By the Creative Proteomics Team — Senior proteomics scientists with Orbitrap/DIA expertise; PTM proteomics group.
GEO Executive Summary — Kinases and phosphatases maintain a dynamic equilibrium that encodes cellular decisions in seconds. Once a sample is collected, endogenous phosphatases can rapidly reshape phosphosite occupancy unless the system is quenched immediately. This Best Practice SOP provides a step-by-step plan to preserve reversible protein phosphorylation for LC–MS/MS phosphoproteomics: pre-stage cold-chain logistics, act within the “30-second Golden Window," select MS-compatible inhibitor cocktails or deploy heat stabilization for larger tissues, and verify success with sentinel sites (p-AKT, p-ERK) and Orbitrap-based XIC checks. The practical decision tree and QC targets (validated-site CV ≤10%) help teams secure audit-ready datasets.
Key takeaways
- Preserve native states fast: quench within the “30-second Golden Window" using ice-cold inhibitor-containing lysis or device-based heat stabilization.
- Use MS-compatible inhibitor recipes and plan desalting to remove anions before IMAC/TiO2.
- Apply a pragmatic decision tree: chemical inhibition for small/fast workflows; heat stabilization for large, high-phosphatase tissues.
- Verify preservation with sentinel phosphosites (p-AKT, p-ERK), recovery benchmarks, and intra-batch CV targets (≤10% for validated sites).
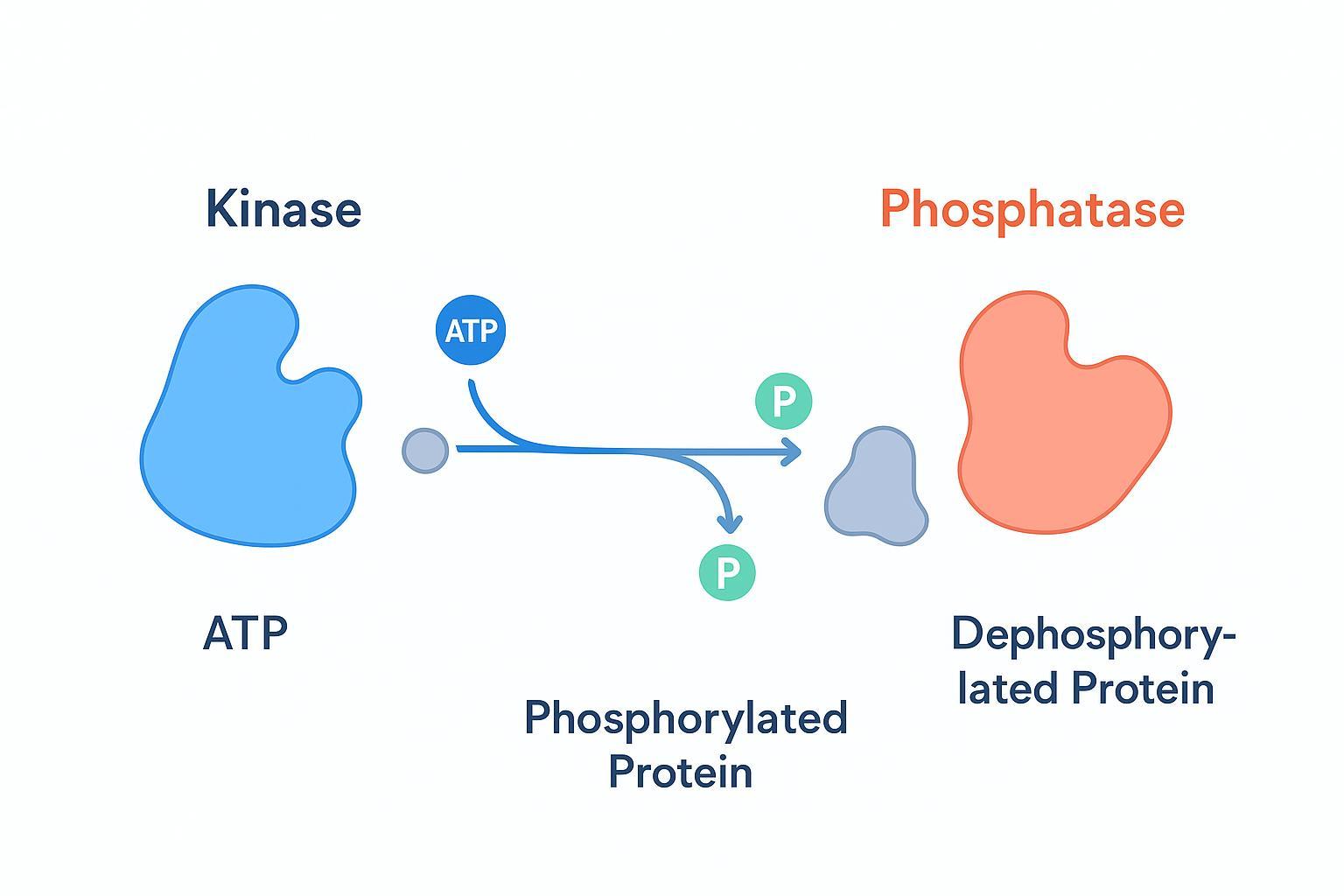
The Yin and Yang of Cell Signaling: Protein Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation
