Lipidomics in HCV Infection
Creative Proteomics is an international contract research organization (CRO). We provide state-of-the-art equipment and wide-ranging expertise in biotechnological applications to academic and industry clients. Our array of services can be tailored to meet global customers' needs. Here, we focus on lipidomics in HCV infection. The life cycle of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) is dependent on various lipid metabolism processes. As the main cause of chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma, HCV has a profound influence on the lipid metabolism of the host by differentially regulating key pathways of lipid utilization, synthesis, and remodeling.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV)
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small-enveloped virus belonging to the family of Flaviviridae. Despite constant progress in HCV diagnosis and treatment, HCV infection remains a serious health problem and a major causative agent of chronic liver diseases. An estimated 1% of the world's population is infected with HCV, and most of those infected do not realize they are infected. In addition, the virus accounts for up to 25% of hepatocellular carcinoma cases worldwide. It is believed that the persistence and pathogenesis of HCV are closely related to the ability of HCV to control host processes, mainly lipid metabolism and innate immunity. For example, chronic hepatitis may be responsible for liver steatosis and dyslipidemia. The correlation between HCV and lipid/lipoprotein metabolism has been observed in clinics many years ago.
HCV and lipid metabolism
Lipids are indispensable for the mechanism of HCV, especially in viral RNA replication, viral particles assembly, and egress. According to the latest data mainly from the past five years, there are several important alterations of lipid metabolism during HCV infections, involving fatty acid content, lipid transfer proteins (LTPs), lipid droplets (LDs), and cholesterol. Fatty acids (FAs) not only constitute cellular lipids but also participate in cellular signaling as well as posttranslational protein modification. Studies demonstrated that HCV changes cellular FA levels and lipid biosynthesis. LTPs are utilized to establish vesicular replication compartments by altering membrane lipid composition to ensure efficient replication, assembly, and secretion. In addition, LDs provide an assembly platform as well as an intracellular lipid source during HCV infection.
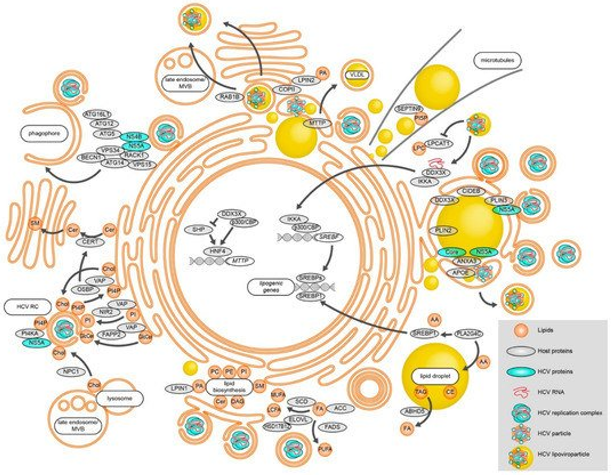 Fig 1. Modulation of lipid metabolic processes during HCV RNA replication, assembly, and egress. (Bley, H., Schöbel, A., & Herker, E., 2020)
Fig 1. Modulation of lipid metabolic processes during HCV RNA replication, assembly, and egress. (Bley, H., Schöbel, A., & Herker, E., 2020)
Lipidomics in HCV infection
As early as 2013, researchers have revealed the underlying connection between chronic HCV infection and lipids. Using a quantitative high-throughput lipidomic platform (including HPLC-MS/MS and HRMS), the plasma lipid profiles of individuals infected with chronic HCV were identified. HCV patients could be discriminated from healthy controls by multivariate analysis of their plasma lipidome. Besides, several lipids showed significant differences between mild and severe intrahepatic inflammation grades, which may be potential noninvasive indicators of intrahepatic inflammation grade (IG). Another study using quantitative shotgun lipidomics showed that efficient HCV replication requires complex lipid metabolic remodeling. Instead of neutral lipids, membrane lipids were increased in abundance in HCV infection. Besides, there was a higher proportion of lipids with longer fatty acyl chains during HCV infection.
Creative Proteomics has been developing metabolomics detection methods and data analysis methods for many years. Based on professional scientists and advanced platforms, we can accelerate our customers' projects to the next level. For more information on how we can help you, please feel free to contact us.
References
- Hofmann, S., et al. (2018). "Complex lipid metabolic remodeling is required for efficient hepatitis C virus replication." Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 1863(9), 1041-1056.
- Qu, F., et al. (2014). "Lipidomic profiling of plasma in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection." Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry, 406(2), 555-564.
- Bley, H., Schöbel, A., & Herker, E. (2020). "Whole Lotta Lipids—From HCV RNA Replication to the Mature Viral Particle." International journal of molecular sciences, 21(8), 2888.
Related services
* For research use only.


 Fig 1. Modulation of lipid metabolic processes during HCV RNA replication, assembly, and egress. (Bley, H., Schöbel, A., & Herker, E., 2020)
Fig 1. Modulation of lipid metabolic processes during HCV RNA replication, assembly, and egress. (Bley, H., Schöbel, A., & Herker, E., 2020)