- Home
- Applications
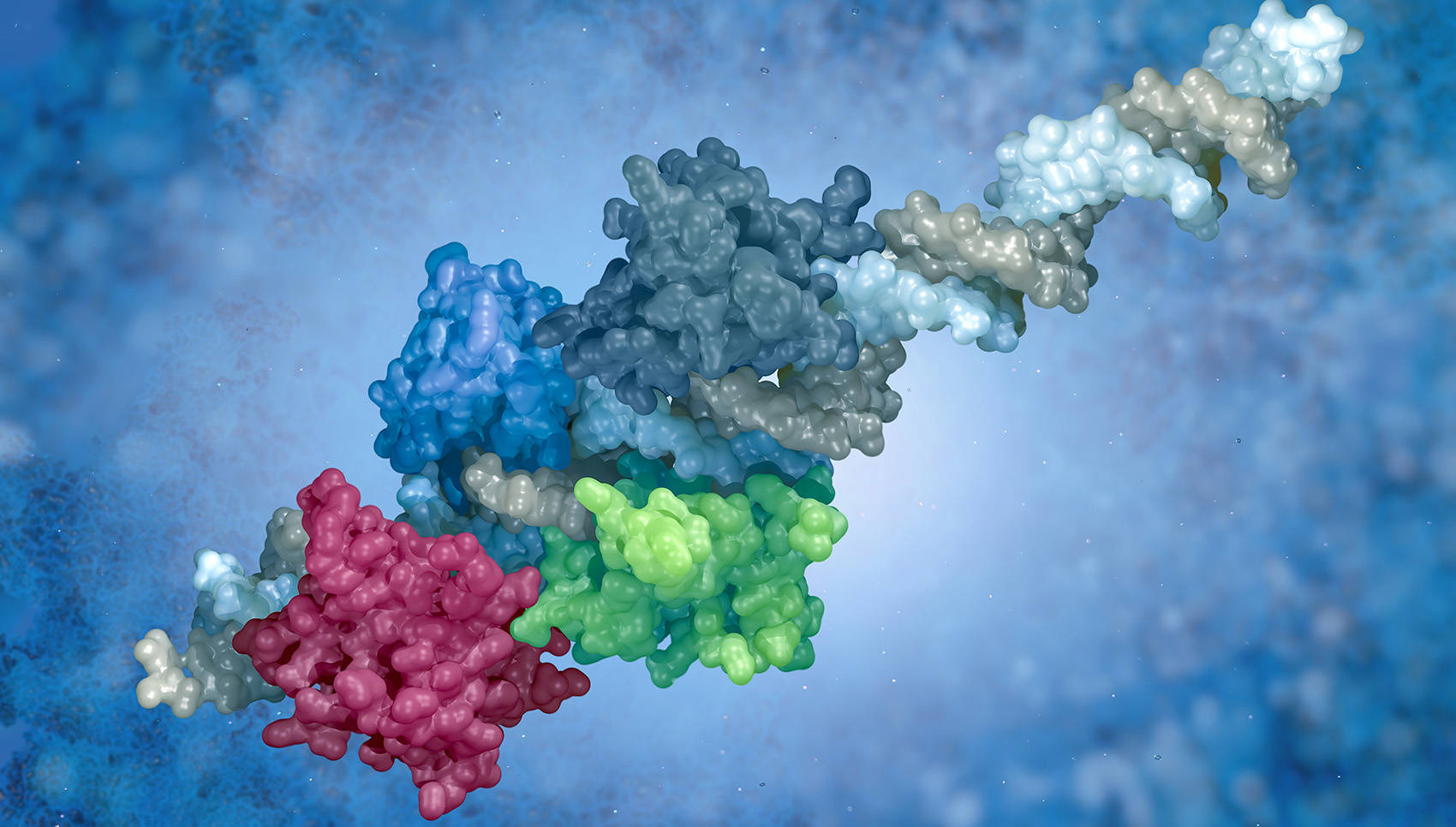
Multiple Applications of Post-Translational Modification (PTM) Analysis
The formation of PTM is a key source of protein complexity and diversity. These modifications regulate protein structure, activity, function, and cellular location, involved in a variety of normal cellular functions and disease pathogenesis.
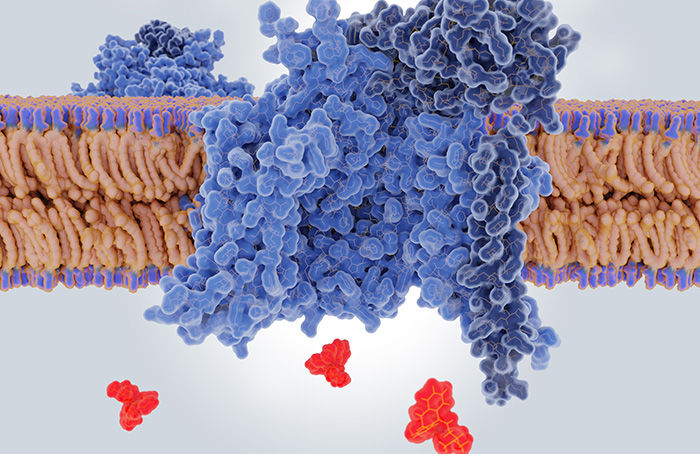