Signal transduction hinges on the rapid, reversible interplay between kinases adding phosphate groups and phosphatases removing them. That push–pull balance dictates whether a pathway is primed, attenuated, or terminated.
Kinetic Balance in Signal Transduction Pathways
Kinase and phosphatase activities operate on overlapping timescales. Perturbations—growth factors, stress, or drug exposure—tip the balance briefly, then feedback loops restore homeostasis. The catch: post-sampling, the balance keeps shifting unless you freeze it in place. Studies emphasize sub-minute quenching because phosphorylation states can change within seconds; ice-cold handling or immediate stabilization minimizes artifactual drift, as noted in a protocol detailing rapid phosphoproteome dynamics in seconds according to the 2023 DIA phosphoproteomic workflow.
Biological Consequences of Phosphatase Hyperactivity
Unchecked phosphatase activity after sampling can blunt signaling in lysates, especially at low-stoichiometry sites.
Signal Attenuation vs. Signal Termination
Attenuation reduces amplitude without fully switching off a pathway; termination collapses downstream signaling altogether. In practice, both can be induced ex vivo if samples sit warm: enzymatic turnover accelerates at room temperature compared to ice, reinforcing the need for cold control during preparation, as general enzymology examples demonstrate in 2022 and 2024.
Impact on Phospho-site Occupancy and Data Interpretation
Losses are not uniform. Labile sites disappear first, skewing apparent pathway activity and fold-changes. Normalization can mask these losses unless inhibition is verified—pilot checks with sentinel phosphosites help avoid misleading conclusions.
