- Service Details
- Case Study
What is Glycosylphosphatidylinositol?
Glycated hemoglobin, often abbreviated as HbA1c, is a form of hemoglobin that becomes glycated when it comes into contact with glucose in the bloodstream. Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and returning carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs.
When glucose levels in the bloodstream are high, some of the glucose molecules attach themselves to hemoglobin. This process, known as glycation, occurs spontaneously and irreversibly over time. The level of glycated hemoglobin reflects the average blood glucose concentration over the lifespan of red blood cells, which is approximately 8-12 weeks.
Measuring glycated hemoglobin levels is crucial for assessing long-term blood glucose control. Unlike traditional blood glucose measurements, which provide a snapshot of glucose levels at a specific moment, HbA1c levels offer insights into overall glycemic status over time. This makes glycated hemoglobin a valuable marker for monitoring diabetes management and risk assessment.
At Creative Proteomics, we provide a comprehensive range of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) analysis services tailored to meet your research needs.
Glycated Hemoglobin Analysis Service by Creative Proteomics
HbA1c Quantification: Accurate quantification of glycated hemoglobin levels using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), immunoassays, or capillary electrophoresis techniques.
Glycation Site Mapping: Identification and characterization of glycation sites on hemoglobin molecules through mass spectrometry-based proteomics approaches, providing insights into the structural alterations induced by glycation.
Glycated Hemoglobin Stability Studies: Evaluation of the stability of glycated hemoglobin under various storage conditions, ensuring sample integrity and reliability of results over time.
Comparative Analysis: Comparative analysis of glycated hemoglobin profiles across different sample types, treatment regimens, or physiological conditions to elucidate disease mechanisms and therapeutic outcomes.
Customized Assay Development: Custom assay development services tailored to specific research requirements, including the development of novel analytical methods or assay optimization for challenging sample matrices.
Data Interpretation and Reporting: Comprehensive data analysis and interpretation, accompanied by detailed reports summarizing experimental procedures, results, and conclusions, to support your research findings and publications.
Technical Platforms for Glycated Hemoglobin Measurement Services
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): Our HPLC systems, such as the Agilent 1260 Infinity II HPLC System or the Shimadzu Prominence HPLC System, enable efficient separation and quantification of HbA1c from complex biological matrices. Leveraging advanced chromatographic columns and detectors, HPLC provides high-resolution analysis with excellent reproducibility.
Mass Spectrometry: Leveraging state-of-the-art mass spectrometers like the Thermo Scientific Q Exactive HF-X Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer, we perform precise and comprehensive characterization of glycated hemoglobin variants. Mass spectrometry enables accurate determination of glycation sites and quantification of HbA1c isoforms, enhancing our understanding of diabetes pathophysiology.
Immunoassays: Utilizing cutting-edge immunoassay platforms like the Bio-Rad D-100 HbA1c Analyzer or the Siemens DCA Vantage Analyzer, we achieve rapid and accurate quantification of HbA1c levels based on specific antibody-antigen interactions. Immunoassays offer high sensitivity and specificity, making them suitable for clinical diagnostics and research applications.
Sample Requirements for Glycated Hemoglobin Measurement Services
| Sample Type | Sample Volume |
|---|---|
| Cell Culture Supernatant | 500 μL - 1 mL |
| Serum/Plasma | 100 μL - 200 μL |
| Tissue Homogenate | 20 mg - 50 mg |
| Urine | 1 mL - 2 mL |
| Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | 100 μL - 200 μL |
| Saliva | 100 μL - 200 μL |
| Synovial Fluid | 100 μL - 200 μL |
| Other Biological Fluids | As appropriate |
Applications of Glycated Hemoglobin Measurement Services
Diabetes Research: Assessing long-term glycemic control and evaluating treatment effectiveness.
Epidemiological Studies: Investigating diabetes prevalence and associated risk factors.
Cardiovascular Risk Assessment: Exploring the link between HbA1c levels and cardiovascular outcomes.
Complications Research: Studying the relationship between glycemic control and diabetes-related complications.
Pharmacological Research: Evaluating drug efficacy in improving glycemic control.
Glycemic Variability Studies: Examining fluctuations in blood glucose levels and their impact on health outcomes.
Predictive Biomarker Studies: Investigating HbA1c's utility as a predictor of future diabetes risk or complications.
Population Health Surveys: Using HbA1c levels to assess the overall burden of diabetes within populations.
Interventional Trials: Implementing HbA1c as an outcome measure to assess the effectiveness of interventions in preventing or managing diabetes.
Health Economics Research: Analyzing the cost-effectiveness of different diabetes management strategies based on HbA1c outcomes.
