- Home
- Applications
- Protein Post-Translational Modifications in Drug Discovery and Development
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) refer to new recognition patterns, enzyme activities, localization and protein turnover that control biological processes and therefore also define disease conditions. PTMs largely enrich the complexity of the proteome and clearly constitute a potential large subset of the biological space. In structure-based drug design, PTMs can be a bridge between an almost infinite chemical and biological space.
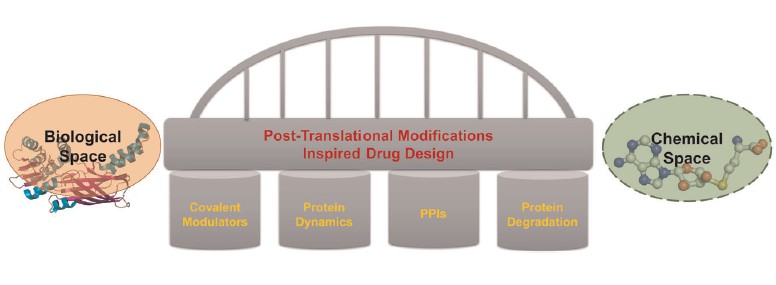 Fig. 1 Proposed PTMI‐DD could function as a bridge linking the infinite chemical space and finite biological space. (Meng, Fanwang, et al, 2021)
Fig. 1 Proposed PTMI‐DD could function as a bridge linking the infinite chemical space and finite biological space. (Meng, Fanwang, et al, 2021)
The formation of PTM is a key source of protein complexity and diversity. These modifications regulate protein structure, activity, function, and cellular location, involved in a variety of normal cellular functions and disease pathogenesis. In addition to promoting biomarker discovery in a variety of disease conditions, research on PTMs has also facilitated the discovery and development of targeted drugs. The introduction of PTM functional groups will greatly expand the target space for drug design and is highly selective. With the introduction of PTMs, two levels should be considered, including the effect of PTMs on protein structure and dynamics at the molecular level, and the analysis of protein-protein interactions at the system level.
| Involvement of PTMs in diseases | ||
|---|---|---|
| PTMs | Biological functions | Diseases |
| Phosphorylation | Cell signaling, transcriptional regulation, cell metabolism, apoptosis, immunological responsiveness, aging development. | Cancer, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, heart disease. |
| Acetylation | Chromatin stability, protein-protein interactions, cell cycle control, cell metabolism, nuclear transport, actin nucleation | Cancer, immune disorders, Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, cardiovascular diseases. |
| Methylation | Transcriptional regulation, signal transduction. | Cancer, mental retardation, diabetes mellitus, lipofuscinosis, occlusive disease. |
| Ubiquitylation | Transcriptional regulation, signal transduction, proliferation, DNA repair, intracellular trafficking, and degradation of the protein, cell proliferation and differentiation, myogenesis, stress response. | Cancers, metabolic syndromes, inflammatory disorders, type 2 diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases. |
| SUMOylation | Transcription control, signal transduction, chromatin organization, macromolecule accumulation, gene expression. | Cancer, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, viral infections, heart diseases, diabetes. |
| Glycosylation | Cell adhesion, cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, molecular trafficking, receptor activation, protein folding and signal transduction, protein degradation, protein solubility, protein intracellular trafficking and secretion. | Cancer, liver cirrhosis, diabetes, HIV infection, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis. |
| Palmitoylation | Protein function regulation, protein-protein interaction, membrane-protein associations, neuronal development, signal transduction, apoptosis and mitosis. | Huntington's disease, schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, different cancers. |
| Myristoylation | Cellular structure, stabilizing the protein structure maturation, signaling, extracellular communication, metabolism and regulation of the catalytic activity of the enzymes. | Cancer, epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease, Noonan-like syndrome, viral and bacterial infections. |
| Prenylation | Protein trafficking, protein-protein interactions, endocytosis regulation, cell growth, differentiation, proliferation. | Cancer, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disorders, bone diseases, progeria, metabolic diseases, neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Sulfation | Protein-protein interactions, visual functions, viral entry into cells. | Autoimmune diseases, HIV, lung diseases, multiple sclerosis. |

Protein PTMs plays essential regulatory roles in diverse pathological conditions. To accelerate the discovery of drugs for PTM related diseases, reliable and practical assays and platforms are required. Mass spectrometry (MS)-based on proteomic analysis continues to reveal the central role of PTM in various diseases, and technological advances have improved our ability to identify and characterize these site-specific modifications and to study their control and impact in pathogenesis, opening up new possibilities for chemical intervention and treatment of multiple diseases. Creative Proteomics is a leading custom service provider in PTM proteomics analysis. With a team of experts and state-of-the-art equipment, our PTM proteomics analysis platform can help our customers not only with drug discovery targeting PTMs and their structural isomers but also with the characterization of PTMs in the early stages of biopharmaceutical drug development. Our services are highly flexible and customizable. Please feel free to contact us for more details.
References
Our products and services are for research use only.