
- Home
- PTMs Proteomics
- N-Terminal PTM Analysis
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) play an essential role in modulating protein activity, stability, subcellular localization, function, and protein-protein interactions. PTMs greatly expand the diversity and function of proteome and are the major level of modulations of the total outcome of living cells. Many protein PTMs occur at the protein termini that contain reactive amino- (N-termini) and carboxy-groups (C-termini) of the polypeptide chain. Creative Proteomics provides N-terminal PTM analysis service. Our service performs systematic studies of protein N-terminal PTMs, which can contribute to an in-depth understanding of the multifunctional roles played by proteins in a variety of biological processes.
Proteins with distinct N- and C-termini have specific biochemical properties and functions and are collectively referred to as protein terminome. Protein N-termini, as the beginning of translation, has a major impact on the protein's biological functions. Its sequence and various PTMs often affect protein activation, stability, and cellular localization. Each translated protein initially contains an N-terminal Met because the ribosome recognizes the AUG codon as the translation initiation site. Specialized intracellular machinery removes such residues co- or post-translationally, making the N-terminus a reactive residue and available for many modifications. Moreover, the removal of the signal peptide also facilitates the exposure and modification of the residues at the N-terminal termini. The modifications of protein termini have been shown to be associated with different normal and disease-related processes and constitute a rapidly emerging field of biological regulation.
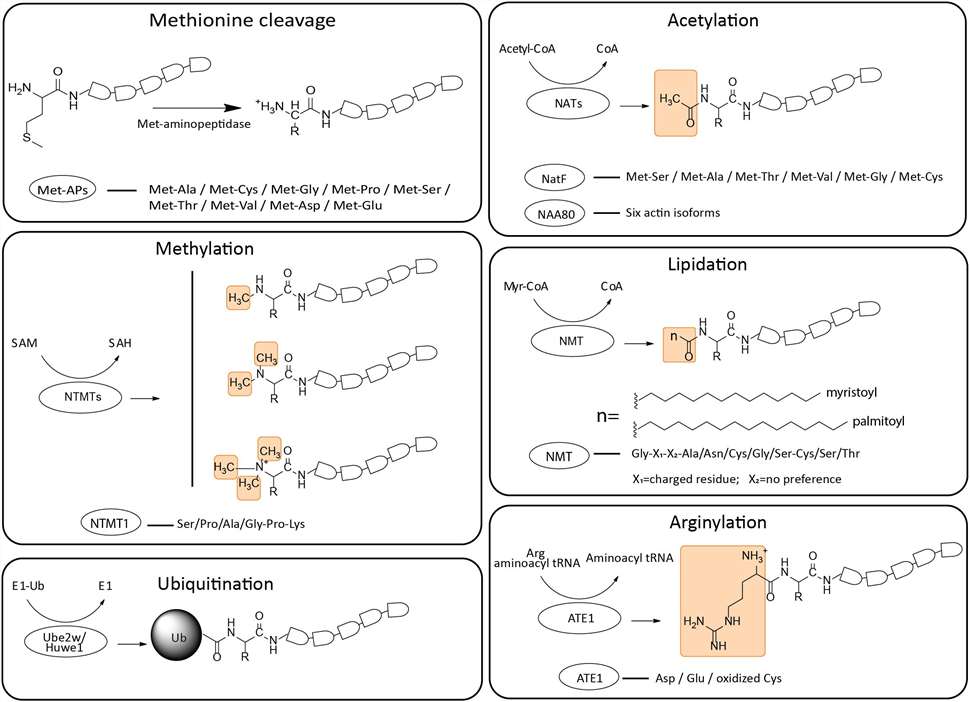 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of structural formulas and enzymatic preferences of N-terminal modifications. (Chen, Li, and Anna Kashina, 2021)
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of structural formulas and enzymatic preferences of N-terminal modifications. (Chen, Li, and Anna Kashina, 2021)
With the combination of specific enrichment strategies and mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis methods, we can identify and quantify the N-termini of proteins, explore the amino acid sequence of the protein N-termini, the PTMs that have occurred, and other information. Since the proportion of N-terminal peptides is low in complex samples, we provide specific strategies for the enrichment of N-terminal peptides, including affinity capture, strong cation exchange chromatography (SCX), and other positive enrichment strategies. These methods can greatly improve the effectiveness of identifying N-terminal peptides. Our rigorous and systematic experimental process minimizes sample degradation during extraction, preparation and labeling, and reduces the loss of N-terminal peptides during enrichment. Specifically, our services support systematic N-terminal PTM analysis, but are not limited to N-terminal acetylation, N-terminal lipidation, N-terminal methylation, arginylation, and N-terminal ubiquitination.
Creative Proteomics is a leading custom service provider in PTM proteomics analysis. We are dedicated to accelerating customers' research in a comprehensive manner. If you are interested in our N-terminal PTM analysis service, please feel free to contact us for more details.
References
Our products and services are for research use only.