
- Home
- PTMs Proteomics
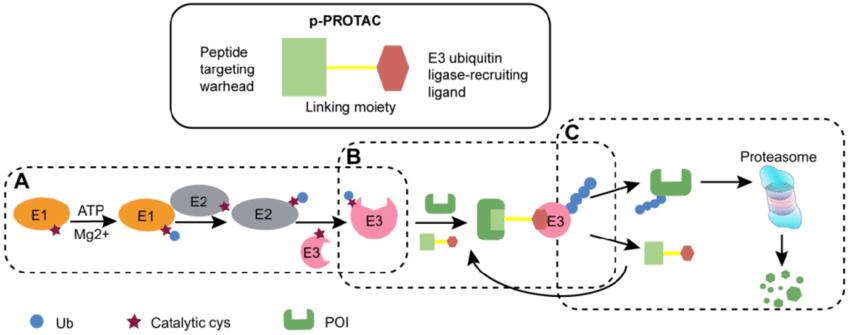
- Modificated PROTACs Proteomics Service
- PROTAC Efficacy Evaluation Service Using Ubiquitination Proteomics
Protein ubiquitination modification is an important post-translational modification that plays a crucial role in protein localization, metabolism, functional regulation, and degradation. It is involved in various cellular processes, including cell cycle, proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, transgene expression, transcriptional regulation, signal transduction, damage repair, inflammation, and immunity. Ubiquitination is closely associated with the development of tumors, neurodegenerative disorders, muscle malnutrition, immune diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic syndromes. Due to the low abundance and wide dynamic range of post-translational modified proteins in biological samples, enrichment of the modification is required prior to mass spectrometry analysis to enhance its abundance. Then, traditional quantitative proteomic approaches are employed to quantitatively analyze the enriched ubiquitinated peptide samples.
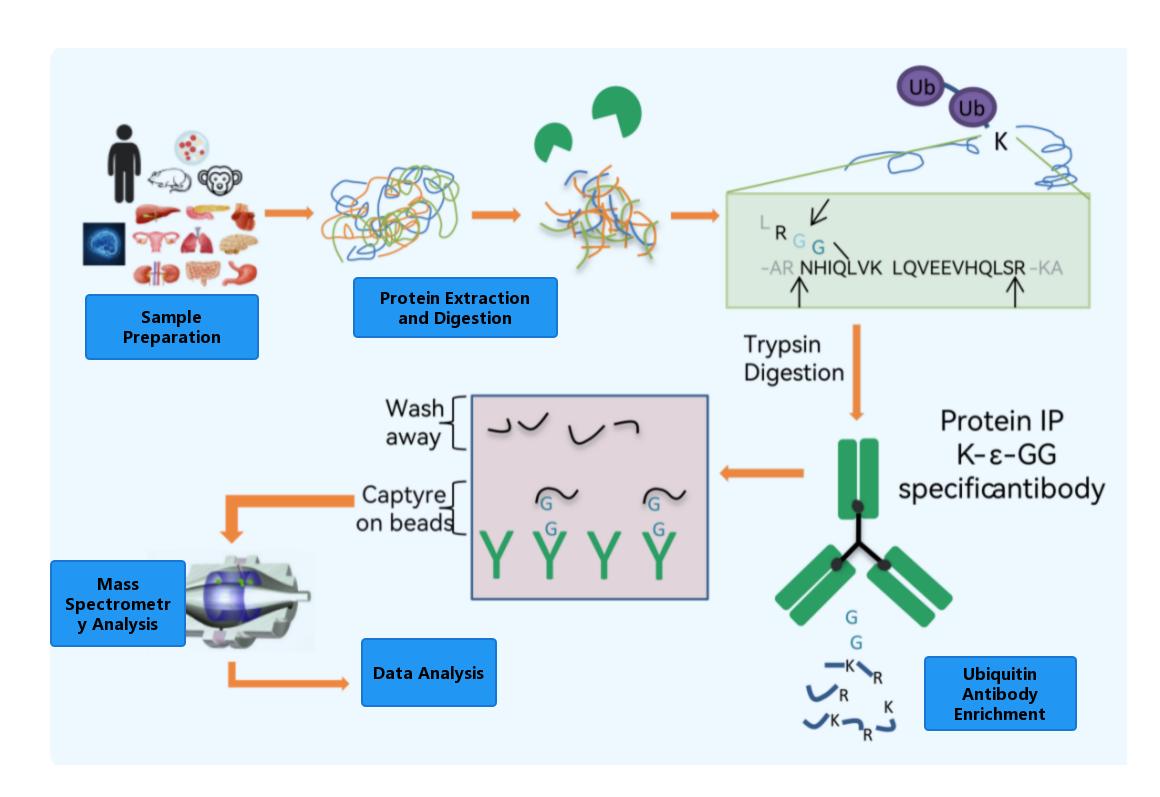
Utilize high-quality antibodies from CST (Cell Signaling Technology) with high specificity.
