What are Globosides?
Globosides are a type of glycosphingolipid, which are molecules composed of a ceramide (a lipid) linked to a carbohydrate chain. They are primarily found in cell membranes, particularly in the outer leaflet. The carbohydrate chain in globosides consists of multiple sugar units, often including glucose, galactose, and N-acetylgalactosamine.
These molecules play important roles in cell-cell recognition, cell signaling, and cell adhesion processes. Additionally, globosides are often associated with blood group antigens, such as the globo-series blood group antigens found on red blood cells. They also serve as receptors for certain toxins and pathogens, including bacteria and viruses. Examples of globosides include globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) and globotetraosylceramide (Gb4).
Understanding the composition, distribution, and dynamics of globosides is fundamental for elucidating their involvement in crucial cellular processes such as cell-cell recognition, immune response modulation, and signal transduction pathways. Moreover, aberrations in globoside metabolism have been implicated in numerous pathological conditions including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and infectious diseases, emphasizing the necessity for precise and comprehensive globoside analysis methodologies.
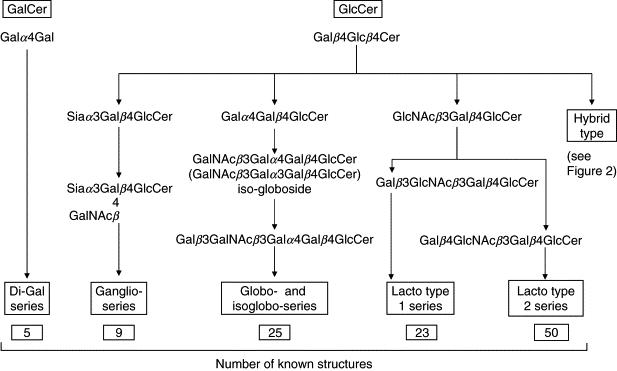 Five series (di-Gal, ganglio, globo, lacto type 1, and lacto type 2) of glycosphingolipids (GSLs), with different core structures. Number of structures characterized in each series is indicated below that series at the bottom of the figure (Kamerling et al., 2007).
Five series (di-Gal, ganglio, globo, lacto type 1, and lacto type 2) of glycosphingolipids (GSLs), with different core structures. Number of structures characterized in each series is indicated below that series at the bottom of the figure (Kamerling et al., 2007).
Globosides Analysis Services by Creative Proteomics
Globoside Composition Analysis
Utilizing advanced mass spectrometry-based techniques, we offer precise characterization of globoside composition. This includes identifying lipid species, carbohydrate moieties, and their relative abundances. Through targeted and untargeted approaches, we unravel the complexity of globoside profiles, providing valuable insights into cellular glycosphingolipid metabolism and dynamics.
Quantitative Profiling of Globosides
Our quantitative mass spectrometry methodologies enable accurate quantification of globoside levels in biological samples. Using stable isotope labeling or label-free quantification strategies, we facilitate quantitative comparisons of globoside abundance across different experimental conditions, aiding in biomarker discovery and understanding globosides' role in health and disease.
Structural Elucidation and Functional Characterization
We employ an integrated approach combining mass spectrometry with techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and chromatography to elucidate the structural intricacies of globosides. By revealing glycosidic linkages, fatty acid composition, and spatial arrangements, we gain insights into the functional implications of globoside diversity and heterogeneity.
Biomarker Discovery and Disease Profiling
Our globoside analysis services facilitate biomarker discovery and disease profiling. By analyzing globoside signatures in clinical samples, we identify disease-specific alterations in globoside metabolism, paving the way for novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for precision medicine initiatives.
List of Detectable Globosides
| Globoside 3 | Globoside 4 | Globoside 5 | Globotriaosylceramide | Sulfatide |
| Glucosylceramide | Galactosylceramide | Lactosylceramide |
Analytical Techniques for Globosides Analysis
- Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
LC-MS combines liquid chromatography's separation capabilities with mass spectrometry's sensitivity and accuracy. It separates Globosides based on their properties and provides structural information. Common instrument models include Agilent 1290 Infinity II LC with Agilent 6545 Q-TOF MS and Thermo Scientific Dionex UltiMate 3000 UHPLC with Thermo Scientific Q Exactive Focus Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap MS.
- Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-MS)
MALDI-MS analyzes intact Globosides directly from complex samples. It involves co-crystallizing the analyte with a matrix, then irradiating it with a laser for ionization. Common instruments are Bruker UltrafleXtreme MALDI-TOF/TOF MS and SCIEX TOF/TOF™ 5800 System.
- Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS)
ESI-MS ionizes Globosides in solution by spraying them through a charged capillary. It's effective for a wide range of compounds. Common instruments include Waters Xevo G2-XS QTof MS and Shimadzu LCMS-8060 Triple Quadrupole MS with ESI Source.
Sample Requirements for Globosides Analysis
| Sample Type | Sample Volume | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Culture | 1 mL | Harvest cells at desired confluency |
| Tissue Biopsy | 10-50 mg | Homogenize tissue in appropriate buffer |
| Serum/Plasma | 100-500 µL | Store at -80°C until analysis |
| Urine | 1-5 mL | Collect in sterile container |
| Cerebrospinal Fluid | 100-500 µL | Collect using aseptic technique |
| Biological Fluids | 100-500 µL | Centrifuge if necessary to remove debris |
| Synthetic Standards | As per experiment | Prepare in appropriate solvent |
Deliverables for Globosides Analysis
- Raw Data Files: Raw data files generated during the analysis, including mass spectrometry spectra, chromatograms, and any other relevant data.
- Processed Data Report: A comprehensive report summarizing the processed data, including peak identification, quantification results, and any relevant statistical analyses.
- Structural Elucidation: Detailed structural elucidation of identified globosides, including glycosidic linkages, fatty acid composition, and any other relevant structural features.
- Quantification Results: Quantification results for each identified globoside species, including relative abundances and concentrations in the sample.
- Quality Control Metrics: Quality control metrics to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the analysis, including instrument calibration data and internal standards performance.
- Interpretation and Recommendations: Expert interpretation of the results and recommendations for further analysis or experimental design considerations.
- Supporting Documentation: Any additional documentation or supplementary information relevant to the analysis, including sample preparation protocols and method validation reports.
- Data Interpretation Session (Optional): Optional data interpretation session with our team of experts to discuss the results, answer questions, and provide guidance on next steps.
Applications of Globosides Analysis
Biomarker Discovery: Globosides have been implicated in a spectrum of pathological conditions, notably cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Through the analysis of globosides in biological matrices such as serum, plasma, and tissue, distinctive globoside profiles associated with pathological states can be delineated. This facilitates the discernment of biomarkers conducive to early disease detection and prognostic assessment.
Drug Development: A comprehensive comprehension of globosides' involvement in cellular signaling and disease pathogenesis is imperative for drug development endeavors. Globosides analysis serves as a pivotal tool in unraveling the molecular intricacies underlying drug efficacy and elucidating potential pharmacological targets. Such insights pave the path towards the formulation of innovative therapeutic modalities tailored to combat globoside-associated maladies.
Glycosphingolipid Metabolism Studies: Globosides, constituting a subclass of glycosphingolipids, intricately participate in diverse cellular processes, encompassing cell-cell recognition and signal transduction. Examination of globoside metabolism furnishes invaluable insights into the biosynthetic and degradative pathways of glycosphingolipids, thereby augmenting our comprehension of cellular physiology and pathophysiology.
Neuroscience Research: Globosides assume a pivotal role in various facets of neuronal biology, spanning neuronal development, synaptic functionality, and myelinogenesis. Analysis of globosides within the central nervous system affords elucidation regarding their implication in neurodevelopmental aberrations, neurodegenerative pathologies, and neuroinflammatory cascades, thereby fostering the inception of novel therapeutic interventions.
Immunochemistry: The involvement of globosides in immune cell signaling and immune modulation underscores their significance in immunological contexts. Profiling of globosides within immune cell populations and tissues facilitates a nuanced understanding of their immunomodulatory roles and inflammatory implications, thereby furnishing insights germane to autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, and immunotherapeutic strategies.
Nutritional Studies: Globosides permeate various dietary sources, including dairy derivatives, meat products, and plant-derived fare. Analytical scrutiny of globosides within nutritional substrates affords elucidation regarding their nutritional import and putative health ramifications, thereby informing dietary guidelines and nutritional interventions.
Environmental Monitoring: The presence of globosides in environmental milieus, encompassing soil, water, and atmospheric domains, renders them plausible biomarkers indicative of environmental exposure to toxins, pollutants, and contaminants. Analysis of globosides within environmental matrices assumes salience in bolstering environmental surveillance endeavors and facilitating risk assessment protocols.
Precision Medicine: Globosides analysis engenders a paradigm shift towards precision medicine paradigms by virtue of discerning patient-specific globoside profiles and tailoring therapeutic interventions commensurate with individual molecular signatures. This bespoke approach holds promise in optimizing therapeutic efficacy whilst mitigating untoward treatment-related sequelae within clinical settings.
Reference
- Kamerling, Johannis P., and Geert-Jan Boons, eds. Cell Glycobiology and Development: Health and Disease in Glycomedicine. Elsevier, 2007.