- Service Details
- Case Study
O-glycan profiling is a powerful analytical technique that is critical to both the biomedical and biopharmaceutical fields. It stands at the forefront of qualitative and quantitative research, unraveling the complex world of O-glycosylation modifications in glycoproteins. In the field of biopharmaceuticals, O-glycan profiling is essential for understanding the structural composition and molecular content of O-glycans in protein drugs and biologics. This knowledge plays a key role in influencing protein function, stability and immunogenicity, thus ensuring the quality and efficacy of therapeutic proteins. At the same time, in biomedical research, O-glycan profiling provides important insights into the broader understanding of glycosylation patterns, contributing to our better understanding of cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
Technology Platform for O-Glycan Profiling Analysis
Creative Proteomics employs a sophisticated and comprehensive technology platform for O-glycan profiling analysis, integrating advanced methodologies to ensure a thorough and precise examination of glycosylation patterns. The analytical process encompasses several key techniques, including O-glycan release technology, fluorescence detection, electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography fluorescence detection (HILIC-FLD), high-performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection (HPAE-PAD), and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
The initial step involves the utilization of O-glycan release technology, enabling the liberation of O-glycans from glycoprotein or glycopeptide samples. Subsequently, a meticulous purification process is undertaken, employing size exclusion chromatography and cation exchange columns to eliminate impurities and polypeptides. The use of acetate acidified glycosaminoglycan derivatives converts the released O-glycans into free non-reducing polysaccharides.
To enhance the accuracy and sensitivity of the analysis, Creative Proteomics employs fluorescence detection and ESI-MS. The large-pore amide HILIC column efficiently separates free O-glycans, facilitating their subsequent labeling for improved fluorescence detection and mass spectrometry. This method ensures the acquisition of a detailed O-glycan spectrum, providing comprehensive insights into the glycan structures.
The integration of high-performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection (HPAE-PAD) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) further enhances the resolution and efficiency of the O-Glycan Profiling analysis. These advanced technologies collectively contribute to the accurate identification, quantification, and characterization of O-glycan compositions within glycoproteins.
Advantages of Choosing Creative Proteomics's O-Glycan Profiling
- State-of-the-art Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS): Utilizing a high-performance electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) platform, we achieve sensitivity with a limit of detection down to femtomole levels. This enables precise analysis and a comprehensive understanding of O-glycan structures.
- Advanced Fluorescence Detection: Our approach incorporates advanced fluorescence detection, enhancing sensitivity and selectivity. This allows optimal visualization and quantification of O-glycans in complex biological samples, with a detection range extending into low nanomolar concentrations.
- Specialized HILIC Column for Macromolecular Separation: Employing a specialized hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) column designed for macromolecular separation, we achieve exceptional resolution. This column provides detailed structural insights through precise O-glycan separation, with a resolution capability of up to 50,000.
- Automation for Efficiency: Our highly automated processes, including robotic systems and liquid handling equipment, streamline sample preparation, reduce errors, and expedite analysis. This leads to a remarkable reduction in turnaround times, with results delivered within 5-7 days.
- Data-driven Insights: The integration of advanced technologies generates rich data sets for O-Glycan Profiling, offering comprehensive information on glycan composition, relative content, and structural details. This data-driven approach facilitates in-depth analysis and informed decision-making, with detailed reports containing up to 200 glycan structures per sample.
- Customized Analysis Solutions: Creative Proteomics offers flexible and customized services, allowing researchers to select specific analysis requirements tailored to their research plans. This ensures that the O-Glycan Profiling service meets the unique needs of each project, with the ability to customize parameters such as glycan type, labeling strategy, and reporting format.
Applications of O-Glycan Profiling
Biopharmaceutical Quality Control: O-Glycan Profiling ensures biopharmaceutical quality and safety by identifying modifications that may impact drug efficacy, stability, and immunogenicity.
Biomarker Discovery in Biomedical Research: O-Glycan Profiling aids in discovering biomarkers by identifying specific O-glycan signatures associated with diseases, contributing to early diagnosis and monitoring.
