Multi-Omics in SARS-CoV-2 Infection
In the context of the current pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), it is critical to quickly identify and understand the SARS-CoV-2 virus and correlated COVID-19 at both the molecular and cellular levels. Multi-omic approaches allow multiple biomolecular types to be examined together, thus offering the potential for a more holistic, path-oriented view of biology. With the advanced development of multi-omic technologies, including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, researchers can get fast and panoramic insight into the pathogen and the disease. Specifically, multi-omic technologies that can help to identify biomarkers and drug targets of SARS-CoV-2 infection as well as enable the early diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19, have made a significant contribution to our fight against the COVID-19 pandemic.
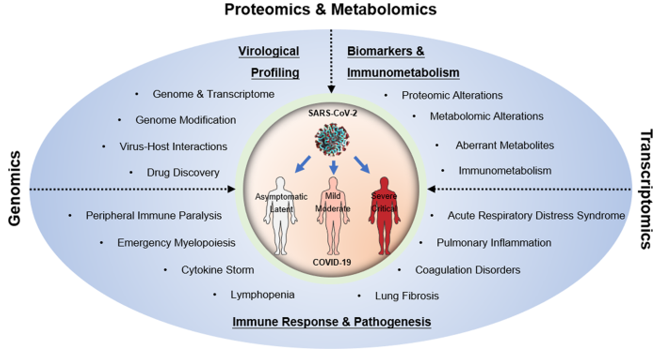 Fig1. Multiomic technologies facilitate the determination of the virological and immunological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 infection, the discovery of biomarkers, and the elucidation of COVID-19 pathogenesis. (Wang, X., et al, 2021)
Fig1. Multiomic technologies facilitate the determination of the virological and immunological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 infection, the discovery of biomarkers, and the elucidation of COVID-19 pathogenesis. (Wang, X., et al, 2021)
Multi-omics in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Application of genomics and transcriptomics in COVID-19 pandemic
High throughput sequencing technology has been widely used in virology research, which can quickly and accurately characterize viral genomes and reveal the detailed molecular architecture of viral RNA. With the progression of the COVID-19 pandemic, genomic analysis has contributed to identifying the mutations of SARS-CoV-2 as well as tracking the emergence of new variants. Similar to other RNA viruses, SARS-CoV-2 is highly dependent on the machinery of the host cell. Transcriptomic analysis has been used to detect the gene expression of SARS-CoV-2 in different biological samples, facilitating the investigation of the cellular mechanisms potential risk factors, pathogenesis, and potential drugs targets. In addition to the next-generation Illumina sequencing, third-generation sequencing, such as nanopore-based sequencing, has been applied to SARS-CoV-2 genome/transcriptome studies. For example, the specific information of novel SARS-CoV-2 open reading frames (including deletions, fusions, frameshifts and modified sites) can be identified using the combination of Illumina and nanopore sequencing.
Application of proteomics and metabolomics in COVID-19 pandemic
Proteomics and metabolomics analyses have been used to identify and quantify proteins and metabolites using different analytical methods, respectively. The application of proteomics in the COVID-19 pandemic includes two aspects, including virus characterization and monitoring the protein levels of infected cells, contributing to the understanding of viral pathological processes and immunogenicity, the discovery of potential therapeutic targets, and the development of biomarkers for disease course and prognosis. Metabolomics, such as lipid metabolism, amino acid metabolism, and glucose metabolism, has been widely used to investigate SARS-CoV-2 infection. According to these metabolomic studies, there are several applications of metabolomics in the COVID-19 pandemic, including identifying pathogenic mechanisms, exploring biomarkers, and discovering antiviral targets of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
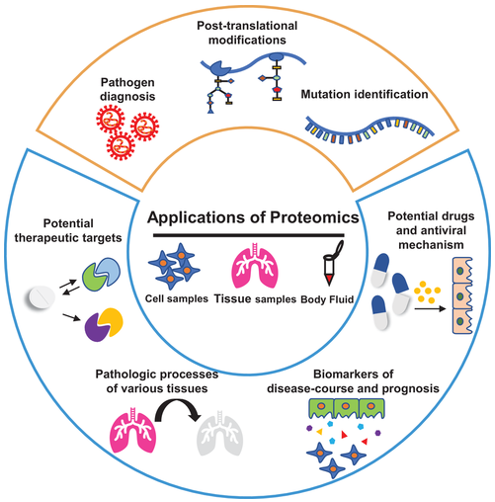 Fig2. Overview of application of proteomics in COVID-19 pandemic. (Yang, J., et al, 2021)
Fig2. Overview of application of proteomics in COVID-19 pandemic. (Yang, J., et al, 2021)
Multi-omics approaches have been widely applied to improve the understanding of the pathogenesis of COVID-19, including transcriptome/ proteome/ metabolome of the virus, the immune landscape, and virus-host interactions. Creative Proteomics is able to provide transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics experiments and multi-omics joint analysis services. Based on well-established longitudinal cohorts and multi-omics technologies, we can greatly promote the study of many viruses, including SARS-CoV-2. Feel free to contact us with any questions about our services. We will be delighted to provide you with all the support we can to help establish a sustaining professional partnership.
References
- Wang, X., et al. (2021). "Multiomics: unraveling the panoramic landscapes of SARS-CoV-2 infection." Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 1-12.
- Yang, J., et al. (2021). "Application of omics technology to combat the COVID-19 pandemic." MedComm.
Related services
* For research use only.

 Fig1. Multiomic technologies facilitate the determination of the virological and immunological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 infection, the discovery of biomarkers, and the elucidation of COVID-19 pathogenesis. (Wang, X., et al, 2021)
Fig1. Multiomic technologies facilitate the determination of the virological and immunological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 infection, the discovery of biomarkers, and the elucidation of COVID-19 pathogenesis. (Wang, X., et al, 2021) Fig2. Overview of application of proteomics in COVID-19 pandemic. (Yang, J., et al, 2021)
Fig2. Overview of application of proteomics in COVID-19 pandemic. (Yang, J., et al, 2021)