
- Home
- PTMs Proteomics
- Glycoproteomics Analysis
- Quantitative Glycoproteomics Analysis Service
Glycosylation is present in approximately 50% of mammalian proteins and is involved in key physiological and pathological processes in human cells. It plays a crucial role in many cellular events such as signal transduction and receptor activation and is associated with many diseases, including glycosylated congenital diseases and cancer. To meet the increasing demand for the identification and quantification of glycoproteins at the proteome scale, Creative Proteomics offers quantitative glycoproteomics analysis service which is part of our integrated portfolio of glycoproteomics analysis services.
Since site-specific glycosylation has macro-heterogeneity (arises from the localization and occupancy of the glycosylation sites) and micro-heterogeneity (the diversity of the glycan structures expressed on a specific site), it is still a challenge for robust and reliable quantification of intact glycopeptides at the proteome scale. At present, a series of MS-based techniques for glycopeptide quantification have been developed. These techniques can be divided into two major parts, including labeling-based quantification and label-free quantification. The former strategy utilizes stable isotope labeling into amino acids or glycans on glycopeptides by chemical, metabolic or enzymatic means. These strategies can be further classified as isobaric chemical labeling (TMT/iTRAQ), isotopic chemical labeling (dimethyl labeling), metabolic labeling (SILAC), enzymatic labeling, and glycan labeling. In contrast, the label-free quantification method aims to quantify glycopeptides without the use of stable isotope labels. Label-free quantification can be divided into data-independent acquisition (DIA) and data-dependent acquisition (DDA)-based quantification depending on the MS acquisition methods.
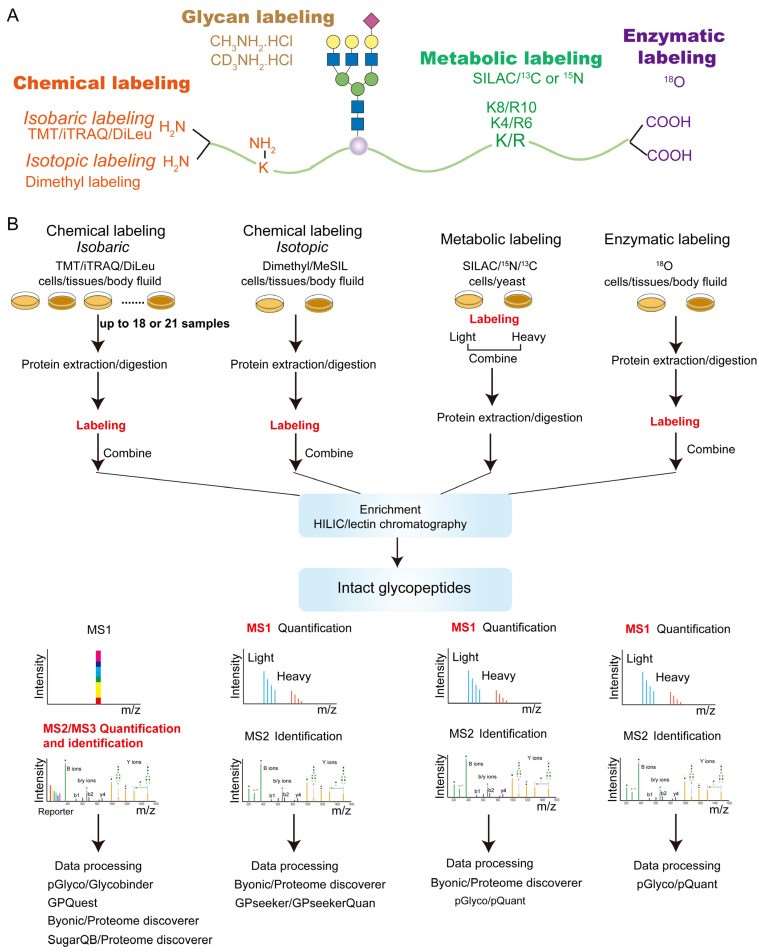 Fig. 1 Labeling-based strategies for quantitative glycoproteomics. (Fang, Pan, et al., 2022)
Fig. 1 Labeling-based strategies for quantitative glycoproteomics. (Fang, Pan, et al., 2022)
With advanced MS-based techniques, various glycopeptide enrichment strategies, and data analysis algorithms, our platform can improve the identification coverage and reliability of intact glycopeptides in complex biological samples. In general, target proteins are usually enriched for glycosylated peptides after enzymatic cleavage, followed by quantitative analysis of glycopeptides using chemical labeling, label-free, or DDA strategies. Our services allow the characterization and quantification of glycosylated proteomes in a wide range of complex samples.
| Methods | Principles | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Isobaric chemical labeling(TMT/iTRAQ) | React with amine on peptides. | High multiplexing capability; simple data analysis; reduced measurement time; applicable to any sample; reduced run-to-run variations; low missing values. |
| Isotopic chemical labeling (Dimethyl) | React with the carboxyl groups of peptides. | Low costs; simple in handling; applicable to any sample types. |
| Metabolic labeling (SILAC) | Metabolic labeling with amino acids containing stable heavy isotopes when culturing cells. | Allow in vivo labeling, minimize system errors; applicable to cells but can be expanded to tissues or model organisms using internal standards. |
| DDA-based LFQ | The number of identified glycopeptide spectra matches. | No labeling required; applicable to any sample; simplified sample handling. |
MS-based glycoproteomics has become an indispensable and highly sensitive tool for studying glycosylation changes in biological samples. Need help starting your quantitative glycoproteomics analysis? We look forward to hearing from you! Please use our contact form for general inquiries.
References
Our products and services are for research use only.