What is N- and O-Glycosylation Site Analysis?
N- and O-glycosylation site analysis refers to the process of identifying and characterizing the locations within a protein where N-linked and O-linked glycans are attached. Glycosylation is a post-translational modification where sugar molecules (glycans) are covalently linked to specific amino acid residues in proteins.
N-linked glycosylation occurs at asparagine (N) residues within the consensus sequence motif Asn-X-Ser/Thr, where X can be any amino acid except proline. O-linked glycosylation, on the other hand, occurs predominantly on serine (Ser) or threonine (Thr) residues.
Analyzing N- and O-glycosylation sites typically involves experimental techniques such as mass spectrometry combined with enzymatic digestion of proteins and glycan analysis. These methods can identify the specific amino acid residues that are glycosylated, the types of glycans attached, and the overall glycosylation profile of a protein or protein mixture. Understanding glycosylation sites is crucial for studying protein structure, function, and regulation, as glycosylation plays important roles in various cellular processes and diseases.
Creative Proteomics offers comprehensive N- and O-glycosylation site analysis services, empowering researchers to unravel the complexities of glycoproteins with precision and efficiency.
Creative Proteomics's N- and O-Glycosylation Site Analysis Services
Creative Proteomics offers the following specific services for N- and O-glycosylation site analysis:
N-Glycosylation Site Analysis:
- Identification of N-glycosylation sites on proteins.
- Characterization of N-glycan structures attached to specific sites.
- Quantification of N-glycosylation occupancy at each site.
O-Glycosylation Site Analysis:
- Detection and mapping of O-glycosylation sites on proteins.
- Profiling of O-glycan structures linked to individual sites.
- Determination of O-glycosylation occupancy levels at designated sites
Technology Platform for N- and O-Glycosylation Site Analysis
Glycopeptide Enrichment Strategies:
- Specific enrichment methods targeting glycopeptides, such as lectin affinity chromatography, hydrazide chemistry, or solid-phase extraction.
- Enzymatic or chemical treatments for selective cleavage of glycans from peptides (deglycosylation) to facilitate glycopeptide analysis.
Liquid Chromatography (LC) Separation:
- Advanced liquid chromatography systems for efficient separation of glycopeptides prior to MS analysis.
- Various chromatographic modes (e.g., reverse-phase, hydrophilic interaction chromatography) optimized for glycopeptide enrichment and separation.
Mass Spectrometry (MS) Analysis:
- High-resolution mass spectrometry instruments for precise measurement of glycopeptides.
- Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS or MSn) capabilities for sequencing glycan structures and identifying glycosylation sites.
- Multiple fragmentation techniques (e.g., collision-induced dissociation, electron transfer dissociation, and higher-energy collisional dissociation) for comprehensive glycopeptide analysis.
Bioinformatics and Data Analysis:
- Specialized software tools for processing mass spectrometry data, including spectral deconvolution, peak picking, and database searching.
- Bioinformatics algorithms for glycopeptide identification, glycan composition assignment, and localization of glycosylation sites.
- Integration of structural information from MS/MS spectra with protein sequence databases for confident glycopeptide annotation.
Quality Control and Validation:
- Rigorous quality control measures to ensure data accuracy and reproducibility.
- Validation of glycosylation site assignments through comparison with known glycoproteins or experimental validation methods (e.g., site-directed mutagenesis).
- Comprehensive reporting of analytical results, including spectra, glycan compositions, and glycosylation site probabilities.