Understanding Cellular Processes: O-Glycan Profiling provides insights into how O-glycans modulate cellular functions, influencing protein interactions and participating in signaling pathways.
Development of Personalized Therapies: O-Glycan Profiling enables personalized therapeutic interventions by characterizing individual glycosylation profiles, optimizing treatment outcomes.
Investigation of Disease Mechanisms: O-Glycan Profiling helps investigate disease mechanisms, unraveling the role of abnormal glycosylation in conditions such as neurodegenerative disorders and autoimmune diseases.
Comparative Glycoproteomics Studies: O-Glycan Profiling facilitates comparative glycoproteomics studies, identifying glycan variations associated with specific physiological states, environmental factors, or disease conditions.
Sample Requirements for O-Glycan Profiling
| Sample Type | Sample Size Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Biopharmaceuticals | 100 µg - 500 µg of Protein |
| Tissue Biopsies | 10 mg - 50 mg |
| Cell Culture Supernatant | 1 mL - 5 mL |
| Serum/Plasma | 100 µL - 500 µL |
| Urine | 1 mL - 5 mL |
| Cerebrospinal Fluid | 100 µL - 500 µL |
| Saliva | 500 µL - 2 mL |
| Synovial Fluid | 100 µL - 500 µL |
| Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid | 1 mL - 5 mL |
| Tumor Tissue | 10 mg - 50 mg |
| Mucus | 500 µL - 2 mL |
Case. Comprehensive Profiling of Serum O-Glycans Reveals Gender-Dependent Changes in Colorectal Cancer Progression
Background:
Aberrant glycosylation in tumorigenesis and metastatic promotion is a well-studied phenomenon. The study focuses on O-glycosylation in cancer, emphasizing the lack of sensitive analytical techniques for serum O-glycans. Existing methods face limitations, prompting the development of a cleaner and more efficient glycan release protocol.
Samples:
Sera from colorectal cancer patients at different stages (Cycle 1 and Cycle 2) and age-matched controls (both male and female) were analyzed. The study includes 62 cancer samples and 20 control samples.
Technical Method:
Modified O-Glycan Release Protocol: Modification and miniaturization of the traditional procedure to improve profiling capabilities. Simultaneous cleavage and immediate permethylation of O-glycans, enhancing structural preservation. This modification enables recording approximately 40 O-glycan components from low-microliter serum volumes.
Mass Spectrometry Analysis: Utilization of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-MS) for glycan analysis. Generation of a comprehensive Excel plot of MALDI-MS data, encompassing about 40 O-glycan components. Presentation of raw spectra, annotated spectral profiles, and dot plots for detailed glycan composition understanding.
Structural Confirmation and Validation: Provision of structural details, including m/z ratios and glycan compositions, focusing on major components like sialyl-T and disialyl-T antigens. Mention of MS/MS fragmentation measurements for structural validation, emphasizing the need for further confirmation.
Statistical Analysis: Application of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for initial evaluation of different cohort groups. Implementation of one-way ANOVA tests, followed by Tukey means comparison, to identify significant glycan alterations between control and cancer samples. Use of Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) evaluation to assess the diagnostic value of individual glycans.
Gender-Specific Analysis: Exploration of gender-specific differences in glycan profiles using ROC analysis, revealing distinct changes in O-glycosylation during cancer progression for males and females.
Results:
The MALDI-MS data reveal approximately 40 O-glycan components, with sialyl-T and disialyl-T antigens increasing in relative abundance during cancer progression. Structural confirmation and statistical analyses, including PCA and ANOVA, highlight significant gender-specific differences in glycan profiles correlating with disease progression. ROC analysis identifies specific O-glycans with diagnostic potential. The study suggests immunomodulatory roles for altered glycosylation in cancer and emphasizes the need for further research into gender-dependent O-glycosylation during cancer progression.
