
- Home
- PTMs Proteomics
- Histone PTM Analysis
- Histone PTM Identification
In recent years, post-translational modifications (PTMs) of histones have become one of the hot spots in epigenetic research. To meet the needs of researchers to identify a wide range of histone post-translational modification types and to facilitate their in-depth research, Creative Proteomics offers histone post-translational modification identification services. Our specialized tools including advanced Mass spectrometry (MS)-based instruments and bioinformatics software, along with rational experimental design, rigorous conduction and quality assurance, will certainly accelerate our customers' histone PTM-related research.
The histones within cells are the building blocks of mammalian chromatin. Several different modifications can be covalently integrated into the histone and change its binding properties, such as phosphorylation, acetylation, and ubiquitination. As a key player in the regulation of chromatin function, histone PTMs have attracted great attention. Currently, two main mechanisms by which histone PTMs exert epigenetic regulation have been identified, one involving modifications that directly influence the chromatin structure and the other implicating the recruitment of chromatin-binding proteins by PTMs. Increasing evidence has shown that histone PTMs are related to a variety of cellular processes, including DNA damage, transcription, cell cycle regulation, and cell apoptosis. The abnormal patterns of histone PTMs can lead to defects in these cellular processes, which may result in human disorders (such as cancer, Alzheimer's disease, and autoimmune diseases), suggesting histone PTMs as novel targets for drug therapy.
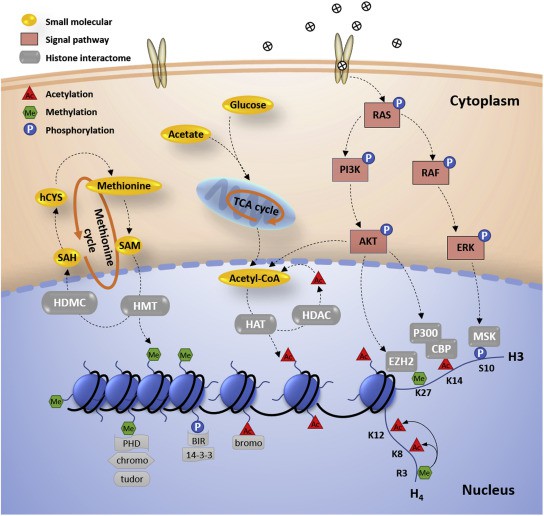 Fig. 1 Histone PTMs in epigenetic regulation. (Lu, Congcong, et al., 2021)
Fig. 1 Histone PTMs in epigenetic regulation. (Lu, Congcong, et al., 2021)
Mass spectrometry (MS) has emerged as a powerful tool in the field of PTM proteomics analysis due to its high throughput, accuracy, and flexibility. Based on MS-based proteomics in combination with various modified peptide enrichment approaches and distinct labeling strategies, we are able to help our global customers achieve comprehensive and unbiased analysis of histone PTMs. We are capable of identifying many different histone modifications, including common histone phosphorylation, acetylation, and methylation, but are not limited to them. Notably, in the process of identifying and analyzing histone PTM identification, we optimized the enzymatic digestion scheme by using a combination of different enzymes for protein samples to improve the peptide coverage of histones during MS analysis and to exclude the loss of histone PTM information due to inappropriate peptide length and low ionization efficiency.
Would you like to know more about our histone PTM identification service? We look forward to hearing from you! Please use our contact form for general inquiries. We will then forward your request to the right contact person.
References
Our products and services are for research use only.