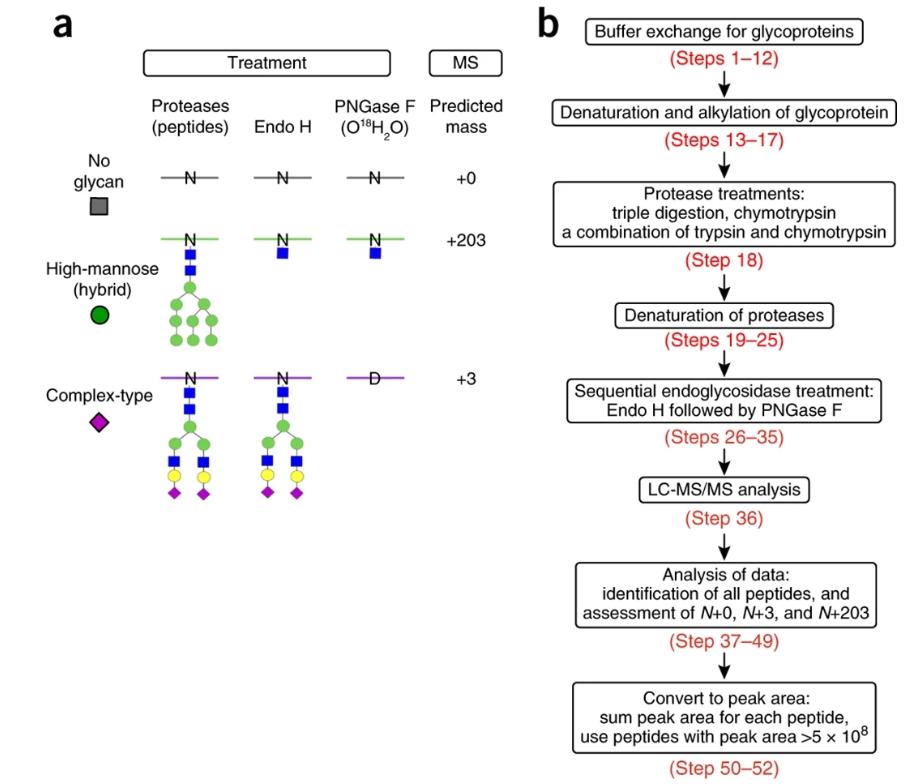 (a) Introduction of novel mass signatures for peptide glycosites that are not occupied, or that are occupied by high-mannose/hybrid or complex-type glycans. (b) The workflow of the protocol (Cao et al., 2018).
(a) Introduction of novel mass signatures for peptide glycosites that are not occupied, or that are occupied by high-mannose/hybrid or complex-type glycans. (b) The workflow of the protocol (Cao et al., 2018).
Sample Requirements for N- and O-Glycosylation Site Analysis Services
| Sample Type | Sample Amount | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Protein Extracts | 50-100 μg | - Solubilized in appropriate buffer (e.g., urea, SDS) |
| Cell Lysates | 1-5 million cells | - Extracted using compatible lysis buffer |
| Tissue Homogenates | 10-50 mg | - Homogenized in suitable buffer (e.g., RIPA, Tris-HCl) |
| Serum/Plasma | 100-500 μL | - Centrifuged to remove debris and lipids |
| Cell Culture Supernatants | 1-5 mL | - Clarified by centrifugation or filtration |
| Biopsy Samples | 1-5 mm3 | - Snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen or preserved in suitable buffer |
| Glycoprotein Standards | As recommended by supplier | - Positive control for method validation |
Differences Between Services in N- and O-Linked Glycosylation Mapping
| Service Name | Difference |
|---|---|
| N- and O-Glycan Profiling Service | - This service is used to analyze the overall composition and structural characteristics of N- and O-glycans in a sample. - Techniques such as mass spectrometry and chromatography are employed to determine the types, structures, and relative abundances of different N- and O-glycans in the sample. |
| N- and O-Glycosylation Site Analysis Services | - This service aims to determine the N- and O-glycosylation sites within proteins, i.e., identifying which amino acid residues are glycosylated. - Techniques such as mass spectrometry, sequence analysis, etc., are utilized to pinpoint the specific locations of glycosylation within proteins. |
| N- and O-Glycan Linkage Analysis | - This service is employed to study the linkage patterns and structures between N- and O-glycans. - Techniques such as mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are used to determine the linkage positions and types (e.g., β-1,4 linkage or α-1,6 linkage) between glycans. |
| N-and O-Glycosylation Site Occupation | - This service focuses on investigating the relative occupancy of N- and O-glycans within protein structures. - Techniques such as quantitative mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are employed to determine the extent of occupancy of different glycan types under specific conditions, as well as the relative occupancy ratios between different glycans. |
To find other services, please contact us. We are more than happy to assist you.
Reference
- Cao, Liwei, et al. "Global site-specific analysis of glycoprotein N-glycan processing." Nature protocols 13.6 (2018): 1196-1212.