N-Glycoproteomics of Viruses
Viruses, including non-enveloped and enveloped viruses, are parasites of host cells that have features such as heredity and replication. All the membrane proteins of enveloped viruses are modified by glycosylation. There are three main types of glycosylation in viruses, including O-linked, N-linked, and C-linked. Among them, N-linked glycosylation is widely studied. The analysis of N-glycans in glycoproteins is an important branch of glycoproteomics. There are several aspects of N-glycan profiling, including,
Release of N-glycans
The release of glycochains from glycoproteins is a necessary step in the analysis of N-glycan of glycoproteins. We provide a widely used enzymatic method for releasing N-glycans.
Purification and enrichment of N-glycans
The enrichment of N-glycans from glycoproteins is essential. To achieve the goal, a series of enrichment methodologies have been applied, including hydrop interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC), porous graphitic carbon (PGC), and so on.
Permethylation of glycans
Due to the hydrophilicity of carbohydrates, native glycans are characterized by structural complexity and low ionization efficiency, thus, MS-based analysis of native glycans is challenging. Permethylation of glycans can enhance the sensitivity for MS detection by greatly increasing the ionization efficiency of glycans.
Structure detection and analysis of N-glycan
To achieve a more detailed analysis and identification of glycans, we offer ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS) and capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry (CE-MS).
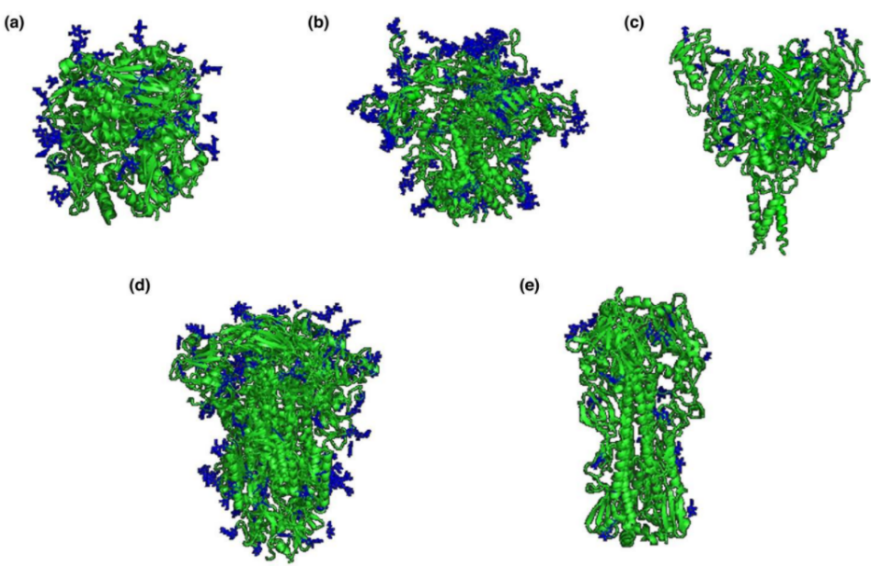 Fig1. Viral Fusion Protein Structures and N-glycosylation Sites (NGS) (blue). (a) Lassa virus (LASV) glycoprotein (GP); (b) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) Envelope (Env) GP; (c) Ebola virus (EBOV) GP; (d) Coronavirus (CoV) spike GP; (e) Influenza virus hemagglutinin. (Hargett, A. A., & Renfrow, M. B., 2019)
Fig1. Viral Fusion Protein Structures and N-glycosylation Sites (NGS) (blue). (a) Lassa virus (LASV) glycoprotein (GP); (b) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) Envelope (Env) GP; (c) Ebola virus (EBOV) GP; (d) Coronavirus (CoV) spike GP; (e) Influenza virus hemagglutinin. (Hargett, A. A., & Renfrow, M. B., 2019)
Technique offering in Creative Proteomics
So far, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) is one of the most commonly used tools in glycan analysis. MALDI-MS combined with lectin microarray is able to provide a more reliable characterization of the glycan structure. Due to the ability of tandem MALDI-MS enabling fragmentation of selected precursor ions, the techniques can characterize the structures of a given composition in more detail, therefore, suitable for analysis of N-glycans on recombinant viral proteins and matu re viral particles. In addition, MALDI-MS has also been applied to compare glycan profiles of recombinantly expressed viral proteins as well as proteins isolated from native viruses.
N-glycan analysis based on MALDI-TOF MS
MALDI-TOF is highly sensitive to the structure characterization of glycosylated compounds and can achieve high throughput detection. In the analysis of the N-glycan mixture, MALDI analyzed the sample through the formation of single-charged ions rather than electrospray ionization. N-glycans are released from glycoproteins by N-glycosidase A or F and detected after methylation.
N-glycan analysis based on HILIC-UHPLC MS
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) is an emerging MS-compatible separation technique and can be applied to the analysis of N-glycan profiling. We offer hydrophilic liquid chromatography (HILIC) ultra-high-performance (UHPLC)-tandem MS, a fast and robust technique, to analyze a large number of samples with N-glycan profiles.
Based on a team of professional and experienced scientists, Creative Proteomics is capable of offering N-glycoproteomics services. We are committed to providing high-quality service to greatly accelerate our customers' project progress and success. If you are interested in our services, please don't hesitate to contact us. We will get back to you soon!
References
- Hargett, A. A., & Renfrow, M. B. (2019). “lycosylation of viral surface proteins probed by mass spectrometry.” Current opinion in virology, 36, 56-66.
- Li, Y., et al. (2021). “The Importance of Glycans of Viral and Host Proteins in Enveloped Virus Infection.” Frontiers in Immunology, 12, 1544.
* For research use only.

 Fig1. Viral Fusion Protein Structures and N-glycosylation Sites (NGS) (blue). (a) Lassa virus (LASV) glycoprotein (GP); (b) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) Envelope (Env) GP; (c) Ebola virus (EBOV) GP; (d) Coronavirus (CoV) spike GP; (e) Influenza virus hemagglutinin. (Hargett, A. A., & Renfrow, M. B., 2019)
Fig1. Viral Fusion Protein Structures and N-glycosylation Sites (NGS) (blue). (a) Lassa virus (LASV) glycoprotein (GP); (b) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) Envelope (Env) GP; (c) Ebola virus (EBOV) GP; (d) Coronavirus (CoV) spike GP; (e) Influenza virus hemagglutinin. (Hargett, A. A., & Renfrow, M. B., 2019)