Viral Infectivity Detection Services
For a virus, viral infectivity is the most important property. Viral infectivity assay is to measure the number of virus particles (viral titer) capable of invading a particular cell type or animal. And viral titer is a given number of infectious viral units per unit volume. To quantify viral infectivity, there are two common methods, including plaque assay and 50% cell culture infectious dose (TCID50) endpoint dilution assay. These methods for viral titer measurement rely on recognizable effects (the morphological change of the cell), such as dot blot immunoreactivity, cytopathic effect (CPE). Both methods are useful and practicable in viral research. Creative Proteomics offers a series of in vitro and chemical/physical methods, including the basic and common methods for virus detection and quantification. We provide the specific implementation strategies that can be chosen and customized to address customers' concerns and needs, involving the improved plaque method as well as the TCID50 method. The improved methods can greatly increase the speed of viral titer measurements, providing significant advantages in virology research and biotechnology applications. In addition, we also provide fast and traceable testing for urgent project needs.
 Although the advent of novel methods, such as RT-PCR, has fundamentally changed the isolation of virus in the lab setting, virus isolation and cultivation remain a standard method for the direct diagnosis of many viral infections. Creative Proteomics provides virus isolation and cultivation service according to specific projects. According to the specific virus and susceptible cell, we can offer a series of customized services, including experimental design, sample collection and treatment, and virus cultivation and identification. Our services are customized and flexible, which can be regulated to the specific research objectives and experimental budget.
Although the advent of novel methods, such as RT-PCR, has fundamentally changed the isolation of virus in the lab setting, virus isolation and cultivation remain a standard method for the direct diagnosis of many viral infections. Creative Proteomics provides virus isolation and cultivation service according to specific projects. According to the specific virus and susceptible cell, we can offer a series of customized services, including experimental design, sample collection and treatment, and virus cultivation and identification. Our services are customized and flexible, which can be regulated to the specific research objectives and experimental budget.
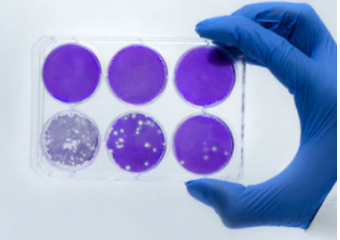 Plaque assays were established in 1952 and first not used to investigate the concentrations of viral samples. Later, the method is considered as the gold standard for investigation of viral infectivity. Although the principle of plaque assay is straightforward, the method is an invaluable tool in the quantification of infectious virus area due to its superior advantages, such as easily reproducible, consistent for analysis. However, the plaque method is labor intensive and susceptible to operation bias, requiring several days to complete a testing. To meet the fast and accurate investigation of viral infectivity, we provide an improved plaque assay service based on the integration of fluorescently labeled plaques and automated imaging.
Plaque assays were established in 1952 and first not used to investigate the concentrations of viral samples. Later, the method is considered as the gold standard for investigation of viral infectivity. Although the principle of plaque assay is straightforward, the method is an invaluable tool in the quantification of infectious virus area due to its superior advantages, such as easily reproducible, consistent for analysis. However, the plaque method is labor intensive and susceptible to operation bias, requiring several days to complete a testing. To meet the fast and accurate investigation of viral infectivity, we provide an improved plaque assay service based on the integration of fluorescently labeled plaques and automated imaging.
 Besides, plaque assays, the TCID50 (50% Tissue Culture Infectious Dose) assay is another common method for infectivity detection. Although plaque assay is the gold standard in quantification of viral infectivity, there are several virus types which do not form plaques in culture. In these cases, the TCID50 method can be a complement to plaque assay. The principle of TCID50 assay to determine viral titer is by providing information of cytopathic effect (CPE), including cell rounding, fusing, and other phenotypical changes. Based on automated analysis and skillful technicians, Creative Proteomics is providing a one-stop solution of TCID50 assays as well as the service that transfer and implementation of existing TCID50 assays.
