
- Home
- Protein Post-Translational Modification Analysis Strategies
Creative Proteomics is a leading custom service provider in post-translational modification (PTM) proteomics analysis. With experienced scientists and technical staff and state-of-the-art technology platforms, we are committed to providing our clients with quality PTM analysis services.
MS-based proteomics is the method of choice for studying proteins and their PTMs. This sensitive technique allows not only the identification of previously unknown modification patterns but also the simultaneous determination of multiple isoforms of one protein with different modifications. To achieve a qualitative and quantitative analysis of various PTM, we mainly use MS-based proteomics methods, including bottom-up, middle-down, and top-down proteomics. Based on our customers' needs, we provide the best analytical strategies and solutions to facilitate biomarker discovery, disease research, protein biopharmaceutical characterization, and more.
We are now proud to offer a range of labeled and unlabeled proteomic-based methods and services for PTM quantification, including metabolic labeling, larger multiplexing chemical labeling, and other novel label-free quantification approaches such as DIA/SWATH. Based on a variety of PTM enrichment strategies and robust PTM analysis workflows, we are committed to helping our clients achieve accurate, efficient and flexible PTM analysis on a variety of complex samples, greatly accelerating the success of their projects.
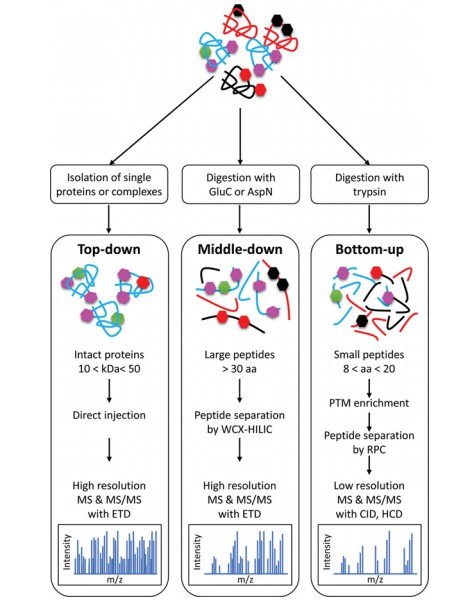 Fig. 1 Detection of PTMs by top-down and bottom-up MS approaches. (Smith, Lauren Elizabeth, and Adelina Rogowska-Wrzesinska, 2020)
Fig. 1 Detection of PTMs by top-down and bottom-up MS approaches. (Smith, Lauren Elizabeth, and Adelina Rogowska-Wrzesinska, 2020)
Due to the large number of potential modification sites on proteins, accurate localization of the modifications is a prerequisite for studying the regulation of protein function by the modifications. Currently, MS is the main method for protein PTM research. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) based analysis can accurately characterize the molecular mass of a protein or peptide and can detect which modifications have occurred at the site of the protein or peptide. Based on effective protein extraction methods, peptide separation and enrichment strategies, and advanced mass spectrometers, we are dedicated to providing protein PTM identification services, including the identification of a targeted PTM and the global profiling of PTMs within the proteome.
Due to the wide dynamic range of protein abundances, substoichiometric occupancy, and instability of PTMs, it is necessary to conduct enrichment strategies of the modified peptides prior to LC-MS/MS analysis. These modification-specific enrichment techniques are able to separate modified peptides from complex peptide mixtures, reducing sample complexity and improving the efficiency and reliability of the analysis. We apply a wide range of separation and enrichment methods to facilitate peptide separation in order to reduce sample complexity and expand PTM detection and coverage, including ion exchange chromatography (IEC), immunoaffinity precipitation, immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC), and so on.

Protein microarrays are miniaturized immunoassays with the ability to effectively analyze thousands of proteins/peptides without the need pre-isolate or enrich complex samples. This technique offers the advantage of quantitatively identifying protein PTMs in an unbiased manner under specific cellular conditions. We have established a high-quality antibody-based protein microarrays platform for the global profiling of a wide range of protein PTMs.
Creative Proteomics strives to be a guide and assistant in protein PTM research for our customers worldwide. Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day from Monday to Sunday. Contact us now for all the details!
References
Our products and services are for research use only.