Virus Quantification Using TCID50 Assay
The definition of viral infectivity is the number of virus particles capable of invading a particular cell type or animal. For vial infectivity assay, Besides, plaque assays, The TCID50 (50% Tissue Culture Infectious Dose) assay is another common type of infectivity method. Although plaque assay is the most useful approach, the gold standard in quantification of infectious viral titer, there are several virus types which do not form plaques in culture. In these cases, the TCID50 method can be a supplement of plaque assay. In addition, it seems more sensitive when comparing plaque assay. When shortage of experimental material or cost budgeting, the TCID50 method is a good choice due to cheap and easy to implement. Creative Proteomics is glad to offer TCID50 assay with treatment differences as well as good estimates of titers based on automated analysis, to meet the specific needs of today's researchers all over the world. Professionalism, excellence, and high-quality service are at the center of our relationship with our customers.
TCID50, a common assay for virus quantification
 TCID50 is the tissue culture infectious dose defined as the dilution of virus required to infect 50% of cells in a culture. The TCID50 assay belongs to endpoint dilution assay, qualitatively measuring the ratio between the infected and uninfected cells. The principle of TCID50 assay to determine viral titer is by providing information of cytopathic effect (CPE), including cell rounding, fusing, and other phenotypical changes. As a common assay for virus quantification, the method has the advantage of being cheap and easy to achieve, no requirement for lots of virus information. Therefore, it is available to study new and emerging pathogens. In general, the TCID50 assay includes the following steps. First, virus-susceptible cells are inoculated with culture plates. After cultured for a period of time, the cells are infected at specific dilutions of virus. Finally, the wells are observed and scored for the presence or absence of CPE. And to calculate the TCID50 of the virus sample, there are a variety of mathematical approaches, such as the method of Muench-Reed and Spearman-Karber.
TCID50 is the tissue culture infectious dose defined as the dilution of virus required to infect 50% of cells in a culture. The TCID50 assay belongs to endpoint dilution assay, qualitatively measuring the ratio between the infected and uninfected cells. The principle of TCID50 assay to determine viral titer is by providing information of cytopathic effect (CPE), including cell rounding, fusing, and other phenotypical changes. As a common assay for virus quantification, the method has the advantage of being cheap and easy to achieve, no requirement for lots of virus information. Therefore, it is available to study new and emerging pathogens. In general, the TCID50 assay includes the following steps. First, virus-susceptible cells are inoculated with culture plates. After cultured for a period of time, the cells are infected at specific dilutions of virus. Finally, the wells are observed and scored for the presence or absence of CPE. And to calculate the TCID50 of the virus sample, there are a variety of mathematical approaches, such as the method of Muench-Reed and Spearman-Karber.
TCID50 Assay in Creative Proteomics
Virus quantification is an integral and key part in the development of virus products, including product manufacturing as well as quality control. Here, we are providing virus quantification as a standalone service, offering our customers with a series of options to quantify viruses. Among them, TCID50 assay is the widely used method. According to the specific type of viruses and virus-susceptible cells, we choose the suitable readout parameter to perform the assay. Our service includes one-stop solution of TCID50 assays, transfer and implementation of existing TCID50 assays. Based on automated analysis and skillful technicians, we are confident to complete the rapid and accurate detection of viral titer assay, achieving real-time monitoring of virus infections both during and after production.
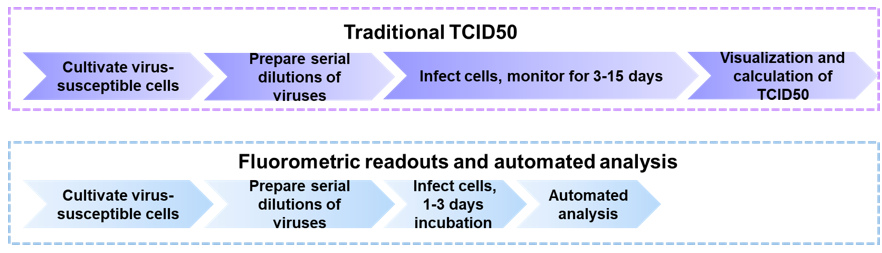 Flow diagrams of traditional and improved TCID50 assay
Flow diagrams of traditional and improved TCID50 assay
The benefits of Creative Proteomics
- An optimization & scale up platform
- Professional technical support
- A rapid and tailored viral quantification for specific research applications
The goal of Creative Proteomics is to provide our customers with high quality service and deliver accurate and reliable experimental reports. In addition to providing improved plaque assays, we also provide another common and reliable method for assessment of infectious viral titer, the TCID50 assay. Based on automated analysis, we have the capability to achieve a better understanding of sample infection through the accurate measurement of novel phenotypic changes. To improve research outcomes and the speed of success, please don't hesitate to contact us for more details.
References
- Lei, C., et al. (2020). "On the Calculation of TCID 50 for Quantitation of Virus Infectivity." Virologica Sinica, 1-4.
- LaBarre, D. D., & Lowy, R. J. (2001). "Improvements in methods for calculating virus titer estimates from TCID50 and plaque assays." Journal of virological methods, 96(2), 107-126.
* For research use only.

 TCID50 is the tissue culture infectious dose defined as the dilution of virus required to infect 50% of cells in a culture. The TCID50 assay belongs to endpoint dilution assay, qualitatively measuring the ratio between the infected and uninfected cells. The principle of TCID50 assay to determine viral titer is by providing information of cytopathic effect (CPE), including cell rounding, fusing, and other phenotypical changes. As a common assay for virus quantification, the method has the advantage of being cheap and easy to achieve, no requirement for lots of virus information. Therefore, it is available to study new and emerging pathogens. In general, the TCID50 assay includes the following steps. First, virus-susceptible cells are inoculated with culture plates. After cultured for a period of time, the cells are infected at specific dilutions of virus. Finally, the wells are observed and scored for the presence or absence of CPE. And to calculate the TCID50 of the virus sample, there are a variety of mathematical approaches, such as the method of Muench-Reed and Spearman-Karber.
TCID50 is the tissue culture infectious dose defined as the dilution of virus required to infect 50% of cells in a culture. The TCID50 assay belongs to endpoint dilution assay, qualitatively measuring the ratio between the infected and uninfected cells. The principle of TCID50 assay to determine viral titer is by providing information of cytopathic effect (CPE), including cell rounding, fusing, and other phenotypical changes. As a common assay for virus quantification, the method has the advantage of being cheap and easy to achieve, no requirement for lots of virus information. Therefore, it is available to study new and emerging pathogens. In general, the TCID50 assay includes the following steps. First, virus-susceptible cells are inoculated with culture plates. After cultured for a period of time, the cells are infected at specific dilutions of virus. Finally, the wells are observed and scored for the presence or absence of CPE. And to calculate the TCID50 of the virus sample, there are a variety of mathematical approaches, such as the method of Muench-Reed and Spearman-Karber.  Flow diagrams of traditional and improved TCID50 assay
Flow diagrams of traditional and improved TCID50 assay