Besides, plaque assays, the TCID50 (50% Tissue Culture Infectious Dose) assay is another common method for infectivity detection. Although plaque assay is the gold standard in quantification of viral infectivity, there are several virus types which do not form plaques in culture. In these cases, the TCID50 method can be a complement to plaque assay. The principle of TCID50 assay to determine viral titer is by providing information of cytopathic effect (CPE), including cell rounding, fusing, and other phenotypical changes. Based on automated analysis and skillful technicians, Creative Proteomics is providing a one-stop solution of TCID50 assays as well as the service that transfer and implementation of existing TCID50 assays.
The advantages of our service
- Ready to start your project once the contract is signed.
- An optimized and well-established platform
- Fully developed and improved analytical methods
- Fast and traceable testing for the urgent project needs
Simply let us know about your research needs. We will propose the best strategy to best match your research objectives. Contact us right now!
Reference
- Payne, S. (2017). "Methods to study viruses." Viruses, 37.
* For research use only.

 Although the advent of novel methods, such as RT-PCR, has fundamentally changed the isolation of virus in the lab setting, virus isolation and cultivation remain a standard method for the direct diagnosis of many viral infections. Creative Proteomics provides virus isolation and cultivation service according to specific projects. According to the specific virus and susceptible cell, we can offer a series of customized services, including experimental design, sample collection and treatment, and virus cultivation and identification. Our services are customized and flexible, which can be regulated to the specific research objectives and experimental budget.
Although the advent of novel methods, such as RT-PCR, has fundamentally changed the isolation of virus in the lab setting, virus isolation and cultivation remain a standard method for the direct diagnosis of many viral infections. Creative Proteomics provides virus isolation and cultivation service according to specific projects. According to the specific virus and susceptible cell, we can offer a series of customized services, including experimental design, sample collection and treatment, and virus cultivation and identification. Our services are customized and flexible, which can be regulated to the specific research objectives and experimental budget. Plaque assays were established in 1952 and first not used to investigate the concentrations of viral samples. Later, the method is considered as the gold standard for investigation of viral infectivity. Although the principle of plaque assay is straightforward, the method is an invaluable tool in the quantification of infectious virus area due to its superior advantages, such as easily reproducible, consistent for analysis. However, the plaque method is labor intensive and susceptible to operation bias, requiring several days to complete a testing. To meet the fast and accurate investigation of viral infectivity, we provide an improved plaque assay service based on the integration of fluorescently labeled plaques and automated imaging.
Plaque assays were established in 1952 and first not used to investigate the concentrations of viral samples. Later, the method is considered as the gold standard for investigation of viral infectivity. Although the principle of plaque assay is straightforward, the method is an invaluable tool in the quantification of infectious virus area due to its superior advantages, such as easily reproducible, consistent for analysis. However, the plaque method is labor intensive and susceptible to operation bias, requiring several days to complete a testing. To meet the fast and accurate investigation of viral infectivity, we provide an improved plaque assay service based on the integration of fluorescently labeled plaques and automated imaging. Besides, plaque assays, the TCID50 (50% Tissue Culture Infectious Dose) assay is another common method for infectivity detection. Although plaque assay is the gold standard in quantification of viral infectivity, there are several virus types which do not form plaques in culture. In these cases, the TCID50 method can be a complement to plaque assay. The principle of TCID50 assay to determine viral titer is by providing information of cytopathic effect (CPE), including cell rounding, fusing, and other phenotypical changes. Based on automated analysis and skillful technicians, Creative Proteomics is providing a one-stop solution of TCID50 assays as well as the service that transfer and implementation of existing TCID50 assays.
Besides, plaque assays, the TCID50 (50% Tissue Culture Infectious Dose) assay is another common method for infectivity detection. Although plaque assay is the gold standard in quantification of viral infectivity, there are several virus types which do not form plaques in culture. In these cases, the TCID50 method can be a complement to plaque assay. The principle of TCID50 assay to determine viral titer is by providing information of cytopathic effect (CPE), including cell rounding, fusing, and other phenotypical changes. Based on automated analysis and skillful technicians, Creative Proteomics is providing a one-stop solution of TCID50 assays as well as the service that transfer and implementation of existing TCID50 assays.