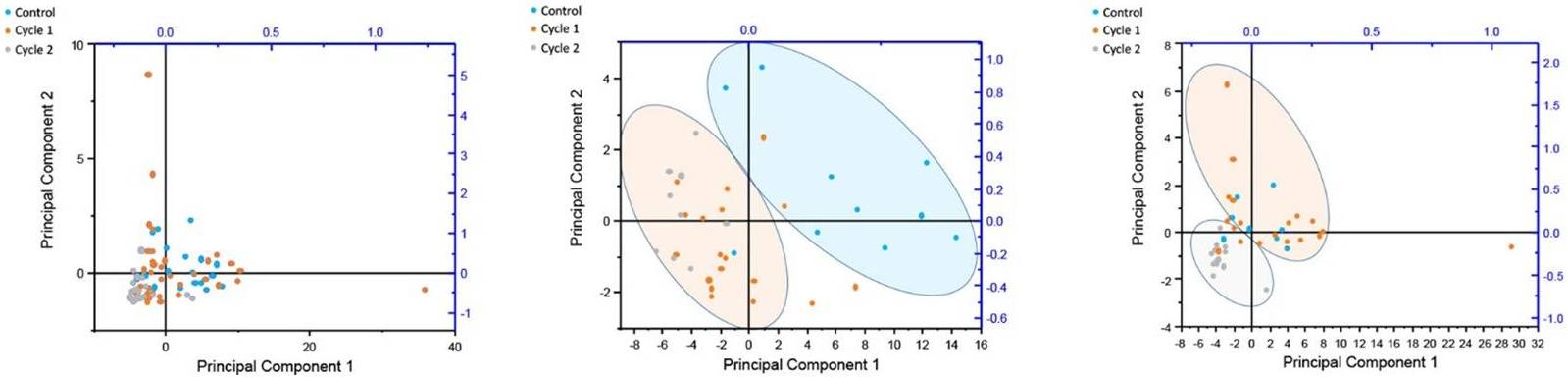 PCA plot of principal component 1 and 2 of 39 O-glycansfrom three different cancer conditions
PCA plot of principal component 1 and 2 of 39 O-glycansfrom three different cancer conditions
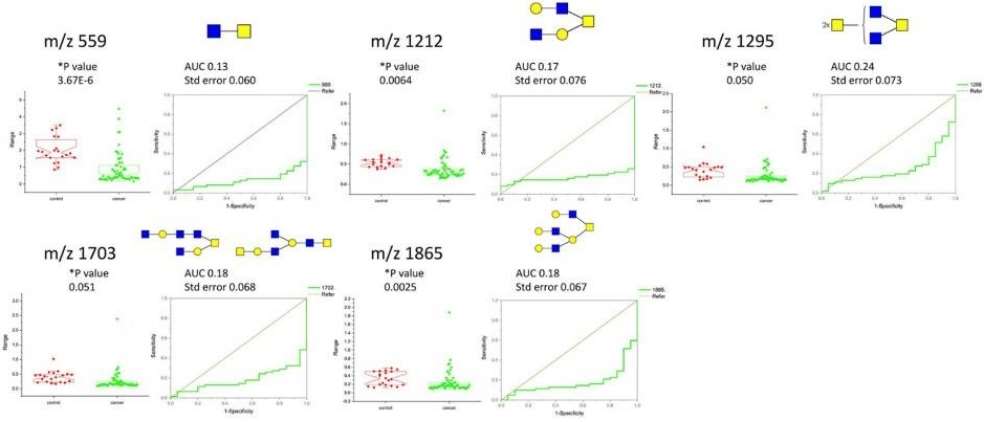 Boxplots of O-glycanssignificantly altered in cancer as determined with one-way ANOVA (at appropriate p = 0.05 values) and ROC curves with AUC values and associated standard errors.
Boxplots of O-glycanssignificantly altered in cancer as determined with one-way ANOVA (at appropriate p = 0.05 values) and ROC curves with AUC values and associated standard errors.
Reference
- Gizaw, Solomon T., Stefan Gaunitz, and Milos V. Novotny. "Highly sensitive O-glycan profiling for human serum proteins reveals gender-dependent changes in colorectal cancer patients." Analytical chemistry 91.9 (2019): 6180-6189.