
- Home
- PTMs Proteomics
- SUMO Proteomics Analysis
Small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) is a conserved, reversible, and dynamic post-translational modification (PTM) of protein. Over the past 20 years, there have been more than 3,000 SUMOylated proteins identified in cells. This modification has been found to regulate the activity of proteins and thus affect many intracellular processes involved in the regulation of cellular physiological and pathological processes. Creative Proteomics is a leading service provider of PTM analysis. We have launched a powerful and high-throughput method combining stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC)-based quantitative proteomics and peptide enrichment strategies to analyze SUMOylated proteins and identify SUMOylation sites. Our services have a wide range of applications, including identifying unknown SUMO targets and characterizing changes in SUMOylome in response to drugs, toxins, environmental stresses, or bacterial and viral infections, helping researchers explore the role of SUMOylome in cell physiology and disease.
SUMOylation refers to the process by which a member of the SUMO family proteins binds to a lysine (Lys) residue in a target protein. This modified protein can be deSUMOylated by sentrin/SUMO-specific proteases (SENPs), which is controlled by an enzymatic pathway, similar to the ubiquitination pathway. Unlike ubiquitination, SUMOylation does not target proteins for protein hydrolysis, but rather regulates protein function in a variety of cellular processes, such as protein-DNA binding, protein stability, DNA repair, stress response, and cell cycle progression. In addition, accumulating evidence suggests that abnormal SUMO regulation is highly associated with a variety of diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. In recent years, SUMOylation has become one of the hotspots of research as a competitor to ubiquitination.
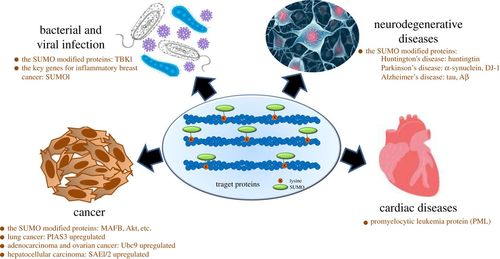 Fig. 1
Relationship of SUMO-modified proteins with different diseases. (Yang, Yanfang, et al., 2017)
Fig. 1
Relationship of SUMO-modified proteins with different diseases. (Yang, Yanfang, et al., 2017)
In order to help researchers and professionals better understand the role of protein SUMOylation modification, identify proteins modified by SUMO, and understand the exact sites of SUMO conjugation, we offer protein SUMOylation analysis services, ranging from protein processing, SUMOylated peptide enrichment, LC-MS/MS analysis, to various bioinformatics analysis. Since the low abundance of most SUMOylated proteins, the identification of SUMOylation has faced several challenges. Based on experienced experts and optimized workflows, we are able to provide faster and more sensitive SUMOylation analysis. Our services can help our customers achieve the following lists, including:
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Please feel free to contact us for more details.
References
Our products and services are for research use only.