
- Home
- PTMs Proteomics
- Malonylation Proteomics
Lysine malonylation is a type of protein acylation modification that has been founded in eukaryotes and bacteria. Protein malonylation is the reversible addition of a malonyl group into a lysine residue, regulating protein stability, protein localization, enzyme activity, and so on. The regulatory role of lysine malonylation in many biological processes has been established in a variety of organisms such as affecting mitochondrial function, fatty acid synthesis, and energy metabolism. Given the potential importance of lysine malonylation, the identification and investigation of lysine malonylation sites are extremely urgent and may provide useful information for biomedical research. Creative Proteomics offers the lysine malonylation analysis service to identify malonylated proteins and lysine malonylation sites in proteins. We specialize in the analysis and identification of protein post-translational modifications (PTMs) based on high-resolution mass spectrometry (MS), aiming to provide quality and efficient solutions for our customers' research projects.
Lysine malonylation was first discovered in 2011 in mammals and Escherichia coli. This type of acylation modification requires malonyl-coenzyme A (CoA) as a substrate to be added to lysine residues, modulating protein structure and function by interfering with electrostatic interactions. As an evolutionarily conserved acyl modification, Lysine malonylation has been found to take part in modulating various cellular processes. Lysine malonylation is abundant in mitochondrial proteins that regulate metabolic pathways (e.g. glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation, and inflammation) in animal cells (e.g. endothelial cells and macrophages). Lysine malonylation has been reported to play an important role in metabolic processes and stress responses, and is closely associated with angiogenesis-related diseases, fatty acid oxidation, the associated genetic disease, and metabolic diseases (such as diabetes and inflammation).
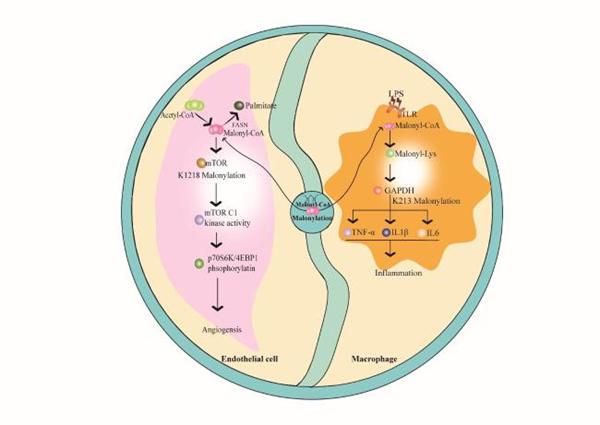 Fig. 1 Production of
malonyl-CoA and its regulation in malonylation. (Lu Zou, et al., 2022)
Fig. 1 Production of
malonyl-CoA and its regulation in malonylation. (Lu Zou, et al., 2022)
Due to the limitations of experimental techniques, it is a great challenge to fast and accurately identify malonylation sites. Creative Proteomics combines affinity enrichment and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis to provide comprehensive and accurate identification of lysine malonylated proteins and lysine malonylation sites in mammalian and plant cells. With our well-established platform, we can help our customers achieve the following lists:

Protein malonylation is an important member of the large family of acyl modifications. With continuous research, malonylation modifications have been found to be widely involved in important life activities of the organism, and gradually become a hot research topic in the life science field. You only need to place an order and send samples, we provide a one-stop protein malonylation analysis service. Please contact us if you are interested. We are looking forward to cooperating with you.
References
Our products and services are for research use only.