- Home
- Applications
- Protein Post-Translational Modifications in Viruses
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) are critical for the regulation of various cellular processes. They play vital roles in protein maturation, activity, protein life span, and function. PTMs of viral proteins are essential for regulating viral biological processes, including the production of infectious viral particles, viral infection, and so on. The study of PTMs of viral proteins contributes to the identification of effective diagnostic markers and the development of antiviral drugs.
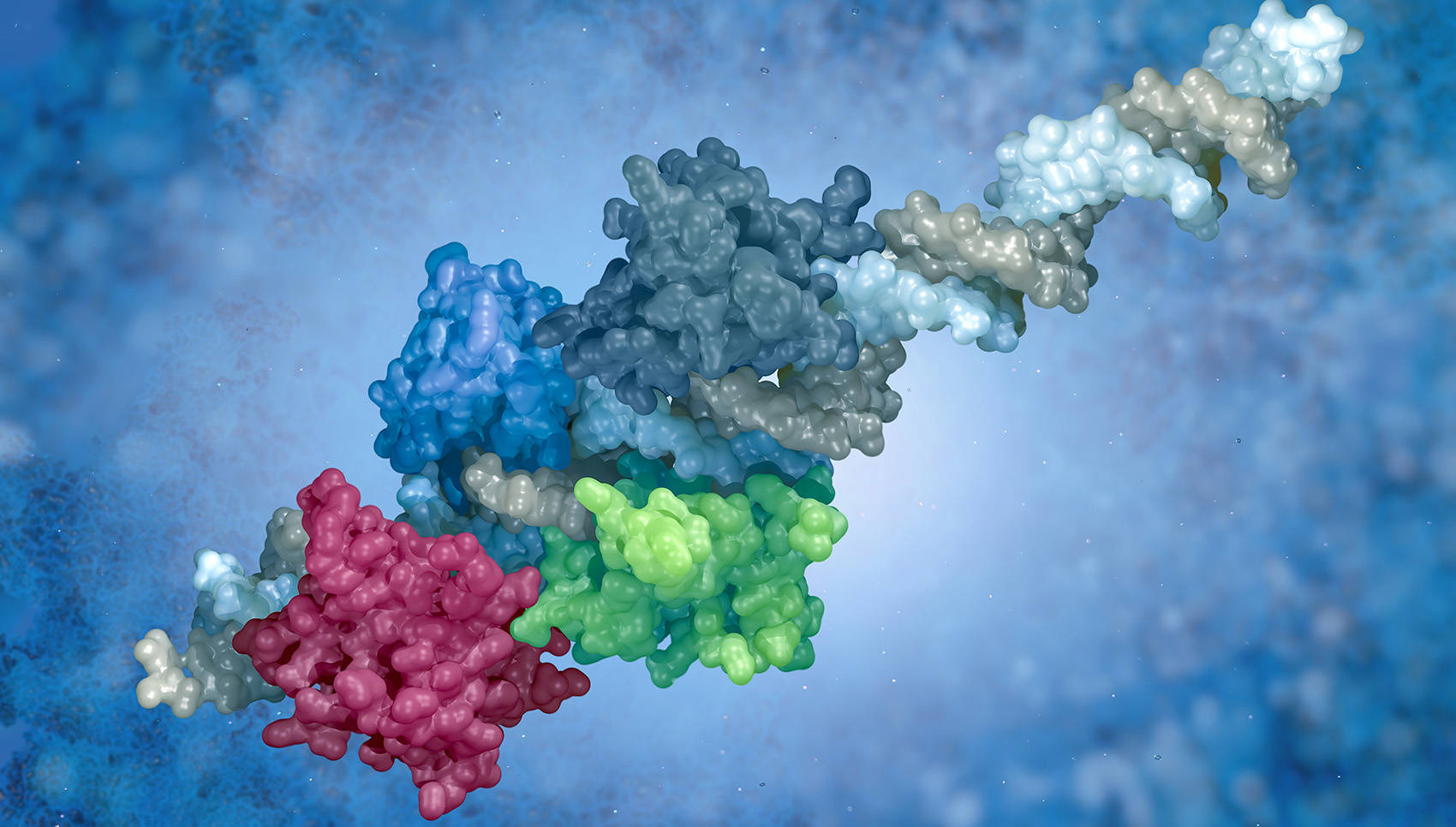
PTMs are present at all steps of the viral replication cycle, beginning with the signaling event of viral particle attachment to the host cell and continuing with the modification of the viral particle released at the end of the infection. Diverse PTMs have been shown to take part in many viral biological processes by regulating viral survival and proliferation. PTM sites and PTM pathways are potential diagnostic markers as well as pharmacological targets for antiviral drug development. There is much work to be done to unveil the precise PTM sites and the underlying mechanisms of viral proteins.
PTMs, including phosphorylation, glycosylation, acetylation, methylation, and ubiquitination have been proven to play important roles in HBV replication, transcription, and immune evasion. The targets of these modifications include not only the viral essential proteins but also host-related components. In addition, PTMs also have been reported to control processes of HBV-related liver diseases, including hepatocarcinogenesis.
PTMs of HCV viral proteins ensure proper protein functions by regulating protein subcellular localization, activity, and protein-protein interactions, such as phosphorylation, glycosylation, methylation, palmitoylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, and disulfide bridging. These PTMs of HCV proteins are not only essential for the production of HCV virion but also play a regulatory role in virus replication.
PTMs occur during all steps of the influenza replication cycle, including the viral entry, RNA synthesis, and virion assembly phases. There is a diverse array of PTMs of influenza virus, most notably phosphorylation, ubiquitination, glycosylation, SUMOylation, acetylation, acylation, NEDDylation, ISGylation, and ADP-ribosylation. Notably, influenza viruses do not encode any proteins that perform PTM and therefore rely exclusively on host enzymes for post-translational control.
Coronaviruses (CoV) are a group of enveloped RNA viruses that can cause disease in humans and animals. There are many PTMs identified in CoV proteins, such as glycosylation, phosphorylation, palmitoylation, and ADP-ribosylation. Spike and envelope proteins are modified by glycosylation and palmitoylation, membrane proteins are modified by N- or o-linked glycosylation, nucleocapsid proteins are modified by phosphorylation and ADP-ribosylation, and non-structural and accessory proteins are modified on other PTMs. PTMs have an important role in the function of coronavirus proteins. For example, N-linked glycans are not only an important component of protein mass, profoundly affecting the conformation of mature S proteins and their binding to surface receptors, but also facilitating the folding and intracellular transport of coronavirus S proteins. Moreover, coronavirus proteins have been reported to be subjected to various PTMs by the host cells, including glycosylation of transmembrane structural proteins, non-structural proteins and accessory proteins. Conversely, coronaviruses also interfere with host protein PTMs through multiple mechanisms.
Creative Proteomics is a leading custom service provider in PTM proteomics analysis. We are able to provide reliable and customized mass spectrometry (MS)-based PTM analysis services to accelerate customers' virus research in a comprehensive manner. Our team of experts can confidently and comprehensively identify many PTMs beyond simple phosphorylation of viral proteins, including acetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, glycosylation, and other historically intractable protein modifications. Our services are customer oriented and dedicated to providing a cost-effective and high-quality service experience. Please feel free to contact us for more details.
References
Our products and services are for research use only.