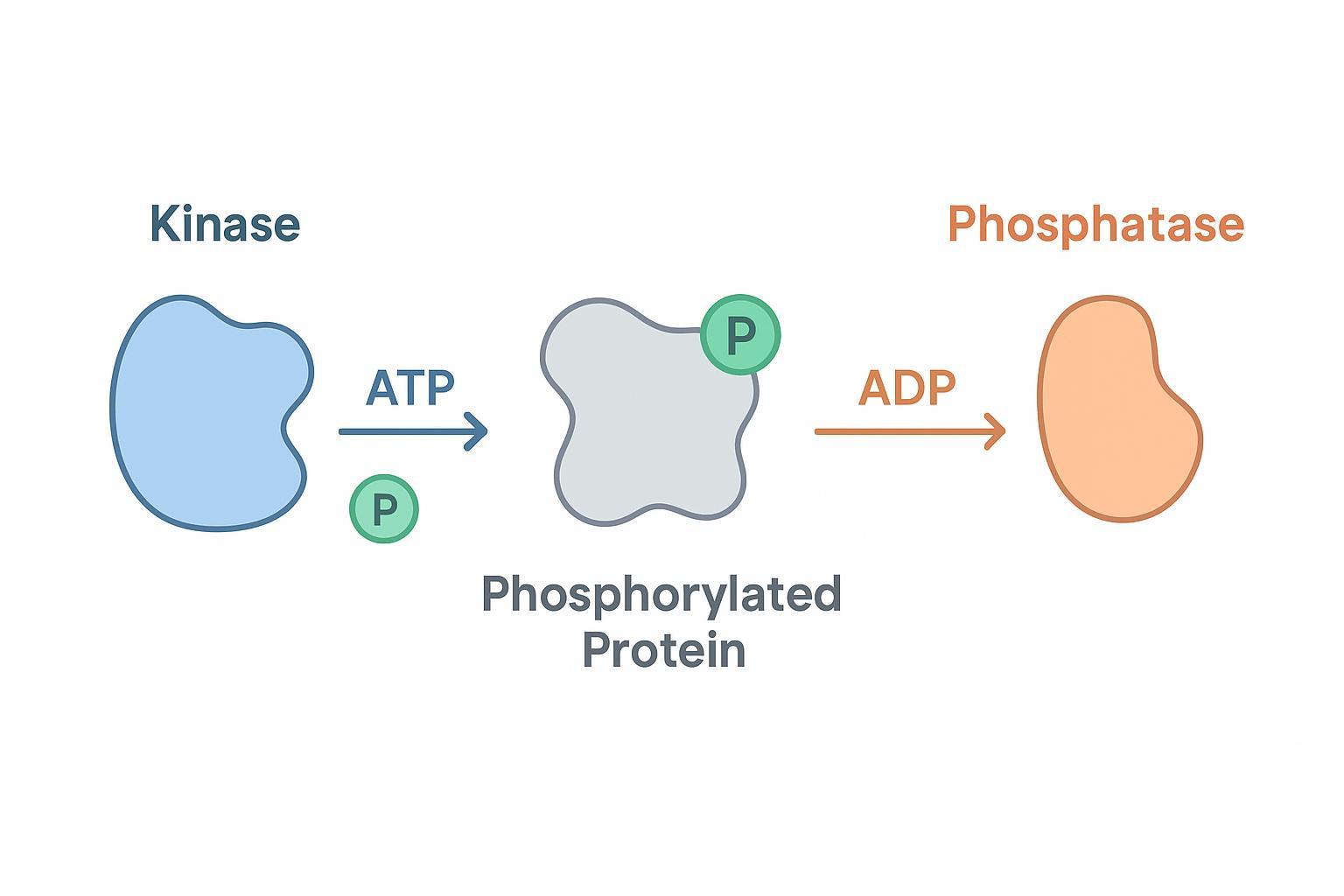 Figure 1: The dynamic equilibrium of protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation governing cellular signal transduction.
Figure 1: The dynamic equilibrium of protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation governing cellular signal transduction.
The Dephosphorylation Crisis: Why Your Quantitative Results May Be Underestimated
Post-Sampling Signal Degradation: The Silent Data Killer
From excision to lysis, every second counts. If stabilization lags, phosphatases reshape occupancy. The net effect is reduced signal-to-noise, fewer confident identifications, and distorted effect sizes.
Quantifying the Rate of Dephosphorylation in Raw Lysates
Exact half-lives vary by tissue and site, but the trend is clear: warmer, longer exposures favor dephosphorylation. In pilot designs, pair an “uninhibited" aliquot and an “inhibited" aliquot and track area ratios for sentinel phosphopeptides by Orbitrap XICs to quantify preservation.
S/N Ratio Decline and Loss of Low-Abundance Phospho-sites
Labile, low-abundance phosphopeptides drop below detection first, shrinking identifications disproportionately. Expect broader peaks and lower intensities in uninhibited controls.
