
- Home
- Technology
- PRM Analysis of Post-translational Modification Site
Protein post-translational modifications (PTMs) play important roles in regulating protein functions and cellular processes. Identification and verification of PTM sites is critical for understanding their functional implications. Among various proteomics techniques, targeted mass spectrometry-based approaches such as Parallel Reaction Monitoring (PRM) have emerged as powerful tools for PTM site verification.
Creative Proteomics provides PRM (parallel reaction monitoring) service a targeted protein analysis technology based on LC-MS/MS, which can specifically detect target post-translationally modified peptides, thereby realizing target modified protein/peptide Relative or absolute quantification with high specificity and accuracy.
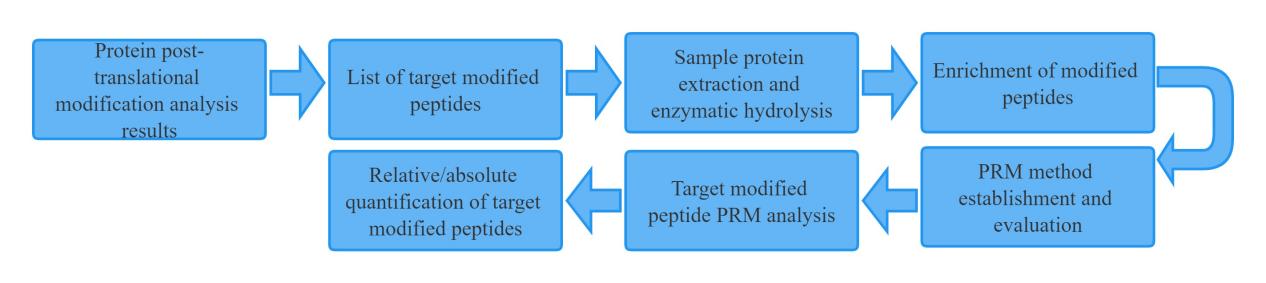
Sample preparation: We provide sample preparation protocols optimized for various sample types, including tissues, cells, and biological fluids.
PRM assay development: We design and optimize PRM assays for specific proteins of interest, using our expertise in mass spectrometry-based proteomics.
Sample multiplexing: We use isobaric labeling techniques such as TMT or iTRAQ to enable the multiplexing of up to 10 samples in a single analysis.
PRM analysis: We perform PRM analysis on a high-resolution mass spectrometer to detect and quantify the target proteins in each sample.
Data analysis: We provide comprehensive data analysis, including peak integration, normalization, statistical analysis, and visualization of the results.
Principles of PRM Analysis
| WB/ELISA | PRM | |
|---|---|---|
| Experimental Principle | Antigen-antibody recognition is used to indirectly detect the concentration of the target protein/peptide by detecting the antibody content. | Mass spectrometry is used to directly quantify the target protein/peptide by identifying its mass characteristics. |
| Interference factors | The antigen epitope specificity and the non-specific recognition of the antibody itself. | The abundance of the target protein/peptide is also a factor. |
| Detection range | Species limitations | No species limitations |
| Detection throughput | One target protein per experiment | Twenty proteins per experiment |
| Standard Data Analysis Contents | Data analysis content |
|---|---|
| Ion chromatogram | Ion chromatogram of target peptide |
| quantitative differential analysis | PRM-based quantitative analysis of target peptide |
| Quantitative results of target peptide and protein | |
| Univariate statistical analysis, such as t-test |
| Sample Type | Recommended Amount | |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Tissue | brain, heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, muscle, skin, etc. | 50mg-2g |
| Plant Tissue | Leaves, flowers, etc. of woody plants, herbaceous plants, algae, ferns, and large fungi, etc. | 200mg-2g |
| Microorganisms | Bacteria | 100mg-20g |
| Cell Samples | Suspension/adherent cultured cell | 2-10×10^7 |
PTMs omics + PRM analysis
Reference
Our products and services are for research use only.