High-throughput identification, capable of detecting nearly ten thousand ubiquitination modification sites in a single analysis.
Basic medical clinical diagnosis: cell proliferation, differentiation, cycle, apoptosis; biomarkers for tumor occurrence and development; neurodegenerative diseases; disease mechanisms and pathways; disease classification; personalized treatment, etc.
Biopharmaceuticals: cell proliferation, differentiation, cycle, apoptosis; mechanisms of action of drugs for tumor occurrence and development; evaluation of drug efficacy; drug development, etc.
Food and nutrition: optimization of food storage and processing conditions; identification of food components and quality; development of functional foods; food safety monitoring and testing, etc.
① Prediction of protein-protein interactions (PPI) involving targets of drugs such as PROTACs.
② Capture of protein modification signals, including ubiquitination, inside cells.
③ Identification of targets and off-targets of drugs such as PROTACs.
④ Systematic study of downstream effects of various cellular processes and drug treatments, including PROTACs.
⑤ Analysis of downregulated protein ubiquitination levels to investigate whether the degraded proteins are ubiquitinated by the drug.
⑥ Identification of peptide segments and sites of protein ubiquitination modifications.
Lenalidomide selectively ubiquitinates and degrades IKZF1 and IKZF3 in multiple myeloma cells.
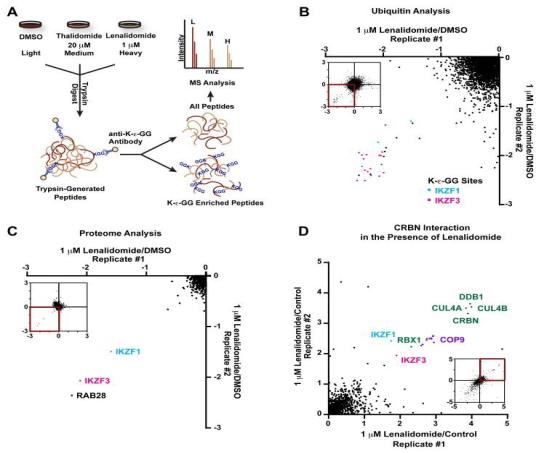
(1) Extensive non-targeted protein detection using DIA and TMT, analyzing the degradation efficiency of target proteins and off-target effects after PROTAC treatment.
(2) Targeted quantitative detection based on MRM/PRM technology, quantifying the degradation level of target proteins after PROTAC treatment.
(3) AP-MS (Affinity Purification-Mass Spectrometry) proteomics technology to validate the interaction between target proteins and E3 ubiquitin ligases.
(4) Ubiquitin proteomics technology to study the ubiquitination mechanism of target protein degradation after PROTAC treatment.
(5) Simple/Digital Western protein quantification technology, providing accurate, highly reproducible, and efficient protein quantification
Our products and services are for research use only.