The Fallacy of Normalization without Phosphatase Inhibition
Global normalization cannot recover erased phosphosites. Validate inhibition first, then normalize. Use sentinel peptides to confirm that the biological signal is preserved before downstream statistics.
SOP Guide: How to Prevent Dephosphorylation during Sample Pre-treatment
The Chemist's Shield: Selection and Use of Phosphatase Inhibitors
Choose MS-compatible inhibitors and prepare stocks correctly. Sodium orthovanadate (Na3VO4) is widely used to preserve tyrosine phosphorylation. Prepare and activate carefully: dissolve in water, adjust pH to ~10, boil until colorless, cool and readjust pH; repeat until stable, then aliquot and store. Before use, heat at ~95 °C for ~15 minutes to depolymerize, cool on ice, and mix into the lysis buffer. Method papers and product notes describe these steps, including Na3VO4 preparation guidance (2022, 2023).
- Typical working ranges (tune empirically by matrix and downstream cleanup):
- Na3VO4 ~1 mM
- Sodium fluoride (NaF) ~10–50 mM
- β-glycerophosphate ~10–50 mM
- Sodium pyrophosphate ~5–10 mM
- Optional okadaic acid (PP1/PP2A) 50–200 nM (use with caution)
Note: Anionic inhibitors can compete with phosphopeptide binding in IMAC/TiO2 and suppress ionization. Plan rigorous desalting prior to enrichment.
Cocktails vs. Single Inhibitors (Sodium Orthovanadate, Fluoride, Pyrophosphate)
Cocktails broaden coverage across phosphatase classes and are preferred for complex tissues. Single-agent approaches (e.g., vanadate-only) may suffice for targeted tyrosine-focused studies but risk incomplete preservation. Validate with sentinel sites.
Optimized Concentrations for Different Tissue Matrixes (Brain, Liver, Tumor)
Matrix-specific tuning is recommended. As a starting point, use the ranges above and perform pilot XIC checks in each matrix. For brain tissue with high endogenous activity, consider slightly higher NaF/β-glycerophosphate within the given ranges and prioritize aggressive desalting before IMAC/TiO2.
