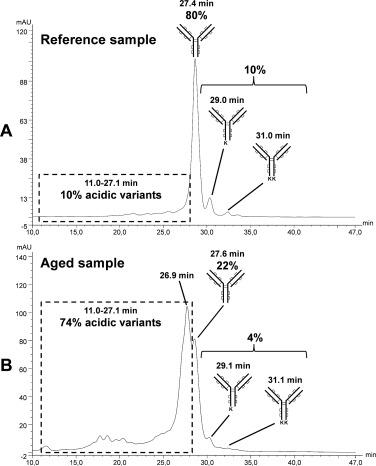 Fig 2. Ion exchange chromatograms of the reference sample (A) and the degraded sample (B) with UV detection at 280 nm. (Leblanc, Y., et al.; 2017)
Fig 2. Ion exchange chromatograms of the reference sample (A) and the degraded sample (B) with UV detection at 280 nm. (Leblanc, Y., et al.; 2017)
Recently, the characterization of charge variations has been carried out using on-line, intermediate-up, two-dimensional liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (2D-LC-MS). The IEX peaks of the first-dimensional chromatography can be allocated directly using second-dimensional reversed-phase chromatography that is compatible with mass spectrometric detection. Other methods for directly connecting mass spectrometry to nondenaturing chromatography with volatile salts have emerged because two-dimensional liquid chromatography is still a difficult and time-consuming procedure.
How is Charge Variant Analysis Performed?

Challenges in Charge Variant Analysis
1. Heterogeneity
Proteins can have a high degree of heterogeneity in their charge variants, with multiple variants present simultaneously. Separation and characterization of such complex mixtures can be difficult.
2. Sample Complexity
Protein samples used in charge variant analysis can be complex mixtures containing multiple proteins with different charge variants. Isolating and analyzing the charge variants of interest within these complex samples is a challenge.
3. Sensitivity
Some charge variants may be present at low abundance levels, making their detection and quantification challenging. The sensitivity of the analytical techniques used for charge variant analysis needs to be high enough to detect and characterize these low abundance variants.
Service Workflow
Our Goals
Creative Proteomics has a wealth of knowledge in the characterisation of protein drugs. Our ability to provide thorough data analysis and expert project design in accordance with your project's needs also allows us to combine our protein charge variation analysis service with other protein characterization services for multi-analysis. Please get in touch with us for additional details if you are interested in our services.
References
- Füssl, F., et al.; Charge Variant Analysis of Monoclonal Antibodies Using Direct Coupled pH Gradient Cation Exchange Chromatography to High-Resolution Native Mass Spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry. 2018, 90(7), 4669–4676.
- Leblanc, Y., et al.; Charge variants characterization of a monoclonal antibody by ion exchange chromatography coupled on-line to native mass spectrometry: Case study after a long-term storage at +5 °C. Journal of Chromatography B. 2017, 1048, 130–139.
Related Sections
Services
Applications
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.

 Fig 1. Charge variant analysis (CVA) of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). (Füssl, F., et al.; 2018)
Fig 1. Charge variant analysis (CVA) of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). (Füssl, F., et al.; 2018) Fig 2. Ion exchange chromatograms of the reference sample (A) and the degraded sample (B) with UV detection at 280 nm. (Leblanc, Y., et al.; 2017)
Fig 2. Ion exchange chromatograms of the reference sample (A) and the degraded sample (B) with UV detection at 280 nm. (Leblanc, Y., et al.; 2017)