Genetic Studies: Exploring the genetic determinants of HbA1c levels and their implications for diabetes susceptibility.
Precision Medicine: Tailoring diabetes treatment approaches based on individual HbA1c profiles and other clinical parameters.
Title: Influence of Albumin Glycation on Hemoglobin Glycation in Diabetes Management
Background
Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is a crucial marker for assessing glycemic status in diabetes. Various factors, such as age, erythrocyte lifespan, and intracellular glucose levels, can influence HbA1c values. Among these factors, albumin, the most abundant protein in circulation, plays a significant role in regulating hemoglobin glycation. However, the impact of albumin glycation on HbA1c levels and its clinical significance in diabetes management remain unclear.
Sample
The study utilized in vitro erythrocyte culture experiments and clinical analysis involving 75 subjects, including controls, prediabetic, and controlled diabetic individuals. Blood samples were collected and analyzed for various biochemical parameters, including HbA1c, albumin, and plasma protein fructosamine.
Technical Methods
In vitro experiments involved the synthesis of modified albumin variants, including carboxymethylated serum albumin (CMSA) and acetylated serum albumin (AcSA), to mimic glycated forms of albumin. Erythrocytes cultured in different glucose concentrations were treated with these albumin variants, and hemoglobin glycation was assessed through various methods, including HbA1c analysis, AGE-Hb fluorescence measurement, and Western blot analysis. Clinical analysis included the quantification of glycated peptides of hemoglobin and albumin using SWATH-MS analysis.
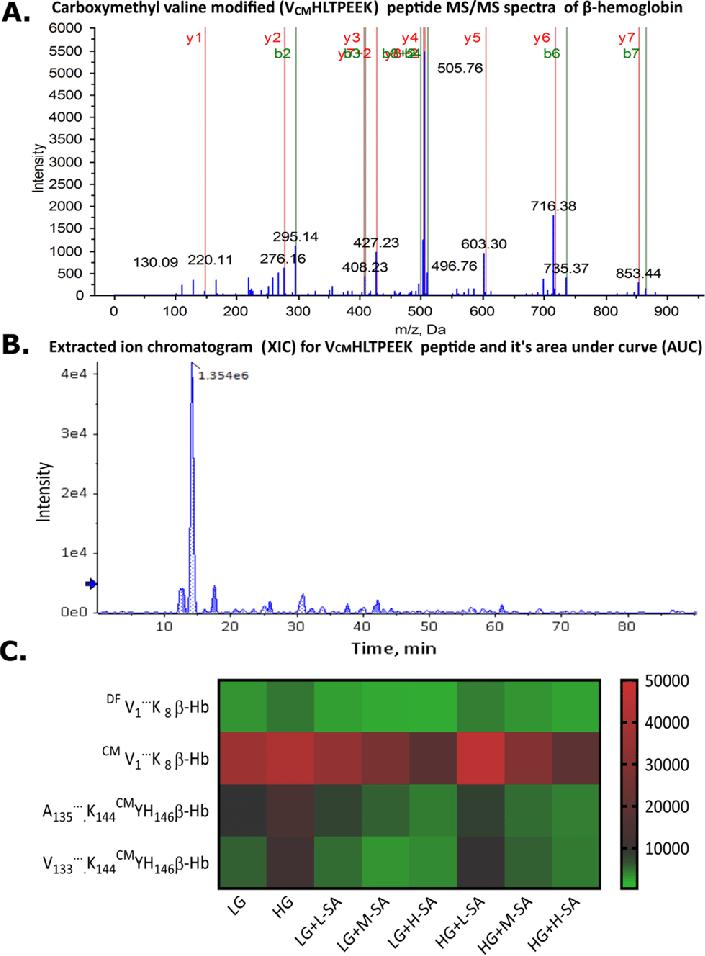 Glycated hemoglobin peptide analysis was performed using targeted SWATH-MS analysis.
Glycated hemoglobin peptide analysis was performed using targeted SWATH-MS analysis.
Results
The study demonstrated that albumin abundance and its glycation status influence hemoglobin glycation, with higher levels of glycated albumin associated with increased HbA1c levels. Modification of lysine residues of albumin impaired its ability to inhibit hemoglobin glycation. Clinical analysis revealed correlations between albumin, glycated albumin, and HbA1c levels in diabetic subjects, highlighting the clinical significance of monitoring albumin and glycated albumin alongside HbA1c in diabetes management.
Reference
- Jagadeeshaprasad, Mashanipalya G., et al. "Albumin abundance and its glycation status determine hemoglobin glycation." ACS omega 3.10 (2018): 12999-13008.