Temperature Control and Rapid Lysis Strategies — The Golden 30 Seconds
Act within ≤30 seconds from excision or pellet retrieval:
- Pre-chill everything (tubes, rotors, pestles) and stage ice-cold lysis buffer with inhibitors.
- For small samples: add 3–5 volumes of inhibitor-containing lysis immediately; keep on ice.
- For solid tissues: snap-freeze in liquid nitrogen within 30 seconds or heat-stabilize on device, then store at −80 °C until processing.
- Homogenize at 4 °C; clarify by cold centrifugation; proceed to proteolysis.
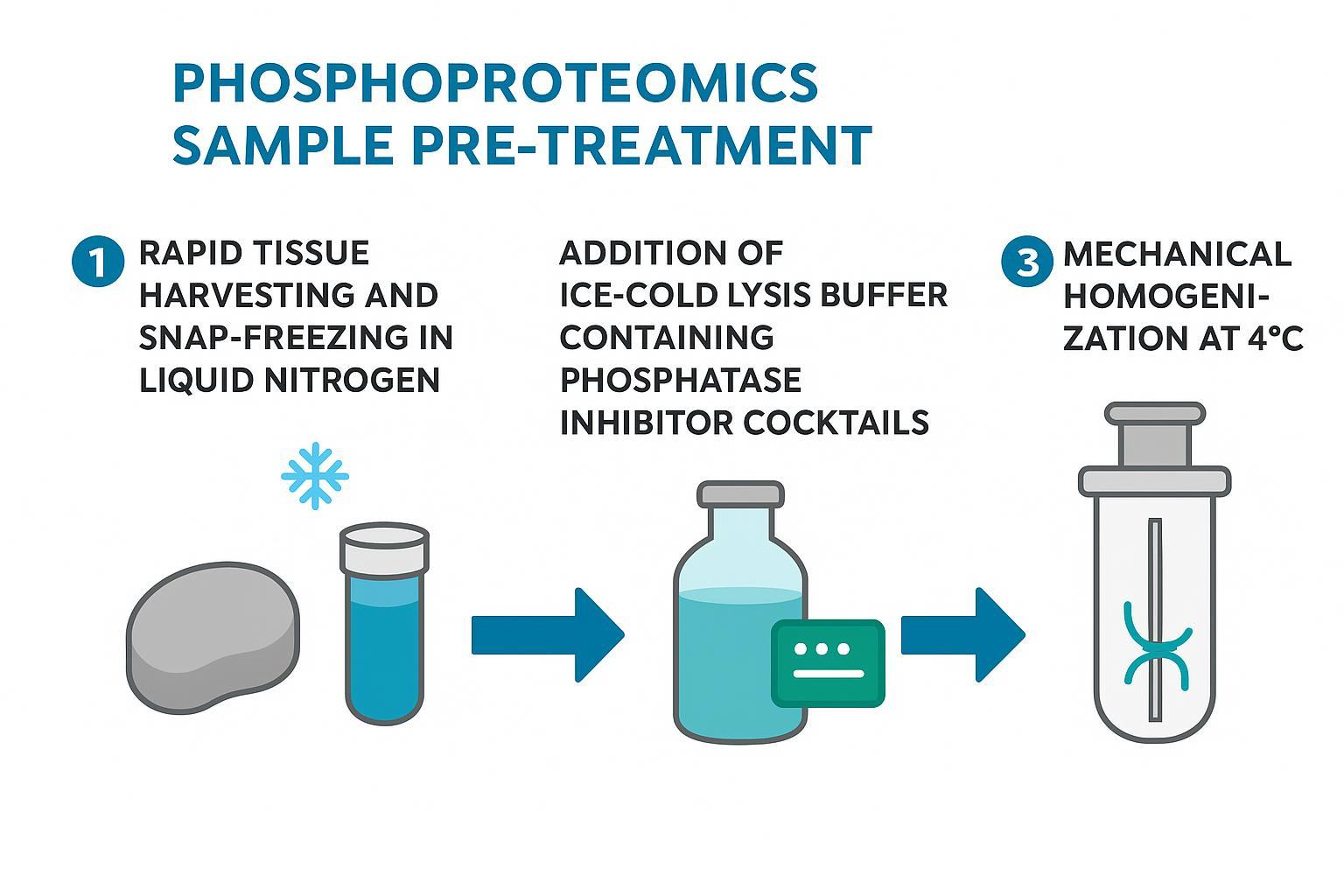 Figure 2: Optimized sample pre-treatment SOP to preserve reversible protein phosphorylation for high-accuracy proteomics.
Figure 2: Optimized sample pre-treatment SOP to preserve reversible protein phosphorylation for high-accuracy proteomics.
Methodological Reliability: Measuring the Efficiency of Signal Preservation
QC Metrics for Assessing Phosphatase Inhibition Success
Define acceptance targets up front and keep them auditable.
Monitoring Sentinel Sites: Stability Benchmarks for p-AKT and p-ERK
Use p-AKT (T308/S473) and p-ERK (T202/Y204) phosphopeptides as sentinel signals. Expect higher, sharper XIC peaks in stabilized samples. Record precursor m/z, charge state, retention time windows, and area ratios (inhibited vs uninhibited).
Recovery Rates and Intra-batch CV% Targets (≤10% for Validated Sites)
For validated sentinel peptides, target intra-batch CV ≤10% when instrument performance and workflow stability allow—Orbitrap DIA methods commonly achieve median RSDs near ~11–13% across phosphosites in recent studies, supporting tight QC. See reproducibility context in Orbitrap DIA performance reports (2024) and DIA acquisition guidance (2024).