PTMs take part in various cellular processes, such as signal transduction, protein-protein interactions, cellular metabolism, protein trafficking, protein stability and localization, DNA repair, and more.
Read moreDisruption of PTMs can lead to the dysfunction of important biological processes, which can result in a variety of diseases. Thus, the footprints of PTM dysregulation can be seen in many diseases.
Read more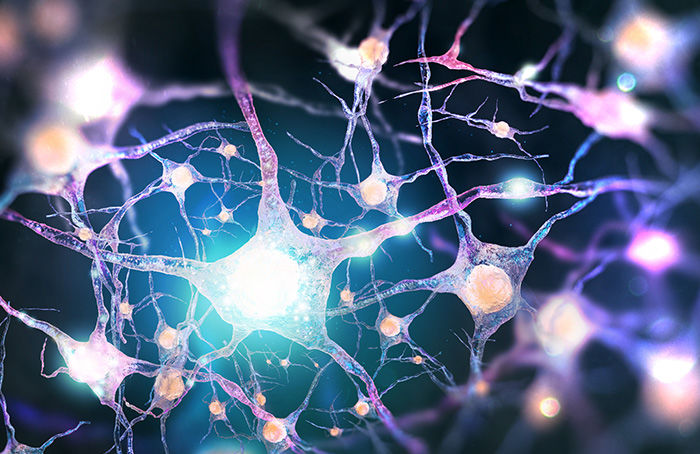

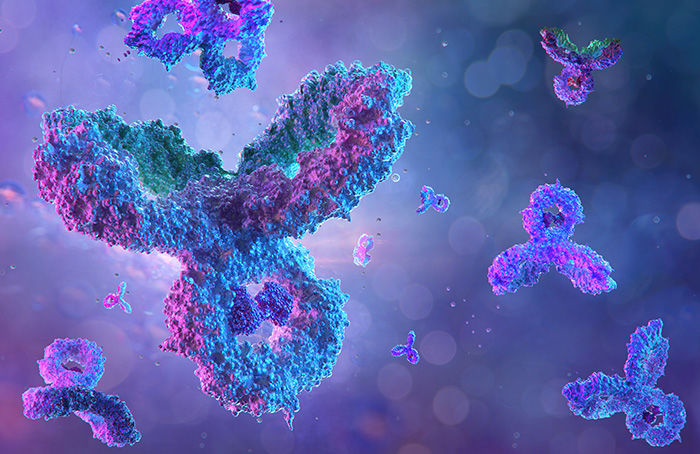

In addition to promoting biomarker discovery in a variety of disease conditions, research on PTMs has also facilitated the discovery and development of targeted drugs.
Read moreIn addition to eukaryotes, PTMs are widely found in microbiota, including bacteria and viruses. As one of the important strategies of microbiota for environmental adaptation, protein PTMs control a number of fundamental features of microbial biology by regulating protein complexity.
Read more



Protein PTMs play key roles in almost all plant biological processes, including plant signal transduction, metabolism, plant immunity and disease resistance, cell differentiation, and other cellular events.
Read more