As external benchmarks, modern Orbitrap/DIA workflows report technical replicate CVs of roughly 8–15% pre-correction and commonly achieve <10% after normalization, supporting the ≤10% sentinel goal. See reproducibility data from Lancaster 2024 Orbitrap DIA performance and deep‑coverage single‑run reports using the Orbitrap Astral (2024) for identification depth context.
Orbitrap-Based Verification of Labile Site Stability
Verify with paired aliquots (uninhibited vs inhibited or heat-stabilized). Inspect XICs for sentinel peptides and quantify area ratio improvements. Retain settings (model, gradient, DIA windowing) for audit. QC frameworks suggest longitudinal system suitability and internal standards to maintain CVs—see a 2024 QC framework overview.
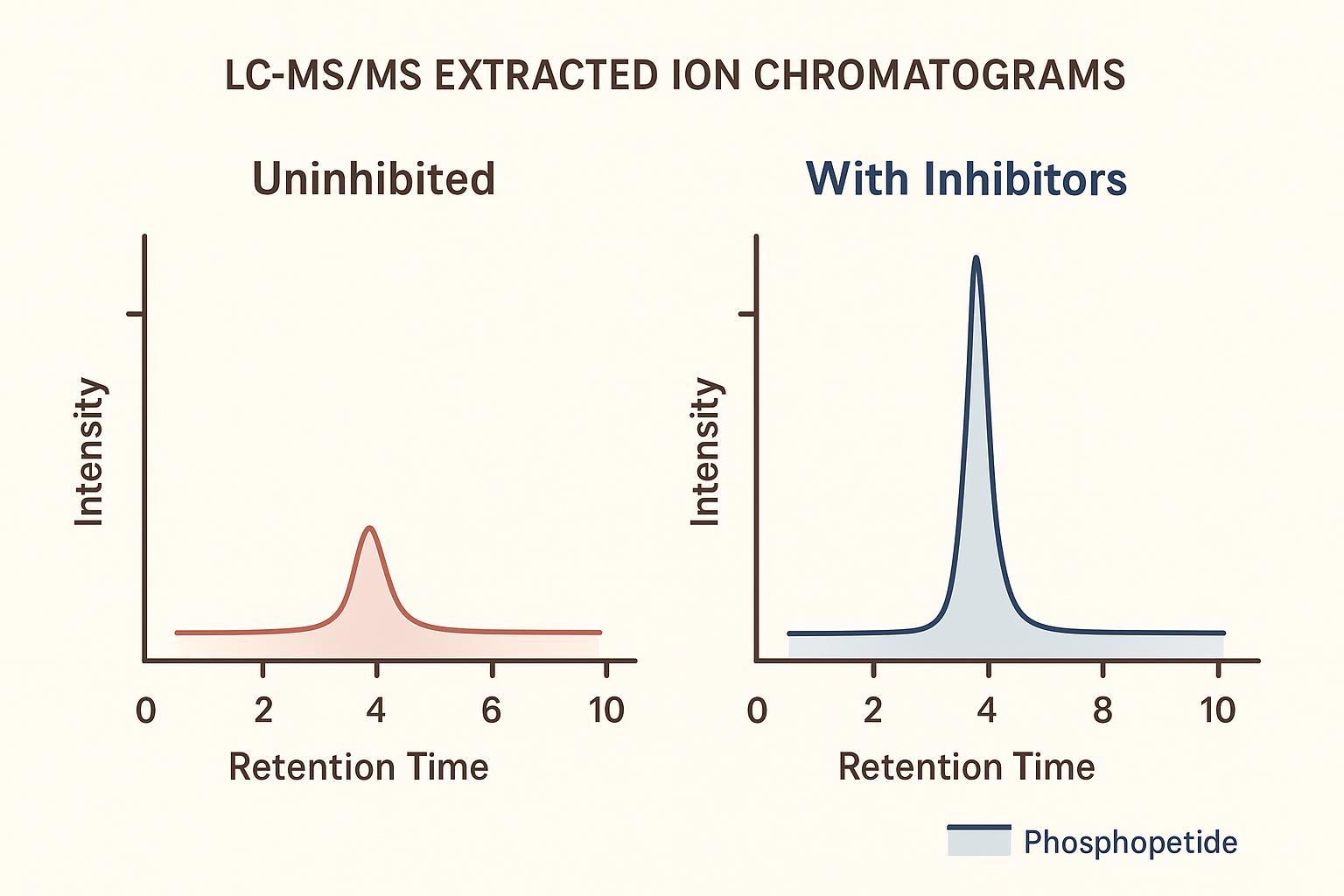 Figure 3: Mass spectrometry evidence demonstrating the impact of proper inhibition on protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation analysis.
Figure 3: Mass spectrometry evidence demonstrating the impact of proper inhibition on protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation analysis.
Chemical Inhibition vs Heat Stabilization — A Practical Decision Tree
- If you can place the sample into ice-cold, inhibitor-containing lysis within ≤30 seconds → choose chemical inhibition; plan desalting prior to enrichment (IMAC/TiO2).
- If the tissue piece is large (>100 mg) or has very high endogenous phosphatase activity (e.g., brain) and rapid lysis is impractical → choose heat stabilization at point-of-collection or snap-freeze immediately and pulverize under liquid nitrogen before inhibitor-containing lysis.
- If downstream enrichment is highly sensitive to anions and cleanup capacity is limited → favor heat stabilization or validate stronger desalting to offset inhibitor effects.
For more background on end-to-end workflows, see the internal resource on phosphoproteomics workflow.
CRO Insights: Managing Large-Scale Cohorts with Consistent Data Integrity
Milestone Management: From Cold-Chain Logistics to Transparent Reporting
Coordinate SOPs across sites; standardize timestamps for collection and stabilization; ship on dry ice; predefine acceptance criteria and reporting templates.
Data Governance: Ensuring NDA-Compliant Audit Trails for Clinical Samples
Use chain-of-custody forms, versioned SOPs, and instrument logs. Keep inhibitor recipes and QC outcomes in the audit trail; protect PII under NDA.
Future Directions: Real-time Phospho-stabilization Technologies
Heat Stabilization vs Chemical Inhibition: Pros and Cons
Heat stabilization can inactivate enzymes without adding anionic inhibitors but may introduce denaturation artifacts; chemical inhibition is flexible and low equipment but demands thorough cleanup. Comparative LC–MS/MS studies are limited; teams should validate locally.
External benchmarking
Thermal proteome profiling documents phospho‑isoform stability shifts (Smith et al., 2021 TPP; Burtscher et al., 2024 TPP integration), while chemical‑inhibitor studies report signaling preservation in cells/tissues (Eguchi et al., 2024). We found no peer‑reviewed, multi‑tissue Orbitrap/DIA head‑to‑head quantitative comparisons.
Integrating Global Protein Phosphorylation Databases for Baseline Normalization
Baseline maps can contextualize site occupancy and help flag unexpected losses. Combine sentinel-site monitoring with public datasets to improve interpretation.
Practical micro-example (neutral, disclosed)
Disclosure: Creative Proteomics is our product. In a recent internal QC run on an Orbitrap platform, we paired uninhibited and inhibitor-treated aliquots from pilot tissues and monitored p-AKT and p-ERK sentinel peptides. The inhibited aliquots consistently showed sharper, higher-intensity XIC peaks and lower intra-batch CVs for validated sites (≤10%) relative to uninhibited controls. Detailed XIC images and anonymized QC tables are available to clients under NDA. For general preparation guidance, see Phosphoproteomics Sample Preparation and Troubleshooting common pitfalls.
How to stop dephosphorylation in 30 seconds: pre-stage ice-cold inhibitor-containing lysis; add 3–5 volumes immediately upon excision for small samples; else snap-freeze or heat-stabilize at collection, then process at 4 °C.
Next steps: For audit-ready phosphoproteomics projects, explore the Phosphoproteomics Service to align SOPs, QC targets, and reporting templates.
Our products and services are for research use only.